AY2025–2026 College Catalog
Buenas yan Håfa Adai!
Welcome to Guam Community College for Academic Year 2025–2026! We are thrilled to have you as part of our vibrant and growing campus community. Whether you're returning or just beginning your journey with us, this year is full of exciting opportunities to learn, grow, and connect.
As you explore campus, you will notice the energy of a thriving college community along with upgrades and improvements throughout. GCC continues to stand strong on the foundation of programs that have shaped our workforce, from the trades to professional services. At the same time, we’re evolving with new and innovative programs designed to meet the evolving needs of our island and region.
As a GCC student, you are joining a powerful network of alumni and professionals who are making an impact across every sector — from healthcare and education to culinary arts, business, technology, and beyond. Many of them started just where you are now, taking the first steps on a path toward meaningful careers and leadership in our community.
I encourage you to embrace every opportunity here. The skills you gain will serve you well, the people you meet may become lifelong friends or mentors, and the experiences you have will shape not only your future but the future of Guam.
We’re glad you’re here. Biba GCC!
Mary A. Y. Okada, Ed.D.
President, Guam Community College
Dear Students,
Hafa adai and welcome to a brand-new academic year at Guam Community College! Whether you are a returning student or joining us for the first time, we are excited to have you as part of our GCC family.
At GCC, we are committed to providing a learning environment that fosters academic excellence, personal growth, and career readiness. This year brings new opportunities to challenge yourself, build meaningful connections, and work toward achieving your goals. Our faculty and staff are here to support you every step of the way, offering guidance, resources, and encouragement as you embark on this journey.
We encourage you to take advantage of the many services available to help you succeed, from tutoring and academic advising to student organizations and career development programs. Stay engaged, ask questions, and don’t hesitate to seek help when needed. Your education is a journey, and we are here to support you.
We look forward to seeing all that you will accomplish this year. Let’s make this a year of learning, growth, and success!
Virginia Charfauros Tudela, Ph.D.
Vice President for Academic Affairs
The Guam Community College Catalog Academic Year (AY) 2025-2026 is in effect from 08/13/25 to 07/10/2026. Any changes to catalog content during this time will be noted on an addenda posted on the GCC website (https://guamcc.edu).
Guam Community College is a public postsecondary educational institution, created by Public Law 14-77 in 1977 (as amended by P.L. 31-99 in 2011 to strengthen and consolidate Career and Technical Education (CTE) on Guam. The College operates secondary and postsecondary CTE programs, adult and continuing education, community education, and short-term specialized training. These programs are delivered both on and off-campus, in satellite programs and on site at businesses, as needed. The College also serves as the State Board of Control for career and technical education under the United States Vocational Education Act of 1946, 1963, and subsequent amendments.
The College offers over 50 fields of study, and prepares students for entry into the workforce, or transfer to four-year colleges and universities with advanced standing in professional and technical degree programs. The College offers a variety of community service and special programs to prepare students for college experiences, including adult education (English as a Second Language, Adult Basic Education, and Adult High School) and GED® high school equivalency exams.
Guam Community College will be the premier educational institution for providing globally recognized educational and workforce development programs.
Sinangan Misión (CHamoru translation):
Guiya i Kulehon Kumunidåt Guåhan, i mas takhilo’ mamanaguen fina’che’cho’ yan i teknikåt na kinahulo’ i manfáfache’cho’ ya u na’ guáguaha nu i manakhilo’ yan manmaolek na tiningo’ ni i manmafananågui yan i fina’na’guen cho’cho’ para Maikronesiha.
Diversity
We value an engaged, inclusive culture that embraces diverse points of view and collaboration to accomplish the College’s common goals.
Accountability
We value a culture of institutional and individual responsibility, transparency, and continuous assessment and improvement
Service
We support and recognize service at all levels of the College. We strive to contribute to the benefit of the College, students, community, and our neighboring islands within Micronesia.
Integrity
We hold high standards of character and integrity as the foundation upon which the College is created.
Learning-Centered
We foster intellectual flexibility, knowledge, and skills by integrating teaching, assessment, and learning to promote continuous improvement of our programs and services to support our scholarly community.
Student-Focused
We are committed to education, inquiry and service in order to meet our students’ ever growing and changing needs. We promote lifelong learning, civic and social responsibility, leadership, and career growth.
Regional Accreditation
Guam Community College is accredited by the Accrediting Commission for Community and Junior Colleges, Western Association of Schools and Colleges, 428 J Street, Suite 400, Sacramento, CA, 95814, (415) 506-0234, an institutional accrediting body recognized by the Council for Higher Education Accreditation and the U.S. Department of Education. Additional information about accreditation, including the filing of complaints against member institutions, can be found on ACCJC’s website (accjc.org),Complaint Process. Documents describing the accreditation of the College may be examined at the Vice President for Academic Affairs’ (VPAA) office, Bldg. 2000, Suite 2234.
Program Accreditation
The Associate of Arts in Culinary Arts program is accredited by the American Culinary Federation Education Foundation's (ACFEF) Accrediting Commission, which is recognized by the Council of Higher Education Accreditation (CHEA). Initial accreditation was granted on December 31, 2014. A reaffirmation of accreditation of the Culinary Arts program was granted for the period of February 2, 2018 to December 31, 2022. A reaffirmation of programmatic accreditation was received on February 1, 2023 and expires on December 31, 2029. Additionally, in October 2016, the College received notification that the World Association of Chefs' Societies (WACS) or Worldchefs, awarded WACS Recognition of Quality Culinary Education to Guam Community College.
For complaints, questions or inquiries, contact:
American Culinary Federation
6816 Southpoint Parkway Ste. 400
Jacksonville, FL 32216
Telephone Number: 800-624-9458 or 904-824-4468
Fax: 904-940-0741
Email: acf@acfchefs.org
The College is located in Mangilao, Guam on a campus over 22-acres in size. Standard classroom facilities are housed in permanent concrete buildings. Metal buildings are used primarily for shop facilities in career and technical education.
Shop spaces are provided for Automotive Service Technology, Auto Body, Construction Trades, Welding, and Air Conditioning and Refrigeration courses. Special laboratories are used for instruction in the Allied Health, Computer Science, Office Technology, Networking Systems Technology, Visual Communications, and the Culinary Arts programs.
The GCC faculty are qualified by their education and experience to offer courses and programs that achieve the educational objectives of the College. Faculty credentials are found at the back of this student catalog. Please refer to the GCC Fact Book for more detailed information on the College’s instructional facilities and faculty profile. The latest version of GCC’s Factbook can be found at https://guamcc.edu/Publications.
GCC also serves secondary schools by offering Career and Technical Education (CTE) programs in the Guam Department of Education (GDOE) high schools. Presently, there are six (6) GDOE high schools located throughout the island where various CTE classes are taught by GCC faculty.
Catalog Content Disclaimer
Guam Community College has made reasonable efforts to provide information that is accurate at the time of this catalog’s publication. However, the College reserves the right to make appropriate changes in procedures, policies, calendars, requirements, programs, courses and fees. When feasible, changes will be announced prior to its effective date.
It is the student’s responsibility to be familiar with the information presented in this publication and to know and observe all regulations and procedures relating to the program he or she is pursuing. In no case will a regulation be waived or an exception granted because a student pleads ignorance or contends that he or she was not informed of the regulations and procedures. Responsibility for following all policies and meeting all requirements and deadlines for degree and certificate programs rests with the student.
Guam Community College adheres to the provisions of the U.S. copyright law (Title 17, United States Code, Section 101, et sep.). Additional copyright information is available at the College Learning Resource Center.
Guam Community College complies with all federal and territorial rules and regulations and prohibits discrimination on the basis of age, race, color, national origin, gender, sexual orientation or disability. This holds true for all students who are interested in participating in educational programs and/or extracurricular activities. Further information may be obtained in the GCC Student Handbook available online or the Dean’s Office, School of Technology & Student Services in the Student Services & Administration Building, 2nd Floor, Suite 2229.
The Guam Community College has broad responsibilities for the education of the student and the College’s standards of behavior can be considered part of the educational process. Guam Community College expects that each student will obey federal and territorial laws as well as College regulations. Any act that interferes with the rights of others, disrupts or impairs the normal function of the College, damages or destroys property, or impairs health or safety is grounds for disciplinary action. Students who interfere with the personal liberty of others on campus are liable to expulsion and to such other penalties as may be imposed by law.
Students are provided due process in disciplinary adjudication. Student conduct at all times should reveal mature judgment and a sense of moral, civic and academic responsibility. For a detailed explanation of GCC’s Student Rights and Responsibilities and the Student Code of Conduct, see the GCC Student Handbook or go online at https://guamcc.edu/StudentHandbook. Each GCC student is responsible for reading and understanding the GCC Student Handbook.
Academic integrity is fundamental to learning and is consistent with the Institutional Learning Outcomes (ILOs) espoused at Guam Community College. The concept of academic integrity lies at the very heart of any college, and learning and scholarship cannot thrive without this fundamental value. Academic dishonesty, therefore, will not be tolerated. Students who commit such acts expose themselves to sanctions as severe as expulsion from the College.
Academic dishonesty can take different forms, including, but not limited to: cheating, plagiarism, and technology misuse and abuse. In any situation in which students are unsure of what constitutes academic dishonesty, it is the students’ responsibility to raise the question with their instructor. It is also the students’ responsibility to be familiar with the student guidelines on academic integrity.
Some common violations of these basic standards of academic integrity include, but are not limited to:
Cheating
Providing unauthorized assistance, using or attempting to use unauthorized assistance, material, or study aids in examinations or other academic work, or preventing or attempting to prevent another from using authorized assistance, material, or study aids.
Plagiarism
Passing off someone else's work as his or her own. This can range from failing to cite an author for ideas in a student's paper to cutting and pasting paragraphs from different websites to handing in a paper downloaded from the internet.
Consequences will be severe and will include anyone who enabled or contributed to the act of plagiarism. College policy will be implemented, regardless of the feelings of either the students or the instructor. Students found guilty of plagiarism will have this entered into their record and may be expelled from the College.
Fabrication
Submitting contrived or altered information in any academic exercise. Examples: making up data for an experiment; “fudging” data; citing nonexistent or irrelevant articles; presenting fraudulent excuses, lies, and letters of recommendations.
Multiple submissions
Submitting, without prior permission, any work submitted to fulfill another academic requirement. Example: submitting the same paper for two different classes without the expressed consent of both professors.
Misrepresentation or falsification of academic records
Misrepresenting or tampering with or attempting to tamper with any portion of a student’s transcripts or academic record, either before or after enrolling at Guam Community College.
Facilitating academic dishonesty
Knowingly helping or attempting to help another violates any provision of this code. For example, working together on a take-home exam or other individual assignment, discussing an exam with a student who has yet to take it, giving tests or papers to another student, etc.
Unfair advantage
Attempting to gain unauthorized advantage over fellow students in an academic exercise. For example, gaining or providing unauthorized access to examination materials (either past or present); obstructing or interfering with another student’s efforts in an academic exercise; lying about a need for an extension for an exam or paper; continuing to write even when time is up during an exam; destroying, hiding, removing, or keeping library materials, etc.
Guam Community College is committed to providing a safe environment for students and employees. GCC can best perform its missions of teaching, training and public service when faculty, students, staff and visitors share a climate that supports a safe learning environment that is free from disruptive, threatening and violent behavior. Special Workplace Violence Policies and Procedures can be accessed in the GCC Student Handbook, at the office of the Associate Dean responsible for Student Services, Bldg. 5000, Suite 5203 or at the Human Resources Office located in the Student Services & Administration Building 2000, suite 2212 or 2213.
As a way to promote the health and welfare of the College campus community, the Board of Trustees established Board of Trustees Policy No. 175 that requires the Guam Community College premises to be Tobacco and Betel Nut (Pugu’a)-Free, effective June 1, 2007. The policy was further amended on May 30, 2013 to include electronic cigarettes. To comply with the Board of Trustees Policy No. 175 and Administrative Directive No. 2006-05, all employees and students are expected to adhere to the following:
- Do not use tobacco products while on Guam Community College property.
- Do not use electronic cigarette (e-cigs) devices while on Guam Community College property.
- Do not chew or spit pugu’a while on Guam Community College premises.
- Assist with the enforcement of Board of Trustees Policy No. 175.
Violation of the Board of Trustees Policy and Administrative Directive will be addressed in accordance with the disciplinary actions outlined in the Personnel Rules & Regulations, the GCC Student Handbook, and the Board-Faculty Union Agreement, 2023-2029.
As required by the Higher Education Amendments of 1992, the College has a Sexual Harassment Prevention Policy to promote awareness of rape, acquaintance rape and other sex offenses and the procedures for reporting such offenses among all College constituents. More details regarding the Board of Trustees’ Policy 185 are available in the GCC Student Handbook, which is posted on the College’s website, https://guamcc.edu/StudentHandbook.
Fall 2025 | |
08/11/2025 | Faculty Start Date |
08/13/2025 | First Day of Monday – Wednesday Classes |
08/14/2025 | First Day of Tuesday – Thursday Classes |
08/15/2025 | First Day of Friday Classes |
08/16/2025 | First Day of Saturday Classes |
09/01/2025 (Observed) | Labor Day - Campus closed |
09/05/2025 | Last day to Withdraw - First 8 Week Courses |
10/17/2025 | Last day to Withdraw - Full Term Courses |
11/03/2025 | All Soul's Day - Campus closed |
11/04/2025 | Last day to Withdraw - Second 8 Week Courses |
11/11/2025 | Veteran's Day - Campus closed |
11/21/2025 | Last day of Friday Classes |
11/22/2025 | Last Day of Saturday Classes |
11/27/2025-11/30/25 | Thanksgiving Break |
12/01/2025 | Last day of Monday-Wednesday Classes |
12/02/2025 | Last day of Tuesday-Thursday Classes |
12/05/2025 | Grades Due |
12/08/2025 | Our Lady of Camarin Day - Campus closed |
Spring 2026 | |
01/05/2026 | Faculty Start Date |
01/07/2026 | First Day of Monday – Wednesday Classes |
01/08/2026 | First Day of Tuesday – Thursday Classes |
01/09/2026 | First Day of Friday Classes |
01/10/2026 | First Day of Saturday Classes |
01/19/2026 | Martin Luther King, Jr. Day - Campus closed |
01/30/2026 | Last day to Withdraw - First 8 Week Courses |
03/02/2026 | Guam History &CHamoru Heritage Day - Campus closed |
03/13/2026 | Last day to Withdraw - Full Term Courses |
03/27/2026 | Last day to Withdraw - Second 8 Week Courses |
03/30/2026 – 04/05/2026 | Spring Break |
04/28/2026 | Last day of Tuesday-Thursday Classes |
04/24/2026 | Last day of Friday Classes |
04/25/2026 | Last day of Saturday Classes |
05/04/2026 | Last day of Monday-Wednesday Classes |
05/07/2026 | Grades Due |
05/15/2026 | Commencement Exercise |
05/25/2026 | Memorial Day - Campus closed |
Summer 2026 | |
05/29/2026 | Faculty Start Date & First Day of Classes |
06/19/2026 | Last Day to Withdraw |
07/03/2026-07/04/2026 | Independence Day - Campus closed |
07/10/2026 | Last Day of Classes |
07/15/2026 | Grades Due |
07/21/2026 | Liberation Day - Campus closed |
A full range of counseling services is offered to students including orientation to college programs and services, college placement tests, career counseling, limited personal counseling, and student rights advocacy. Counselors are available in the Student Services & Administration Building on a walk-in, virtual, or appointment basis. Counselor hours are posted in the Student Services & Administration Building and on the GCC website, https://guamcc.edu/AssessmentandCounseling.
Students who have applied for admission or who are planning to enroll for the first time are encouraged to contact a counselor for educational and/or career and technical education guidance services. Students are provided with information regarding admissions procedures, placement testing requirements, instructional programs, and other services. Students who are undecided about career goals or objectives are provided with career guidance services, which may include assessment of interests and aptitudes and exploration of career fields.
Counseling services are accessible through GCC’s public website. Under the Student life header is the counseling main page where information regarding services can be found.
Announcements will be made on MyGCC to inform the college community of counseling services and how they may avail of the service. Counseling services will be provided either by email, face-to-face, phone call, or through a virtual meeting via ZOOM or Google Meet. If students prefer to communicate via email only, that option will be provided.
Effective October 2016, ACCUPLACER replaced COMPASS as the College’s placement test. Placement test results are valid for two (2) years. While placement testing is not mandatory for admission to the College, it is required for enrollment in English and Mathematics courses if other placement means are not applied (e.g. CLYMER or WorkKeys® results). Students can schedule their test online after making payment by visiting https://guamcc.edu/PlacementTest and clicking on Placement Test under the Admissions tab. The College reserves the right to require students to be re-evaluated using its placement test at any time.
Under GCC's CLYMER (Classroom Learning Yields Math & English Readiness) program, a recent GDOE or private high school graduate (within two years) who has earned a minimum GPA of 3.2 and taken higher level math or senior English courses can enroll into college-level math and English courses without taking a placement exam. Learn more about the CLYMER program at https://guamcc.edu/CLYMER under the Admissions Tab.
In addition, GCC accepts valid WorkKeys® Gold and Platinum Certificates for enrollment into MA110A and/or EN110 instead of a placement exam.
Information, materials, and counselor assistance are available to students who need help in career educational planning and assessment of their interests, abilities, goals and values. Computer-assisted career search programs and information on schools and colleges that provide additional training for occupations are also available.
Counselors provide personal growth and development counseling. Students experiencing adjustment problems, stress, anxiety, difficulties in relationships with others, or other symptoms of emotional distress may receive limited personal counseling, or in some cases may be referred to services in the community as GCC counselors are not licensed therapists. All information related to the student receiving counseling is confidential and may be released only with the written permission of the student.
Counselors are responsible for promoting the welfare of students and assisting them in the protection of their basic human rights. Counselors will, when requested, take an active role in advising students of their rights to confidentiality, privacy, freedom of expression and viewpoints, and rights to due process. Counselors will assist in mediation of disputes and grievances and act as the advocate of the student. Related policies and procedures are found in the GCC Student Handbook
Academic Advising at the College is a process that assists students in clarifying their life and career goals as they develop their educational plan. Since academic advising is also a decision-making process, the ongoing communication is the responsibility of both the student and his/her advisor.
Academic Advising goes beyond requirements and registration. Working collaboratively with the program advisor, students develop education and career plans consistent with the students’ interests, abilities, values, and life goals.
Guam Community College partners with its students to succeed. This process is reflected in the following activities:
- Assisting students in clarifying, articulating, and attaining academic and life goals;
- Facilitating each student’s academic adjustment to the campus;
- Educating students to assess academic progress and develop appropriate educational plans;
- Explaining and clarifying graduation requirements and academic rules and regulations;
- Serving as advocates and mediators for students; and
- Referring students to appropriate departments or programs, or resources to meet student needs.
The student is expected to meet with his/her program advisor regularly to view progress with the educational plan, make necessary changes, and/or make referrals for resources to support retention and completion. Students may also work with their program advisor remotely by receiving academic or career advisement via email, telephone, or Google Meet or Zoom (i.e.). Students may request an appointment with their program advisor via telephone call and/or email.
Program advisor assignments are made in accordance with the student’s program of study and are intended to be continuous throughout the student’s college career. Additional information may be obtained from the Admissions and Registration Office, Student Services & Administration Building, 1st. floor.
The Health Services Center is staffed by a licensed practical nurse and an administrative assistant. Students and employees of the College may utilize its services.
The services available at the Health Services Center are:
- basic first aid for injuries and medical conditions that occur on campus;
- annual screening of employees for tuberculosis (TB) as required by law;
- screening of students for TB in compliance with public law and school policy;
- administration of TB skin test;
- immunization program;*
- immunization audit in compliance with public law and school policy;
- Brief Tobacco Intervention program;
- screening of height and weight, blood pressure, vision, and pediculosis
- pregnancy testing and prenatal follow-up;*
- advocacy for persons with disabilities;
- referral services on health management;
- counseling on health and health-related issues;
- health promotion/education through class presentations; and
- STD and HIV testing and treatment in partnership with DPHSS.
*Services are rendered upon the availability of staff and resources
The health requirements for students include:
- TB clearance within one (1) year prior to school registration. For any individual entering from an area other than the U.S. states or territories, Public Law 22-130 requires that a tuberculosis test must be conducted within 6 months prior to enrollment. Those with positive test results must obtain medical evaluation from their private medical clinic first and then proceed to the TB Section of the Department of Public Health & Social Services for clearance;
- Measles, Mumps, Rubella (MMR) - Students must at least have two doses on or after their first birthday. Guam Immunization Protocol indicates that it is strongly recommended that individuals born in or after 1957 receive two doses of MMR, if they never had measles (physician-diagnosed), or if they do not have confirmed laboratory evidence of measles immunity. Those born prior to 1957 are exempted from the MMR requirement; Tetanus & Diphtheria (TD) received within the last 10 years;
- Oral Polio Vaccine (OPV) for students below 18 years of age
- Emergency and Health Information form
Note: Students whose choice of study will place them at risk with the exposure to blood-borne pathogens are advised to follow further instructions by their respective program advisor regarding other health requirements such as hepatitis B vaccine and physical examination.
The College reserves the right to control parking and the flow of traffic on the campus. Accessible parking for students with disabilities is clearly marked and available in front of the Student Support Services, Building B, the North Parking Lot, by Building 500, and in front of the Student Services & Administration Building. There is also accessible parking in front of Building E. Improperly parked vehicles may be towed away at the owner’s expense. The College will not be responsible for any damage done to any vehicle parked on campus. The College does provide security services throughout the campus.
Food Service
Food service on campus is offered during the Fall and Spring semesters through local vendors Monday -Thursday 7:30a.m. – 8:00pm and Friday 7:30a.m. -5:00pm. The concessions are closed on Saturdays, Sundays and holidays. For more information, visit the Materials Management Office, Bldg. 2000, suite 2104, 2105 or contact 735-5540/5542.
Bookstore
The Bookstore is located in the Foundation Building 6000. The Bookstore is located in room 6104. The Bookstore is open Monday through Friday from 9:00a.m. to 3:00p.m. and closed on weekends and holidays. You may contact the Bookstore at 735-6018 or via e-mail at bookstore@guamcc.edu. Special Bookstore hours are set during the registration period and posted online at MyGCC.
Student I.D. Cards
Students are expected to have a GCC I.D. card on their possession at all times. All students are required to present an I.D. to access services at computer labs, library, Bookstore and Health Services Center, to name a few.
The Center for Student Involvement (CSI) oversees an array of student activities, such as New Student Orientation, Leadership Development, Service-Learning, Student Governance, and Student Organizations. Each of these initiatives is designed to foster a sense of empowerment and responsibility to the campus community and is guided by the belief that students must become intentionally involved in campus programs and activities to become fully prepared for the workplace and other life commitments. CSI assists students and student organizations in planning and implementing programs, activities, and events, and plans and implements campus-wide programs to address the needs and interests of GCC's students.
The New Student Orientation program introduces new students to Guam Community College services, resources, and opportunities that will support their academic and career goals. Title IX training is also included as part of the Student Orientation program.
Orientation for all new students is conducted in a face-to-face environment. Students have the opportunity to engage with their peers and meet representatives from various GCC departments and offices. An overview of Moodle Classroom will also be covered during orientation.
Leadership Development assists students in realizing their leadership potential. Training and development opportunities are offered at individual and organizational levels tailored to fit the students’ unique leadership needs and interests.
Student leadership development may also be held online via Zoom. Recordings of training, workshops, and conferences will be shared with students. Student Organization Officer and Advisor Training may be held online via Zoom.
Service-Learning is a way of teaching and learning that engages all learners in hands-on academic projects in the community to meet learning objectives and strengthen communities. Students who are civically engaged in their education are better able to connect classroom learning with real life situations through participation in community service projects.
The Council on Postsecondary Student Affairs (COPSA) is the official representative body for student governance at GCC. As the Student Senate, COPSA plans student activities, approves student organization budgets, and ensures that the College fully considers the needs and interests of students in its decisions and offerings.
The Council on Postsecondary Student Affairs (COPSA) meets regularly. The Center for Student Involvement (CSI) also works directly with the student leaders through teleconferencing and email correspondence. COPSA holds General Membership and Executive Committee meetings.
Student organizations provide excellent opportunities for students to develop personally and professionally. Student organizations work in conjunction with the Council on Postsecondary Student Affairs (COPSA) in planning and implementing activities, events, and campus-wide programs to address the needs and interests of GCC students. Through active involvement in their campus community, students expand their circle of influence, gain an understanding of diversity, are instilled with a sense of ownership over their educational experience, and are committed to making GCC and their community a better place.
The following are GCC student organizations:
The Administrative Professionals Society (APS) builds office knowledge and expertise by providing valuable learning opportunities in technology, communication, and professional skills to meet the needs of the individual and the community.
The Adult High School Student Organization (AHSSO) serves as a voice for addressing student issues, problems, and concerns for all Adult High School students.
The Aspiring Professional Executives (APEX) Student Organization serves as a support group for all students seeking a degree in Supervision & Management, and teaches members to be socially aware by providing service to the community.
The Association of Junior Accountants (AJA) fosters the growth of the accounting and finance communities in Guam Community College (GCC) and aids organizations associated with these communities.
The Automotive Club creates awareness and helps facilitate activities within the Automotive program, serving as a voice and official liaison for the Automotive students.
The Business Organization for Student Success (BOSS) serves its diverse membership as a business-oriented student organization, providing leadership and career-oriented opportunities to develop and enhance tomorrow’s leaders.
The Computer Coding Club (3) provides a computer coding culture among students and empowers, informs, and educates fellow students and the community of the significances of computer programming and technical literacy.
The Cosmetologists United Together (CUT) provides opportunities for students pursuing an Industry Certification in Cosmetology to engage in fellowship and creative self-expression.
The Criminal Justice Students' Association (CJSA) facilitates social and criminal justice networking and career-building activities to create a more cohesive and professional student community.
The Culinary Arts Student Association (CASA) creates opportunities and activities for culinary students and takes the lead in fostering Culinary Arts educational growth, cultural and social assimilation, ethnic appreciation and equal access to all college Culinary Arts programs and activities.
The Digital Arts Society (DAS) brings together students interested in the digital arts to assist in their growth and development, building their leadership skills through experiences in social, economic, educational, and community activities relative to the field of visual communications.
The EcoWarriors raise awareness and educate the community on sustainability issues, including recycling, energy management, and conservation of natural resources.
The Education Student Organization (ESO) supports students seeking a degree under the Education Department, including those studying Early Childhood Education, Education, and Sign Language Interpreting.
The Fencing Club is dedicated to encouraging, promoting, supervising, and developing the modern sport of fencing at GCC and to the participation of its members in competitions.
The His Plan Student Movement offers opportunities for students to explore personal development and spirituality in a non-judgmental environment and to foster meaningful relationships through regular gatherings, discussions and fellowship events.
The Hospitality and Tourism Society (HosTS) promotes the hospitality and tourism industry on campus and in the community.
The Human Services Student Organization (HSSO) promotes the fields of Human Services and Social Sciences through volunteerism and community service activities.
The Korean Club promotes Korea’s language and culture through various activities and events that will educate and entertain the campus and community.
The Medical Assistant Student Organization (MASO) enables Medical Assisting students to enhance and demonstrate the knowledge, skills, and professionalism required by employers and patients.
The Phi Theta Kappa International Honor Society (Beta Xi Chapter) recognizes the academic achievement of GCC students and provides opportunities for its members to grow as scholars and leaders.
The Practical Nursing Student Association (PNSA) provides support and leadership opportunities to undergraduate nursing students.
The Sci-πath-Club (SπC) promotes interest, understanding, and knowledge of the mathematical and scientific world throughout the college and the local community.
The Veterans Club provides a network of support among student veterans and promotes an understanding of student veteran issues.
The Visual Voices Club (ViVo) educates and shares the rich culture of the Deaf and Hard of Hearing community, promoting accessibility and inclusion in the community.
A complaint covers any concern or issue regarding employees (faculty, support staff, and administrators) or visitors on campus about a matter related to a student’s educational experience with GCC that is not academic in nature. Examples of non-academic concerns or issues could include: perceptions and/or allegations of discrimination based on color, age, sex (to include sexual harassment and sexual/gender orientation), national origin, race, religion, political affiliation or disability condition; other forms of harassment; disruptive, threatening, or violent behavior; conduct associated with drugs and/or alcohol; and violations of other College Board policies and/or administrative regulations/directives that do not have specified procedures in place.
The use of this procedure does not apply to student disciplinary actions outlined in the GCC Postsecondary StudentHandbook and other issues, which are covered under separate Board policies and administrative regulations that have specific procedures in place. In the above instances, the Associate Dean responsible for overseeing Student Support Services (or designee), shall inform the student of the correct procedure to follow for the former and/or refer the student to the College official through whom the request should be addressed for the latter. Complaints against employees alleging forms of misconduct described in the GCC Code of Ethics (Policy 470) shall be referred to the Human Resources Administrator.
Whenever reasonably possible, a student who encounters a non-academic problem is encouraged to seek an informal resolution of the matter directly with the College employee or visitor. If the attempt to reach an informal resolution is not successful or if an informal resolution is not advisable, then the concern or issue can be filed at the Student Support Services Office during regular office hours in order to implement the following steps of the Formal Complaint Procedure:
Step One – Initiating a Complaint
A) Complaint Initiation: The student has ten (10) working days from the date of the incident to file the complaint, utilizing the GCC Complaint Form, to the Student Support Services Office. All supporting documentation must be submitted with the GCC Complaint Form.
B) Notification of Charge: Within five (5) working days, the School of Technology & Student Services (TSS) Associate Dean who oversees the Student Support Services Office (or designee) will begin the investigation and will meet with the person to whom the complaint is addressed (respondent) to inform the respondent(s) that a student has filed a formal complaint.
Step Two – Informal Resolution:
The TSS Associate Dean (or designee) will verify if the student and the respondent met earlier in an attempt to informally resolve the matter. If not, and if the student complainant agrees, within five (5) working days, the TSS Associate Dean (or designee) will attempt to schedule the meeting to allow for an opportunity for an informal resolution between the student and the respondent.
If a satisfactory resolution is reached through the informal meeting between the student and the respondent, both the student and the respondent shall sign or acknowledge receipt via GCC email of the written summary that verifies the resolution of the complaint.
If the student finds the response/resolution through the informal meeting is unsatisfactory, the student may submit a written notice of his/her dissatisfaction to the TSS Associate Dean (or designee), within three (3) working days and request to proceed to Step Three.
If the student expresses concern with scheduling an informal meeting with the respondent that is determined by the TSS Associate Dean (or designee) to be a valid concern; the student may submit a written notice to the TSS Associate Dean (or designee) to proceed to Step Three.
For contract employees or campus visitors:
1) If the student finds the response/resolution through the informal meetingsatisfactory, the TSS Associate Dean (or designee) will prepare a written response of the resolution of the complaint to the student within three (3) calendar days. A copy will be forwarded to the affected GCC contract employee or campus visitor via email. A copy will also be filed with the original GCC Complaint Form.
2) If the student finds the response/resolution through the informal meeting is unsatisfactory, the student may submit a written notice of his/her dissatisfaction to the TSS Associate Dean (or designee) within three (3) calendar days. The TSS Associate Dean (or designee) will then schedule a meeting with the student and the respondent in an attempt to resolve the complaint.
3) If the student is still dissatisfied with the attempted resolution, the student may submit a written notice to the TSS Associate Dean (or designee) to proceed to Step Four.
Step Three – Formal Resolution:
A) Additional Attempt to Resolve: If a resolution is not reached at Step Two or the nature of the complaint is determined to require more than a resolution between the student and the respondent, the TSS Associate Dean (or designee) will:
1. Implement one of the following:
a. For faculty members: refer the student and the faculty member to the faculty member’s Dean. Within three (3) working days, the Dean will meet with the faculty member and the student in an attempt to resolve the complaint;
OR
b. For other College employees: refer the student and the employee to the appropriate supervisor. Within three (3) working days, the supervisor will meet with the College employee and the student in an attempt to resolve the complaint;
2. Prepare a written statement summarizing the actions taken prior to the referral and submit this written summary along with a copy of the GCC Complaint Form to the appropriate Dean/supervisor.
B) Resolution reached during Step Three with the appropriate Dean/Supervisor/TSS Associate Dean (or designee):
For Step Three 1a & 1b above:
The appropriate Dean/Supervisor will prepare a written response of the resolution of the complaint to the student within four (4) working days. A copy will be forwarded to the affected GCC employee within five (5) working days. A copy will also be provided to the TSS Associate Dean (or designee) to file with the original GCC Complaint Form.
C) Resolution not reached during Step Three with the appropriate Dean/Supervisor/TSS Associate Dean (or designee):
The appropriate Dean/Supervisor, will refer the student and/or the affected GCC employee to the President. The referral will include a copy of the GCC Complaint Form and the Dean’s/Supervisor’s written summary of the unresolved complaint. The student referral must be made within five (5) working days.
Step Four - Resolution by the President
For contract employees or campus visitors: The TSS Associate Dean (or designee) will include a copy of the GCC Complaint Form and a written summary of the unresolved complaint to the President’s Office. The student referral must be made within five (5) working days. The President will meet with the student(s) and affected GCC employee/contract employee/campus visitor in an attempt to resolve the complaint. The President’s decision is final. The President’s Office will provide a memorandum of the final decision to the student and the respondent.
Time for complaints and grievances: If GCC is not in session during part of these proceedings or in instances where additional time may be required because of the complexity of the case or unavailability of the parties or witnesses, any of the time periods specified herein may be extended by the Dean of Technology and Student Services. If a time period is extended, the complainant and the person against whom the complaint has been filed will be informed.
Note: Communication with students for conference(s) can be done through class, phone or email. Class and phone communications will be first attempted. If it is difficult to contact the student through these methods, a notice will be emailed via GCC email address or mailed to the student’s address on record.
Learning Resource Center/Library Services
The LRC facility includes a reading area/collection section, computer work areas, a computer lab, small group meeting rooms, audio visual rooms, staff areas, and a large group meeting room.
Reference and instructional services are available for classes and individual library users. The Library presently maintains a permanent collection of about 21,000 items comprising books, periodical titles and videos. Reference books, multimedia materials, magazines and newspapers are available for in-library use. Circulating books may be borrowed for a two-week period; videos may be borrowed for two (2) days. Overdue fines are charged. A coin and bill operated photocopier is also available in the Library. Internet access is provided as well as accessibility to the DYNIX Public Access Catalog (DPAC) and EBSCO host full-text periodical database. The Library web-page with current information can be found on the Guam Community College website.
The Learning Resource Center librarian administers and maintains the online resources for student and faculty use. The online resources such as the SirsiDynix and EBSCO databases help support instruction and are checked to ensure availability and proper functioning of the high-quality digital resources. Individual student guidance and instruction will be provided in searching and using resources such as eBooks and ePeriodicals to help with reference questions, research papers, and other academic and reading needs. Service will be offered for reference, research and technical support via face-to-face, phone, email, or Google Meet from 8:00 am to 8:00 pm, Monday through Thursday.
Faculty assistance with planning and using online resources will be provided on an appointment basis and will be delivered via face-to- face, phone call, email, or Google Meet. This will include assistance with EBSCO ePeriodical and eBook databases, Boolean searches, and presentations about formulating searches and retrieving results from the databases.
Accommodative Services for Students with Disabilities
Students with disabilities can be provided with auxiliary aids when needed for success in attaining their academic/vocational goals. If classes required by students with special disabilities have been scheduled to meet in relatively inaccessible facilities, the College will either reschedule the classes to accessible facilities or make special arrangements to ensure ready access by students with disabilities to those classes. Students with disabilities are urged to contact the Accommodative Services Coordinator well in advance of registration for classes.
For more information concerning services at the College for persons with disability-related needs, contact the Accommodative Services Coordinator at the Student Services & Administration Building, Suite 2139. The office telephone number is (671) 735-5597 or TDD (671) 734-8324.
The Office of Accommodative Services may also provide services remotely to GCC students with disabilities. Contact may be made through email, phone, or virtual meetings. OAS may also provide remote assistance to help register students online and clarify questions regarding course requirements. OAS has access to Banner and will be able to help students identify issues related to courses and assist with health clearances.
Tutoring Services
Guam Community College provides tutoring services for students in an effort to help them meet their educational objectives. The focus of these services centers primarily on English and math skills.
Reach for College provides free tutoring and academic support. Tutoring services are conducted via face-to-face, Google classroom, or Google Meet; every tutor is assigned to a specific Google classroom based on their subject expertise. Students requiring tutoring services are referred to a specific tutor based on the subject. The service is offered daily, Monday through Friday, from 8:00am to 5:00pm. Students may sign up electronically or call the Reach for College office for face-to-face tutoring or online virtual tutoring.
Assessment at Guam Community College is viewed as a collective effort to demonstrate commitment to an institutional dialogue about student learning. There are two major motives that drive all assessment processes at GCC: accountability and improvement. A policy document adopted by the Board of Trustees on September 4, 2002 (Policy 306, Comprehensive Assessment of Instructional Programs, Student Services, Administrative Units and the Board of Trustees) is the institutional mandate that fuels all campus-wide assessment activities. Three goals effectively guide the Office of Assessment, Institutional Effectiveness, and Research (AIER) in its mission of assessment excellence at the College:
- To develop and sustain assessment momentum at the College through capacity building efforts that will empower constituents to use assessment results for accountability and improvement;
- To systematize assessment protocols, processes and policies both in hardcopy and online environments and thereby allow the College to meet its ACCJC/WASC accreditation requirements; and
- To exert and affirm community college assessment leadership regionally and nationally.
At the core of these processes, are three (3) important questions that the institution asks regarding student learning: What do students know? What do they think and value? What can they do? These three questions correspond to the cognitive, affective and behavioral domains of student learning. By continually asking these questions, the College is drawn closer to what it says it can do in both teaching and learning environments and to what it promises its programs and services can deliver in terms of results.
The Office of Assessment, Institutional Effectiveness, and Research (AIER) is located on the 2nd floor of the Student Services & Administration Building, Suites 2226 and 2227 with telephone number (671)735-5520 ext. 5404, 5612.
Although schedules may vary, classes are scheduled between 8 a.m. and 10 p.m. Monday to Friday. Some Saturday classes are offered. Please consult Admissions & Registration for the current schedule.
GCC reserves the right to schedule classes in the order which best suits the overall master schedule and does not violate course prerequisites. Furthermore, GCC also reserves the right to change program content as it aligns with curriculum changes. Such changes are necessary to remain current with professional expectations and industry standards.
Note: Policies and procedures apply to all students, unless otherwise indicated.
A student may be admitted to the College in any one of the following classifications:
Declared Student
A student pursuing a postsecondary certificate or degree. To be eligible, a student must:
- Be a graduate of an accredited or recognized United States high school or international high school with equivalent programs of instruction and comparable standards; or
- Have the equivalent of a high school diploma (e.g., G.E.D); or
- Have an AA/AS, BA/BS or higher degree from an accredited or recognized United States college or university or a foreign college or university with equivalent programs of instruction and comparable standards; or
- Successful completion of at least 45 hours of college credit with a cumulative GPA of 2.0 or higher from an accredited or recognized United States college/university or a foreign college/university with equivalent programs of instruction and comparable standards; or
- Be at least fourteen (14) years of age or older and have the ability to benefit from the education or training offered at the College. Students admitted on the basis of ability to benefit from the education or training offered must pass a U.S. Department of Education approved test such as ACCUPLACER prior to enrollment at the College.
Undeclared Student
A student taking courses who has not formally declared a particular degree, certificate or diploma program at the College. Any person below 16 years of age may only enroll as a postsecondary student in classes held on the College campus, subject to proof of parental consent, home school consent, and College approval. The College will determine if such students are able to benefit from an educational experience delivered in an adult setting.
Full-time international students
Full-time international students at other institutions are also eligible, but international (F-1 Visa) students who are full-time students at the College may not be admitted as Undeclared Students.
Enrichment Student
A student who does not intend to declare a major or pursue a degree program, but who plans to complete more than 18 credit hours of post-secondary work. Such a student would not be required to pursue General Education courses, except in the case where a General Education course is listed as a prerequisite for a course of interest to the student.
Note: Should an individual enrolled as an enrichment student subsequently decide to pursue a Bachelor’s, Certificate, or Associate degree program, he/she would be limited to applying up to 18 GCC credits toward any chosen Degree or Certificate program.
Diploma Student
A student pursuing an Adult High School Diploma. To be eligible, a student must be at least 18 years old, not a high school graduate and not attending a regular high school program.
Special Student
A student admitted to the College to participate in a special training project or taking special courses or is pursuing an educational objective not usually available at the College. Any person is eligible to be a Special Student.
Training Participant
A person enrolled in courses not applicable towards a diploma, certificate, degree, or other formal credential. The courses are designed for professional development or personal enrichment and are not part of the regular schedule of classes.
Acceptance Information
When all information, forms and documents are received, students applying for admission as a Declared Student or as a Diploma Student will be notified via mail or e-mail of their admission to the College and may be assigned a specific date and time for orientation, placement testing, advisement and registration.
In some cases, however, a student may not be permitted to enroll in the beginning courses in their program because:
- Certain prerequisite for the courses has not been met;
- The maximum enrollment for the program has been met; or
- Beginning courses in the program are not offered in that semester.
Only students applying for admission as a Declared Student are formally notified of their acceptance.
Transcripts and Transfer Credit Evaluation
Official transcripts are required for the following:
- To declare into a program of study
- To validate prerequisites completed
- To receive credit for courses completed at another institution
- Students receiving financial aid or veteran’s benefits must have transcripts on file.
Guidelines for submitting transcripts:
- Students are responsible for requesting official transcripts from each institution attended as well as providing military transcripts through the Joint Services Transcript System (JST), if applicable.
- Official transcripts must be received in the original, sealed envelope from the college or university.
- Electronic transcripts are accepted provided they are received from a credible source (Parchment, E-script, National Student Clearinghouse, etc.), scanned and emailed transcripts are not acceptable.
- Opened, faxed, or scanned and emailed transcripts will not be considered official.
Transcripts should be submitted to the Admissions & Registration Office:
Guam Community College
Attn: Admissions & Registration
P.O. Box 23069
Barrigada, Guam 96921
Students who submit transcripts from other post-secondary institutions or equivalent will have their coursework evaluated for potential transfer credit. Please note that all accepted transfer coursework may not be applied to a specific program of study.
Dual Credit Articulated Programs of Study (DCAPS)
According to GCC’s Factbook for AY2024-2025, over 2,670 students are enrolled in GCC's Career and Technical Education programs which offer DCAPS in the six Guam public high schools. These Programs are:
- Automotive Services Technology
- Automotive Collision Repair
- Construction Trades: AutoCADD
- Construction Trades: Carpentry
- Construction Trades: HVAC
- Early Childhood Education
- Health Careers & Sciences
- Hospitality & Tourism Management Program
- Information Technology
- Marketing
- Office Technology
- ProStart (Culinary and Foodservice)
- Telecommunications
- Visual Communications
Under the Dual Credit Articulated Programs of Study (DCAPS), these students can earn college credit in GCC postsecondary programs.
- Students must be declared in the approved GCC program which corresponds with the secondary program.
- There will be a limit of nine (9) postsecondary credits to be awarded upon successful completion of respective aligned secondary courses at NO COST. A dual credit recording fee of $30 will be assessed to award the remaining postsecondary credits should a program contain a DCAPS agreement that states that there are more than nine credits. The cap per program is 15 postsecondary credits to be awarded.
- Students must apply for these postsecondary credits to be awarded within two years after completing high school. If a student fails to apply for DCAPS within two years, the credits will be considered null and the credits must be acquired through the successful completion of its corresponding postsecondary course(s).
- All programs participating in DCAPS must have a course grade of a “B” or better as a minimum requirement for articulation of courses.
Students must provide the following documents to apply for DCAPS:
- Completed Dual Credit Articulated Programs of Study (DCAPS) Application Awarding of Credits Form
- Copy of Certificate of Mastery
- Official copy of high school transcript
- Proof of payment of recording fee (if requesting for more than 9 credits to be awarded)
Consideration for admission is based on the complete submission of all required or requested documents. Admission is based on the semester in which a complete application is made. Failure to submit a complete application may result in denial of requested admissions status.
If the student is admitted, the student must, in addition:
- Clear all health requirements as outlined by the Health Services Center
- Take placement tests, if required, and meet with a College counselor or advisor for advisement and program planning.
- Register for classes during the registration period and pay all tuition and fees in full within the designated payment period (health services clearance is required prior to registration).
All documents, transcripts and forms submitted by the student during the admission process become the property of the College and will not be returned to the student or forwarded on behalf of the student to any other institution.
New Students
For students with no previous college coursework or less than 45 credits of completed college coursework or equivalent, they must submit the following:
- Application for Admissions Form
- Proof of high school graduation or equivalent. Submit an official transcript from an accredited and Department of Education recognized high school, or acceptable evidence of comparable academic achievement (e.g., satisfactory score on General Educational Development-GED®).
- Other information, forms or documents as requested by the College.
Transfer Students
For students with an AA/AS or BA/BS or at least 45 credits of completed college coursework or equivalent, they must submit the following:
- Application for Admissions Form;
- All official transcripts from accredited institutions of higher learning are required to be submitted at the time of admission in order for transfer credit to be reviewed and awarded; and
- Other information, forms or documents as requested by the College.
Diploma Students
For students who have not completed high school or high school equivalency and are requesting to complete the Adult High School program, they must submit the following:
- Application for Admissions as an Adult High School Diploma student
- Submit official transcripts from all former high schools attended
- Other information, forms or documents as requested by the College.
Undeclared Students
Students taking courses who have not formally declared in a particular degree, certificate or diploma program at the College, must submit an Application for Admissions Form.
International Students
The College is authorized under federal law to enroll nonimmigrant alien students. Nonimmigrant alien students (hereinafter referred to as international students) are not citizens of the United States or aliens permanently residing in the United States. International students must meet the same admission requirements as all other declared students. In addition, international students must also meet the following special admission requirements:
- Certified translation of foreign transcripts (if applicable):
- If transcripts are not in English, students must submit, with their Application for Admission as a Declared Student, a certified evaluation of foreign transcript in U.S. equivalencies provided by a National Association of Credential Evaluation Services (NACES) approved member (www.naces.org) or Association of International Credentials Evaluators (AICE) member (www.aice-aval.org). Document by document evaluation is recommended for secondary transcripts. Course by course evaluation is recommended for post-secondary transcripts if the student would like a transfer credit evaluation.
- English Language Requirement: Students must meet the English Language requirement by either submitting one of the following test scores or by providing documentation that meets any of the exemptions.
- Test of English as a Foreign Language (TOEFL) applicants are required to score a minimum of 61 (internet based), 173 (computer-based) or 500 (paper-based) on the TOEFL.
- International English Language Testing System (IELTS). Students choosing to take the IELTS test for admission must take the Academic IELTS. For undergraduate students, the Academic Modules of the International English Language Testing System (IELTS)—a score of 5.5 overall or above for all applicants is needed to meet this requirement.
- Provide proof of exemption.
Have their scores on the Test of English as a Foreign Language (TOEFL) or International English Language Testing System (IELTS) submitted directly to the College. Scores must be from a test taken within the previous two years.
Test Exemptions
International student applicants are exempt from the TOEFL or IELTS examination if they meet at least one of the following:
- Those whose native language is English
- Those who score 510 or better on the verbal and 510 or better on the writing sections of the SAT
- Those who score 22 in English and 22 in reading sections of the ACT
- Those who have completed six years of continuous schooling through the high school or college level in American Samoa, Northern Marianas and/or Guam or in one of the countries listed below:
- Australia
- Britain
- Canada (excluding Quebec)
- Ireland
- New Zealand
- Those who have completed English composition at a regionally accredited U.S. institution with a C or better grade.
- Those who completed at least three years of high school in Guam with a cumulative GPA of 3.2 and SAT critical reading of 460 and SAT writing of 460. Admission to summer ELI classes does not imply a waiver of the TOEFL exam for fall or spring semester admission.
- Those who are placed into EN110 (Freshman Composition) or higher at the Guam Community College or the University of Guam, and have a letter of support from the relevant office of the institution (either GCC or UOG) administering the placement test
Applications and/or requests for scores to be sent to the College should be made by contacting one of the above mentioned entities (e.g. TOEFL, IELTS).
International students will not be notified of their admission to the College until all admission requirements have been fulfilled.
International students must have an official Notice of Admission and Form I-20A-B in their possession before coming to Guam.
International students must also meet the following requirements:
- Submit a Supplementary Information Form for International Students (including evidence of ability to pay all expenses themselves, or through the support of their families in their native country, or through a sponsor who is either a citizen or permanent resident of the United States).
- Submit any other forms, documents or information as may be required by the College.
- International students will be admitted only to an approved specific certificate or degree program. International students, except in extraordinary circumstances, will not be permitted to change their program of study and must enroll for a minimum of 12 credit hours per semester in courses which are required for their approved specific program of study.
- International students are required to register for English their first semester at the College and each subsequent semester until all English requirements of their program of study are met.
- Guam Community College has no dormitory facilities for students. The majority of international students rent rooms or apartments near the College. International students are encouraged to seek housing with English speaking families on Guam in order to facilitate speaking English on all possible occasions.
U.S. Immigration and Customs Enforcement regulations do not permit international students to accept employment while attending college. An international student should not count on being able to accept employment on Guam to work one’s way through college.
MyGCC is Guam Community College’s web-accessible information system that brings all major functional areas such as Student, Financial Aid, Finance, and Human Resources together into a single database information system. With MyGCC, students can register and pay for classes, check grades, and communicate with peers or faculty via student email. The launching of MyGCC is another example of GCC’s commitment to preparing students for success in the classroom and at the workplace using proven and cutting-edge technology. Although students may now register online, the Admissions & Registration Office is always available to assist students and applicants. A Schedule of Classes is published each semester and is available to students before registration.
A Schedule of Classes can be viewed and printed via GCC’s website, https://guamcc.edu/ClassSchedule. Students should plan their program of studies using the Catalog available online at: https://guamcc.edu.
A student is obligated to pay the tuition and fees for registered courses unless officially dropped on or before payment deadline. Failure to make payment by the due date may result in drop from all classes. However, it is the responsibility of the student to verify whether he or she has been dropped for nonpayment prior to the start of the semester. For more information regarding dates and deadlines, please review the academic calendar.
Online Registration
Registration can be performed either at the Admissions & Registration Office or online by logging into MyGCC via the College’s website, https://guamcc.edu. All students are encouraged to seek academic advisement prior to registration in order to discuss course prerequisite, program requirements, or educational goals. Students in certain programs are required to meet with their academic advisors to obtain approval for their schedule before they register. These students include those declared in the Adult High School Diploma Program, Associate of Arts in Culinary Arts, Certificate in Practical Nursing, Criminal Justice Academy, Bachelors of Science in Career and Technical Education, and Cosmetology. All international students must clear with Admissions & Registration and obtain schedule approval from their academic advisor prior to registering. In addition, all students must clear outstanding financial obligations with the College at the Cashier’s Office, and have immunization updated pursuant to Guam public law, P.L. 22-130. Updated health records must be submitted to the GCC Health Services Center by new and returning students. Students who maintain their continuous student status, students enrolled for classes in at least one regular semester (fall or spring) each academic year, do not have to update their health records each academic year unless advised to do so.
Class Withdrawal
The deadline for withdrawing from a class is about six weeks prior to the end of the term, and is published in the academic calendar available in the catalog as well as the College’s website, https://guamcc.edu. Any student who fails to officially withdraw from a class by this deadline will be assigned any grade, except “W” for the class. Classes officially dropped prior to the end of the schedule adjustment period will not appear on a student’s academic record. Classes officially withdrawn will be assigned a “W” on the academic record.
Complete Withdrawal
Students who wish to withdraw completely from the College must do so by the deadline for dropping a class. Students who completely withdraw from the College must reapply for admission to the College, if they subsequently desire to re-enroll in the College.
Change or Addition of Program/Major
Declared Students enrolled at the College with a cumulative GPA of 2.0 or better may change their program or major or add a second program or major at any time during a regular semester but it will not go into effect until the following semester. Request forms are available at the Admissions & Registration Office.
Change of Personal Data
Any change of personal data such as name, address, telephone number and citizenship must be submitted to the Admissions & Registration Office. Copies of supporting documents are required for change of name and citizenship. Some visa restrictions apply to international students.
Auditing Courses
Students wishing to audit a class must complete all admission and registration requirements and procedures, including payment in full of all tuition and fees. Students will be permitted to register on a space-available basis only after all students taking the course for credit have been registered. No credit or grade is given for a course which is audited. Students may participate in class activities only to the extent permitted by the instructor of the class. Students wishing to audit a class must indicate this status at the time of registration.
Class Attendance
Regular and prompt class attendance is expected of all students. Each student is responsible for informing instructors of his or her absences (if possible) and to make arrangements with instructors to complete work missed due to his or her absence from class.
Transfer of Credits from Postsecondary Institutions
GCC will accept credit transfer for all courses successfully completed at any college or university in the United States which is accredited by its regional accrediting body, affiliated accrediting body, the Distance Education Council, or any accrediting body recognized by the United States Department of Education (e.g. MSCHE, NEASC-CIHE, NEASC-CTCI, NCA-HLC, NWCCU, SACS, WASC-ACCJC, WASC-ACSCU, or the DETC) or which is recognized and approved by the Department of Education or Ministry of Education in a foreign country. Transfer credit is given for courses taken at another college or similar institution that closely correspond to those offered at GCC. When transfer credit is granted for a particular course, the requirements for the course have been successfully met (only courses with a minimum grade of “C” are considered for transfer), and credit is indicated on the student’s transcript. No letter grade is provided. Transfer credit will only be considered if:
- Official transcripts are received directly from the institution where the credits were earned or can be hand delivered by the student, provided the transcripts are in their original sealed envelope.
- The course is at the postsecondary level; with GCC, this means the course is at the 100 level or above and receives undergraduate level credit.
- Credits earned outside of GCC are equal to or greater than the credits to be received from GCC.
- The student has earned a “C” grade or higher (or equivalent).
- The course is not a credit awarded for life experience.
Full English translations of course descriptions as well as a NACES approved course by course evaluation are required for any international student seeking to receive transfer credit. Program faculty or Department Chair will determine whether any transfer course does or does not fulfill any program requirement, except where there is clear equivalence between the transfer course and the GCC course, in which case the Registrar makes the decision. Transfer students will be advised to contact the Department Chair of their program for evaluation of any course that does not transfer as equivalent to a GCC course but which the student believes should satisfy a program requirement. A form or template will be utilized for this purpose.
The transfer evaluation provided to the student at the beginning of the student’s matriculation at GCC will be entered into the student’s permanent record unless specific errors are found (e.g. misidentifying the number of credits for a course or giving a student credit for a course more than once) or the student requests and is granted a modification by the Dean and the Vice President for Academic Affairs.
It is the student's responsibility to have transcripts of all previous work sent to the College and to request an Evaluation of Records by the Admissions & Registration Office.
Advanced Placement
Students may be placed in higher-level courses or a sequence of courses on the basis of their high school achievement, training or test results. Credit may be granted for the courses passed but both placement and the granting of credit are at the discretion of the Registrar in consultation with the Department Chairperson, the Deans, or the Vice President for Academic Affairs, as necessary and appropriate.
Credit granted through advanced placement will be recorded with a “CR” (satisfactory completion) grade. Students who wish to be considered for advanced placement must request an evaluation of their high school achievement, training or test results for this purpose.
Credit-By-Examination College Sponsored Examinations
Credit-by-Examination (CBE) is available for some courses at Guam Community College. Interested students should contact the appropriate Dean or Department Chair to determine whether or not this option is available for any particular course.
- Only continuing students in good academic standing may apply for credit by examination.
- Examinations shall be provided to the student no more than 10 working days after the Petition for Credit-by-Examination form has been approved and all applicable fees have been paid.
- No more than 9 credits applicable to a student’s declared Certificate program may be earned through CBE.
- No more than 12 credits applicable to a student’s declared Associate or Bachelor’s Degree program may be earned through CBE.
- Students are allowed no more than three attempts to receive Credit-by-Examination for any course. For each attempt, all applicable fees must be paid, without exception.
- The Department Chair is responsible for determining the examination in consultation with his or her faculty and Dean. Examinations must be no more rigorous or no less rigorous than what a student may experience as a regularly enrolled student.
- Standardized examinations should be prepared by the Department Chair in conjunction with his or her faculty and kept on file by the Department Chair in anticipation for CBE requests.
- Credit-by-Examination should not be used for general education courses (English, math, science, etc.) with the exception of foreign languages offered by the institution (e.g., Japanese, Korean, CHamoru, and American Sign Language).
- A student receives a grade of CR for passing Credit- by-Examination; student receives a grade of NC for failing Credit-by-Examination. Courses passed by examination do not carry grade or grade points.
- Credit-by-Examination is recorded on a student’s academic record for each course challenged through Credit-by-Examination. After an unsuccessful attempt at Credit-by-Examination, students must wait six months before making another attempt.
- Credits earned through CBE do not fulfill the residency requirement of degree, certificate or diploma.
- Credits earned through CBE do not transfer to other higher learning institutions. Typically, Credit- by-Examination is used to award credit for relevant prior training, work experience, or competencies using paper or electronic examinations or practical examinations.
Credit-by-Examination Fees
| Assessment Request | $25.00 per request |
| Challenge Exams | $75.00 per exam, for paper or computer-based exam |
| Practical Exam | $100.00 per practical exam |
*All fees are non-refundable
External Examinations Credit
External Examinations Credit-Granting Procedure includes the following:
- The various forms of credit evaluation are available only to students currently registered at the College.
- Letter grades will not be granted for credits awarded through this program. Instead, “CR” will be used and will not be calculated into the GPA.
- Credits awarded through this program will be identified as such on the student’s academic record. They may not be accepted by other institutions.
- These credits may not be used to meet the 12-credit residency requirement for degrees and certificates unless the requirement is waived by the Dean.
- Credit may be granted for either electives or required courses.
- Credit will be granted only toward a student’s declared program and may require reevaluation if the program is changed.
- Evaluation of alternative learning experiences older than ten years, or any period of time designated by a department, may include review for currency.
- Evaluation resources such as the American Council on Education (ACE) guides will be consulted, but the College reserves the right to set its own credit-granting policies, which may differ from that of ACE or any other external resource.
- The number and type of credits awarded will be governed by the extent to which the knowledge and skills documented in the evaluation process are comparable to the competencies described in existing Guam Community College course documents.
External Examinations Credit is awarded by the College on the basis of the following examinations:
| CLEP General Examinations | Credit Hours |
|---|---|
| English Composition | 6 |
| Humanities | 6 |
| Mathematics | 6 |
| Natural Sciences | 6 |
| Social Sciences & History | 6 |
CLEP general examinations in English (with essay) will be accepted by the Guam Community College if the score reaches or exceeds the 35th percentile. If the English exam (with essay) reaches or exceeds the 35th percentile, the College will allow a transfer credit equivalent to EN110 (3 credit hours).
Other External Exams
- CLEP Subject Examinations
- College Board Advanced Placement Exams
- DANTES Subject Standardized Tests (DSSTs)
- ACT Proficiency Examination Program (PEP)
- USAFI Subject Standardized Tests (USSTs)
- USAFI End-of-Course Examinations
- Straighter Line
A minimum score for credit is determined using the American Council of Education (ACE) recommendations. However, the College reserves the right to reject recommendations from such sources (refer to credit granting procedure above).
Credit for Prior Learning (CPL)
The College recognizes that students may have had prior learning experiences, which might translate to academic credit. The College adheres to the following standards for assessing such experience:
- Credit should be awarded only for learning, and not for experience.
- College credit should be awarded only for college-level learning.
- Credit should be awarded only for learning that has a balance, is appropriate to the subject, and lies between the theory and practical application of the subject.
- The determination of competence levels, and of credit awards must be made by appropriate subject matter and academic experts.
- Credit should be appropriate to the academic context in which it is accepted.
The College recognizes that students may have acquired learning through traditional college experiences as well as from work and life experience, independent reading and study, the mass media and participation in formal courses sponsored by associations, businesses, government, industry, the military, unions and learning reflected in various examinations.
The College will evaluate prior institutional or college learning as transfer credit and as a basis for advanced placement. The College will evaluate extra-institutional or non-college learning using the prior learning assessment process which includes, but is not limited to, departmental challenge exams or portfolio assessment. See also “Educational Credit for Training Programs” In the next section.
GCC's Prior Learning Assessment (PLA) evaluation processes include the following:
- Departmental Challenge Exams (please see Credit-By-Examination College Sponsored Examinations)
- Transfer of credit from other institutions
- Credit articulated through PLA
Prior Learning Assessment (PLA) Fees
| Assessment Request | $25.00 per request |
| CPL Credit Award | 20% of prevailing resident tuition rate |
Note: No charge for CLEP, AP, credit via formal agreements, or military credit.
In addition, a variety of practices exist for awarding credit for learning which has taken place outside of higher educational institutions. These include, but are not limited to:
- The American Council on Education: Military and Corporate
- National College Credit Recommendation Service
- Standardized Examinations such as AP, CLEP, DSST, and Excelsior College Exams
For more information on Prior Learning Assessment at Guam Community College, please contact the Admissions & Registration Office, or visit the PLA webpage at https://guamcc.edu/prior-learning-assessment
Recognition of Sponsored Learning
Military Education
Credit may be granted for armed services school and military experience only as recommended by the American Council on Education (ACE).
Educational Credit for Training Programs
The College awards credit for non-collegiate sponsored instruction as recommended by the National College Credit Recommendation Service (NCCRS) or the American Council on Education in The National Guide to Educational Credit for Training Programs. These credits do not fulfill the residency requirement of (ACE) degree, certificate and diploma programs. Nationally-recognized training and certification programs will be assessed on a case-by-case basis.
Special Project Courses
Special courses are open-entry/open-exit courses. A student may register for a special course during any regular semester or summer session. To register for a special project course, a student must complete the Application to Take Form. A student must work with either a counselor or an advisor as well as the supervising faculty member in preparing the Application to Take Form. The number of credits to be earned must be specified on the form. A student must obtain the approval of the counselor or advisor, supervising faculty member, Department Chairperson, Dean and the Registrar in order to take a special project course. All special project courses must be approved and start no later than two (2) weeks after the first day of classes for each semester for fall and spring, and one week prior to the start of summer terms.
Credit Load
A student may not register for more than 15 credits in any one semester except under special circumstances. If a student’s program of study requires registration for more than 15 credits in any one semester, counselor or advisor approval is required.
Credits
At the College, each credit hour represents one hour per week in class and two hours outside of class devoted to preparation. Credit is granted in recognition of successful work in attaining Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs) in specific courses. See General Requirements for Certificates and General Requirements for Associate Degrees for a statement on SLOs as applied to programs in a later section of this catalog.
Prerequisite
Course Prerequisites are courses to be completed or conditions to be met before a student is eligible to enroll in a specific course. A student who has enrolled in a course without first completing all course prerequisites may be dropped from that course. Waivers for course prerequisite can only be obtained from the Department Chairperson of the department which oversees the course. For example, ED150 requires the completion of EN110; therefore, only the Department Chairperson overseeing education courses may waive the prerequisite. As a general rule, however, prerequisite waivers are strongly discouraged.
Course Waivers and Substitutions
Recommendation for a course waiver is made by the Department Chairperson or academic advisor. For each course waiver there must be an accompanying recommended course substitution. Credit requirements cannot be waived. A declared student wishing to have a course waived or substituted must complete the following steps:
- Submit a Course Substitution Form, which indicates the waiver, to a counselor/advisor who forwards the request to the Department Chairperson.
- The Department Chairperson will confer with department members, and if they concur with the request, will forward the recommendation to the appropriate Dean for approval.
- If the Dean concurs with the request, it will be forwarded to the Registrar for verification and recording. If the Dean does not concur with the request, it will be returned to the student with justification via the Department Chair. The Dean’s decision is final.
It is important to note that course substitution takes the place of a required course in a program, for as long as the course substitution meets the content and/or spirit of the requirement. The Department Chair must consult with the Dean to make this determination.
Repeating a Class
Credit is allowed only once for a course. A course may be repeated if a grade of “D,” “F,” “NC,” or “Z” was received. Only the newly earned grade will be counted and used in computing the grade point average. If a student received a “C” or better and the course is repeated, the first grade will be counted towards grade points even if the second grade is higher.
Note: Prior to fall 2007, the class being repeated will be assigned a repeat grade of “R” before the original grade. Beginning fall 2007, all repeated courses will appear as a letter grade with the repeat indicator appearing in a separate column. All classes being repeated will not affect grade point average.
Official Transcripts
Official transcripts will be prepared for students upon request. Students must complete the following steps:
Submit a transcript request either in person or through the National Student Clearinghouse. There is a fee for transcripts, so please review the transcript request form for fees. The student must not owe any financial obligations to the school nor have any other holds preventing the release of an official transcript.
It is the student’s responsibility to update their address and mailing information in their student records. Such information may be updated online via MyGCC or submitted to the Admissions & Registration Office.
See National Student Clearinghouse for additional information. Official transcripts will not be faxed or emailed. Additionally, transcripts will not be released to a third party without the student’s written authorization.
Final grades can be accessed by students via the College’s self-service portal, MyGCC.
Grading
The assignment of final course grades is the responsibility of each faculty member, which begins with a clear statement in the course syllabus and in discussion with the students in the class. Defining the criteria upon which grades will be determined, is established by the curriculum documents. Instructors must identify the components and the weight of each that make up the final grade in the class syllabus.
In addition to defining the criteria, instructors are responsible for applying the criteria consistently and carefully, using professional judgment for their assessments, and in all cases, being fair to reflect student performance in the context of GCC’s expectations for student achievement and the established grading scale. Faculty evaluation of student work may be appealed using the process described in the Student Grievance Procedure found in the Student Handbook. An Evaluation Review Committee shall be convened to review the faculty member’s evaluation of the student’s work. Students may contact a Counselor for further guidance. The Student Handbook can be found at https://guamcc.edu/StudentHandbook.
Grading System
Grades are earned for each course in which a student is officially enrolled. GCC uses a 4-point grading scale. Grade Point Average (GPA) is determined by letter grades A through F using the designated points assigned to each. The grade points assigned to the letter grades are as follows:
- A 4.0 = Excellent achievement
- B 3.0 = Above average achievement
- C 2.0 = Average achievement
- D 1.0 = Below average achievement
- F 0.0 = Failing
The following are grades issued to students which do not impact the student’s GPA:
- TF = Technical Failure (student is registered for a course and does not attend a class session)
- TW = Technical Withdrawal
- W = Withdrawal
- I = Incomplete
- CR = Satisfactory Completion
- NC = Unsatisfactory Completion
- P = Satisfactory Completion/Test-Out (Used for developmental courses only)
- Z = Unsatisfactory Progress made; repeated enrollment required (used for developmental courses only)
- AU = Audit
- TC = Transfer Credit
Credit/No Credit Option
Students should consult their counselor or advisor before taking courses using the Credit/No Credit option; this option must be declared in writing prior to the first day of instruction. Credit/No Credit is used for all Credit-by-Examination challenges.
Incomplete or “I” Grade
Incomplete (I) grades may be assigned only when academic work has been interrupted by circumstances beyond the student’s control. Incomplete grade requests must be initiated by the student and approved by both the instructor of record and Department Chair by filing an Incomplete Grade Request form. The form must be submitted by the student, along with appropriate documentation if deemed necessary, outlining the circumstances. The instructor and the program chair must approve the request before the last day of the semester in which the Incomplete will be granted.
The student must complete all academic work to replace the “I” grade according to the terms of the agreement with the instructor of record by the end of the next consecutive academic term or the grade will be determined to be an “F” (“Z” for Developmental Education courses). The grade of “I” counts as credits attempted but does not affect GPA.
Technical Failure or “TF” Grade
If a student registers for a class but fails to attend the class, the instructor will award a “TF” grade indicating that the student never attended the class. The “TF” will be entered on the student’s permanent record.
Technical Withdrawal or “TW” Grade
If a student registers for a class but fails to meet all College requirements for registration in that class (e.g., course prerequisite, immunization/health requirements, etc.), that student may be administratively withdrawn from that class. In such instances, a “TW” grade will be entered on the student’s permanent record.
Grade Point Average
A student’s grade point average (GPA) is computed by dividing the total grade points earned by the total credits attempted, excluding those credits for which “AU,” “CR,” “I,” “NC,” “P,” “TF,” “TW,” “W,” or “Z” grades are assigned and courses repeated (see section on Repeating a Class for more information).
Time Limit for Coursework
In areas of study in which the subject matter changes rapidly, material in courses taken long before graduation may become obsolete or irrelevant. Coursework that is more than eight (8) years old is applicable to completion of degree requirements at the discretion of the department of the student’s major course of study. Departments may accept such coursework, reject it or request that the student revalidate its substance.
The eight-year limit on coursework applies except when program accreditation agencies limit the life of coursework to less than eight (8) years. Departments may also require students to satisfy current major requirements rather than major requirements in earlier catalogs, when completing earlier requirements is no longer possible or educationally unsound.
Determining Applicable Catalog
Students maintaining continuous enrollment at Guam Community College may graduate according to the requirements of the catalog in effect at the time of initial acceptance as a Declared Student or according to the requirements of any single catalog in effect during subsequent terms of continuous enrollment thereafter.
Students who are dismissed as Declared Students may only be reinstated using the most current catalog. A semester in which a student earns course credit will be counted toward continuous enrollment. Noncredit courses, audited courses, failed courses, or courses from which the student withdraws do not count toward the determination of continuous enrollment for catalog purposes.
Students who do not enroll for two consecutive regular (fall & spring) semesters are no longer considered continuously enrolled, and must meet requirements of the catalog in effect at the time they return.
Students are not obligated to enroll and earn course credit during summer terms, but summer enrollment may be used to maintain continuous enrollment status.
Students who return during a summer term after an absence must follow the requirements of the catalog in effect for the following fall semester.
Students who do not enroll for two consecutive regular semesters as well as students dismissed from the College as a Declared Student must complete the Application for Re-Entry and must submit it to the Admissions and Registration Office. Students must meet with their advisor or with a counselor prior to the submission of this Application.
Satisfactory Academic Progress
Satisfactory Academic Progress (SAP) standards apply to all Declared Students including all students who receive financial aid at the College. Students receiving financial aid may also visit the Financial Aid Office located in the Student Services & Administration (Building 2000, Room 2114, 2115, or 2116), or call 671-735-5543 ext. 5545 or 5556.
Evaluation of Satisfactory Academic Progress (SAP)
The Admissions & Registration Office evaluates SAP at the end of each semester. Student progress is reviewed for cumulative grade point average (CGPA) and progress toward completion. The minimum CGPA for certificate postsecondary programs is 2.0. In addition, the College will determine the cumulative successful completion rate (CSCR) equals to at least 67% of credits attempted. In determining the total number of credit hours attempted, all credits attempted at GCC under the student’s post-secondary academic history will be counted. Grades from transfer courses will not be included in the CGPA.
Academic Probation
At the end of each term, the academic record of each Declared Student enrolled for that term will be compared to the Standards for Satisfactory Academic Progress. Any Declared Student who is not making Satisfactory Academic Progress toward a degree or certificate will be placed on Academic Probation at the end of that term. Any student on Academic Probation may lose financial aid eligibility. Financial Aid Students may also visit the Financial Aid Office in Room 2114, 2115, or 2116, Student Services & Administration Building or call 671-735-5543 ext. 5545 or 5556. Students will be notified of their academic standing by the Admissions & Registration Office.
A Declared Student who has been placed on Academic Probation may enroll for at least one subsequent, probationary term. If, after the probationary term, the student’s cumulative academic record meets at least the minimum standards, the student will be taken off Academic Probation. If the student’s cumulative academic record does not meet the minimum standards applicable to that student, but the academic record during the probationary term demonstrates progress toward meeting the cumulative minimum standards required for Satisfactory Academic Progress, then that student may enroll for another probationary term at the College at the discretion of the Vice President for Academic Affairs. Such action is limited to two consecutive semesters.
Dismissal
If the student does not meet at least the minimum standards applicable to that student and fails to demonstrate progress toward meeting the cumulative minimum standards required for Satisfactory Progress during the probationary period, then that student is re-classed as an Undeclared Student. Once satisfactory progress is achieved, the student may re-apply for admission as a Declared Student.
Reinstatement as a Declared Student
A student who has been re-classed as an Undeclared Student may continue to enroll at the College (does not apply to an international student, F-1 Visa). Coursework completed as an Undeclared Student may be used as a basis for application for readmission as a Declared Student. A student who applies for readmission to the College as a Declared Student must demonstrate the ability to meet current academic progress standards. A student who is readmitted to the College as a Declared Student following dismissal from the College will be readmitted on Academic Probation and will be subject to current standards as stated in the College Catalog at the time of reinstatement.
Appeals
Any student has the right to appeal placement on Academic Probation and Dismissal from the College as a Declared Student. Any appeal must be in writing and include supporting documentation. All appeals will be first submitted to the Registrar who will adjudicate all appeals. A student may appeal the decision of the Registrar using the Student Grievance Procedure.
Satisfactory Academic Progress (SAP) for students utilizing Veteran Education Benefits
In order to meet SAP, a Veteran student must maintain a minimum cumulative and term GPA of 2.0 and successfully complete a minimum of 67 percent of the courses attempted. Failure to do so will result in Veteran Academic Probation (VAP) being placed on the student's record, restricting open registrations for future terms. Not meeting SAP may eventually restrict a student's ability to use veteran education benefits at Guam Community College.
Veteran Academic Probation (VAP)
A student will be placed on a Veteran Academic Probation (VAP) if the cumulative or term GPA falls below a 2.0, or if the completion of courses attempted falls below 67 percent. The VAP policy requires that the student contact the Financial Aid Office at Guam Community College to be advised on the steps to have the VAP removed, and briefed on the possibility of being placed on Veteran Benefit Denial (VBD) if SAP is not met while on VAP status. A student will be allowed to register while on VAP. If the student achieves a cumulative and term GPA of 2.0 or higher and reaches a completion percentage of 67 percent for all courses attempted, the VAP will be removed, allowing the student to register for future terms without restrictions.
Veteran Benefit Denial (VBD)
If while on a VAP, the student does not meet the minimum cumulative and term GPA of 2.0 and does not successfully complete at least 67 percent of the courses attempted for that term, the student will be placed on a Veteran Benefit Denial (VBD). This action will be reported to the VA by the College through the VA's formal process. Once placed on VBD, the student will be denied the use of any and all VA benefits and will be responsible for payment of tuition and fees. Guam Community College will not certify for veteran education benefits under any chapter while on a VBD. Students on a VBD may continue to take courses at Guam Community College via alternate funding sources, such as financial aid. The VBD will be removed and upgraded to VAP when a cumulative and term GPA of 2.0 or higher and a completion percentage of 67 percent for all courses attempted is reached, allowing the student once again to utilize veteran education benefits at Guam Community College. The College will retroactively certify these successful courses after the grade is posted.
Appealing a Denial
A student can appeal a VBD decision through the College’s administrative appeals process. The appeal should be submitted to the Financial Aid Office, and will be reviewed on a case-by-case basis. Please visit the Financial Aid Office to discuss your appeal or email financialaid@guamcc.edu.
Deans’ List
Guam Community College publishes the Deans’ List in the fall and spring semesters of the academic year. Students qualify and earn the recognition by achieving the semester grade point average of 3.75 or higher with enrollment and completion of 12 or more credits for the semester (Pass/Fail and Credit/No Credit courses will not be counted). The Deans’ List is published at the completion of the semester by the Admissions & Registration Office.
President’s List
Guam Community College publishes the President’s List in the fall and spring semesters of the academic year. Students qualify and earn the recognition by achieving the semester grade point average of 4.0 with enrollment and completion of 12 or more credits for the semester (Pass/Fail and Credit/No Credit courses will not be counted). The President’s List is published at the completion of the semester by the Admissions & Registration Office.
Graduation Honors
Postsecondary students graduating from Guam Community College with a cumulative grade point average of 3.50 or higher based on 24 or more credit hours of credit completed at Guam Community College will graduate “With Honors.”
A Commencement Ceremony is held annually at the end of the spring semester. The College urges all of its graduates to participate in the Commencement Ceremony. Students who receive their degree, certificate or diploma in the fall semester within the same academic year or the summer semester the prior academic year may participate in the Commencement Ceremony.
Degree, Certificate, Apprenticeship, Industry Certification, and Diploma program requirements are separately listed in the Catalog.
The College offers courses outside its regular schedule of courses for students interested in personal enrichment, skill training, or to meet other academic needs. Some courses are also offered to meet employment requirements such as the Techniques of Alcohol Management (TAM®) training, or the procurement basic training modules. The College also hosts various conferences and workshops to enable participants to upgrade their skills and knowledge in a variety of areas.
Continuing Education and Lifelong Learning courses are primarily skill-oriented and are designed to meet the specific training needs of those seeking to upgrade skills in their workplaces, as well as those seeking to develop work skills for entry or reentry into the workforce. The courses vary in length, depending on the breadth and depth of the skill to be taught.
The Office of Continuing Education & Workforce Development, located on the first floor of the Student Services & Administration Building, welcomes requests or suggestions for course or event offerings. A catalog of courses may also be requested from the office. For more information, call 671-735-5640 ext.5579 or email learning4life@guamcc.edu.
The Continuing Education Unit (CEU) is used by Guam Community College to facilitate the accumulation and exchange of standardized information about participation of individuals in noncredit continuing education. Please note the following four (4) points:
- CEU credit is for career enrichment and/or advancement. CEUs may be integrated into regular credit courses, provided that the CEU is clearly defined and there is assurance that the CEU does not replace regular credit requirements approved by GCC.
- CEU contact hours can be structured within a regular credit course, provided that the ten contact hours to one CEU equivalency is maintained. CEUs are awarded on a pass/fail basis. Letter grades are not to be used, as the goal of the CEU experience is learning enrichment/advancement and not mastery of scholarly material.
- CEU programs will be governed by the same standards that GCC imposes on regular programs. GCC will have direct quality and fiscal control over all CEU activity within the institution.
- CEUs cannot be used for degree credit requirements. CEUs and regular credit cannot be earned at the same time for the same learning experience.
Further background information about these units is contained in the following statements:
One CEU is defined as ten contact hours of participation in an organized continuing education experience under responsible sponsorship and capable direction of qualified instructors.
Program objectives, content, format, methods of instruction, methods of evaluation and program schedules will be established prior to the determination of the number of contact hours and appropriate CEUs. CEUs do not convert to degree credit.
Permanent records for individual participants in CEU programs will be kept. Course fees will be negotiated between the requesting agency, organization or individuals and GCC.
Review, evaluation and approval of CEUs for an educational experience is the responsibility of the Office of Continuing Education & Workforce Development, in consultation with the Vice President for Academic Affairs. Contact (671)-735-5640 ext.5579 or email learning4life@guamcc.edu for additional questions.
Individual programs of study are developed based on specific requests made by individuals, organizations, or companies for their immediate and/or long-term needs. Customized programs may be developed by the Office of Continuing Education and Workforce Development (CEWD) to fulfill the needs of these customers. A certificate of enrichment/completion may be awarded by CEWD to individuals who complete the programs and meet these specialized programs. Certification of enrichment/completion is an acknowledgement that the student has completed a combination of courses and related activities organized by the College for the sole purpose of attaining the educational objectives requested by the participant or trainee.
This is recommended for adults who are learning English as a non-primary language. Coursework integrates listening, speaking, reading and writing skills in English. Courses are offered through the Office of Continuing Education and Workforce Development as CEUs only. To register for ESL, please call the Adult Education Office at (671) 735-6010 ext. 5415 or visit the office staff in the Foundation Building, 2nd floor.
All Undeclared or newly Declared Students in regularly scheduled postsecondary courses are required to take a placement exam by the time they have enrolled in 12 credits of classes.
All Undeclared or newly Declared Students enrolled in regularly scheduled postsecondary courses must be enrolled in or have completed their EN096 Basic English Level I or EN097 Basic English Level II (or higher) general education requirement by the time they have enrolled in 12 credits of classes, and must enroll in or have completed MA098 Intermediate Algebra (or higher) general education requirement by the time they have enrolled in 15 credits. This means that students may take only nine (9) credits before they must begin meeting their general education requirements.
Students, who have not met their math and English General Education requirement(s) may be allowed to drop or withdraw from math and English courses only if they wish to withdraw completely for the semester.
Placement testing is not mandatory for admission to the College. Completion of placement testing or equivalent, however, is required for enrollment into English and Mathematics courses. Therefore, students who plan to enroll full-time in a program should take the placement test to be eligible for a full load of courses.
Guam Community College also serves as a testing center for licensure recognized by the following:
- Electronic Technician’s Association International
- Microsoft
- A+ Service Technician
- Federal Communications Commission
- Cisco Systems and General Education Development
- Computing Technology Industry Association (CompTIA)
GCC provides professional examination services for the following:
- American Council on Exercise
- Certified Chef de Cuisine (CCC)
- Nephrology Nursing Certification Commission
- National Academy of Sports Medicine
- National Restaurant Association
GCC Test Center is also recognized to administer testing for the following:
- American Culinary Federation
- Meazure Learning
- Certiport®
- KRYTERION™
- Pearson VUE
- Performance Network Assessment (PAN)
- Prov Inc.
- PSI Services LLC
- WorkKeys®
For more information regarding testing services, contact the Office of Continuing Education & Workforce Development at (671)-735-5640 ext.5579 or email learning4life@guamcc.edu.
The end of fall 2009 marked the formal adoption of GCC’s Institutional Learning Outcomes, also known as ILOs. The ILOs were developed as a task of the General Education Committee with input from all faculty, the Faculty Senate, the College Governing Council (CGC), and the Board of Trustees. These ILOs represent what knowledge, skills/abilities, and values students should develop and acquire as a result of their overall experiences with any aspect of the College. The ILOs link all divisions, departments, units, and programs at the College regardless of whether they are directly (academic) or indirectly (non-academic) involved with students. Every employee and office at the College exists to support students and help them excel; this includes the administration, student support services, faculty, maintenance, procurement, etc.
The five (5) ILOs represent broad outcomes in various areas depicted as the College’s core values. Due to their universal and broad coverage, it is not expected that a single course, or program for that matter, addresses all identified outcomes. Rather, it is through the culminating integrated experience students have in their academic and campus life which will enable them to acquire these ILOs. The emphasis on ILOs and outcomes-based assessment has helped transform the College into a more learner-centered institution. Guam Community College remains committed to strengthen its focus on learning outcomes, ultimately leading to quality education and a productive workforce. In keeping with its mission that Guam Community College is a leader in career and technical workforce development, providing the highest quality student centered education and job training for Micronesia, the College community has established the following Institutional Learning Outcomes which were recommended by the Faculty Senate, approved by the President, and adopted by the Board of Trustees (December 2, 2009):
Guam Community College students will acquire the highest quality education and job training that promotes workforce development and empowers them to serve as dynamic leaders within the local and international community.
Students will demonstrate:
Use of acquired skills in effective communication, and quantitative analysis with proper application of technology
Ability to access, assimilate and use information ethically and legally
Mastery of critical thinking and problem solving techniques
Collaborative skills that develop professionalism, integrity, respect, and fairness
Civic responsibility that fosters respect and understanding of ethical, social, cultural, and environmental issues locally and globally.
Tuition
Resident/Military & Dependents/Veteran Students/Federated States of Micronesia/Republic of the Marshall Islands/Republic of Palau - $130.00 per credit hour
A “Resident Student” is a student whose permanent home is on Guam and pays Guam income taxes or is claimed as a dependent by someone who pays Guam income taxes. Active duty military personnel and their dependents as well as Veterans fall under the Resident Tuition rate.
Nonresident Student - $155.00 per credit hour
A “Nonresident” is a student whose permanent home is away from Guam and does not pay Guam income taxes.
International Student - $180.00 per credit hour
An “International Student” is a non-citizen that holds a non-immigrant visa, e.g., B, C, D, F, H, J, L or M visa. All students will be classified as resident, nonresident or international students for tuition purposes when they register for classes. When the College is unsure of a student’s residency classification, the College will assess the higher tuition rate. The burden of showing that the residence classification should be changed is on the student.
The Residence Classification Policy and Procedures of the College are available for inspection at the Admissions & Registration Office.
The College reserves the right to periodically adjust tuition, but will conduct public hearings in compliance with the Administrative Adjudication Act.
Fees
The following fees are charged each semester:
| Registration Fee | $22.00 |
| Student Identification Card | $7.00 |
| Library Fee | $15.00 |
| Technology Fee | $73.00 |
| Student Activity Fee | $15.00 |
| Student Health Fee | $15.00 |
| Total Fees | $147.00 |
Notes on fees
Student Identification Card Fee - All students are required to have a Student Identification Card except for students enrolled exclusively in short-term courses and special offerings.
Library Fee - The Library fee is considered to be a special fee for tuition and fee refund purposes.
Technology Fee - Of this amount, $36.50 will cover costs of current operations and the remaining $36.50 will be set aside in a special fund to systematically upgrade computer labs, software and other technology-related student services.
Student Activity Fee - Funds are used to support student activities organized under the purview of the Center for Student Involvement (CSI) Office.
Student Health Fee - Students may receive PPD, MMR vaccinations, and emergency care services at the Student Health Center free of charge. Students failing to appear to have test results read and who are required to repeat a test will have to pay a second student health fee.
Laboratory Fees
Some courses offered by the College involve the consumption of materials and supplies by each student enrolled in them; lab fees are charged for these classes. Lab fees are listed in the Schedule of Classes each semester.
Educational Records
Copies of a student’s educational records made pursuant to the provisions of the Family Educational Rights and Privacy Act of 1974 will be made at a cost of $1.00 per page.
Audit Fees
Audit fees are the same as those for regular credit classes.
Late Fee
The College will charge a non-refundable late fee of $37.00 to be assessed for the following:
Students under “Payment Plan,” or Students under financial assistance whose financial assistance does not cover 100% of student obligation by the end of the semester. The College will not assess a Late Fee if a student registers only for non-credit courses, special courses, or open-entry courses.
Application for Graduation for Degree, Certificate or Diploma
The College will charge a non-refundable $15.00 fee. The Application for Graduation fee includes one Diploma and will be distributed during the Commencement Ceremony. The Commencement Ceremony is held each year at the end of Spring Semester.
Diploma Re-Order Fee
The College will charge $15.00 to reorder a degree, certificate or diploma to be picked up by a student. If it has been over a year since graduation, the reorder fee is $35.00. A $15.00 postage fee will be charged for a degree, certificate or diploma to be mailed to a student.
Placement Test Fee
The College will charge $22.00 for the College English and Math placement tests.
Official Transcript Requests
Students may request copies of their academic record (transcript) either online via the National Student Clearinghouse (https://tsorder.studentclearinghouse.org/school/select) or at the Admissions & Registration Office in the Student Services & Administration Building. Transcripts are usually prepared within five (5) working days. Each copy of a student’s transcript costs $5.00. A rush service request for transcripts costs $15.00 per transcript. Transcripts will be available in 2 business days. No transcript will be issued by the College if the student has an outstanding financial obligation with the College. Transcripts will not be faxed or emailed.
Tuition & Fee Waiver
On a space available basis, individuals who are residents, live on Guam for at least the last 5 years, and who are 55 years of age and older do not pay tuition and fees for classes appearing in the regular term. Proof of age and residency will be required at the time of registration. All applicable tuition and course fees will be charged for courses taken outside of the regular term.
Veteran Benefits and Transition Act of 2018, Section 3679 of Title 38, United States Code
Effective August 1, 2019, Guam Community College will allow a Covered Individual who is entitled to educational assistance under Chapter 31, Vocational Rehabilitation and Employment or Chapter 33, Post-9/11 GI Bill benefits, and dependents under the Chapter 33 Transfer of Entitlement, to remain registered in their courses without being dropped or otherwise penalized due to delay in payment of tuition and fees by the VA. In order to receive this benefit, the student must apply for benefits by filling out the "Certification Request Form" and providing the "Certificate of Eligibility" and/or an approval from the VA Vocational Rehabilitation Counselor. These forms are available at the Guam Community College Financial Aid Office, Tiyan VA Benefits Office, or the va.gov.
It is the student's responsibility to pay the school any balance remaining should the student register in courses that are not within the approved education plan, or if the student is not entitled to 100% education benefits. Any award returned to the VA eligible for return of funds is the student’s responsibility.
Payment in full of all current tuition and fees and outstanding obligations is required. Payment may be made at the Cashier’s Office or online using the following payment methods:
Payment Methods Accepted at Cashier’s Office: Cash, Check, VISA, and Mastercard.
Payment Methods Accepted Online: VISA, Mastercard, and American Express. To make payment online, please visit our website at mygcc.guamcc.edu/MyAccount.
Payment by Check: Make check payable to Guam Community College or GCC. Please include the student’s name, student ID number, and contact number of the check writer. Check payments are subject to a ten (10) business day hold for bank clearance. Requests will be processed and documents will be released after check payment has cleared the bank.
Failure to pay full tuition by required due date will result in one or more of the following actions:
- Student will not be allowed to register and receive grades;
- Transcripts and/or diploma will not be processed; and
- Outstanding accounts will be referred to a collection agency.
(The student shall assume responsibility for all collection agency fees, legal fees, and court fees necessitated by default in payment.)
All students are obligated to pay for registered courses unless they officially drop a course(s) before the first day of class. Please refer to the Academic Calendar for specific dates and deadlines. If students do not officially withdraw from courses, they will be liable for the full amount of tuition and fees even if they did not attend classes.
The "Regular Semester" refund policy will be applied as follows to semester long courses offered:
- If the course drop occurs on or before the last day of schedule adjustment, 100% of the tuition, special fees and laboratory fees will be refunded.
- After the last day of registration, no refunds will be made for semester long courses.
- Full (100%) refund of tuition and all special fees and laboratory fees will be made by the College to students for classes cancelled by the College.
Refund Exceptions
Any student facing extenuating circumstances during a semester resulting in withdrawal from credit classes may submit the Tuition/Refund Waiver Request Form. Requests will only be considered if it is submitted with proper documentation. Requests may only be submitted within one year of the end of the registered semester.
Students who wish to withdraw from all registered courses in a semester for the following reasons must submit a written request for a refund.
- Student with a serious illness, verifiable by a doctor's written statement that the illness prevents the student from attending all classes for the semester. The doctor's statement must be submitted with a refund request, and any other documents that will help substantiate the request.
- Serious illness of an immediate family member that prevents the student from attending all classes for the semester. Immediate family members include spouse/partner, father, mother, grandfather, grandmother, child, foster child, grandchild, stepchild in any one incident. Serious illness verifiable by a doctor's written statement that the illness prevents the student from attending all classes for the semester.
- Death of a student's spouse/partner, child, or parent that prevents the student from attending all classes for the semester. Copy of the death certificate must be submitted.
- Death of a student. Copy of the death certificate must be submitted.
- Students who are in the Armed Forces and are called to active duty and assigned to a duty station, verifiable by a copy of the orders, will be allowed to withdraw and receive a 100% refund/waiver of tuition, provided courses have not been completed.
Requests for a total withdrawal from the College or courses for one of the above reasons may result in a class credit, provided courses have not been completed. All decisions made by the College are final.
Limitation
Never attending is not an allowable refund/waiver exception or an excuse of the debt incurred through registration.
Tuition Refund Process
Drop/add refund dates are widely publicized; therefore, appeals based on lack of awareness of the dates will not be reviewed.
Submitting Your Request
Refund requests must be submitted in writing ONLY via-
Mail:
Guam Community College ‐ Refund
c/o Admissions and Registration
P.O. Box 23069 GMF
Barrigada, Guam 96921
Email (preferred):
gcc.refund@guamcc.edu
A decision will be made within 6‐8 weeks of submission and the student will be notified by either their Guam Community College email address or by mail. Please note all decisions are final.
Consideration for Financial Aid Students
It may not be in your best interest to file a request. You may be responsible for repayment of financial aid received. Please check with the Financial Aid Office before submitting a request.
Students receiving federal financial aid, including loans, who completely withdraw (officially or unofficially) before completing 60% of the semester, will be subject to the federal return of Title IV funds calculation. This calculation is based on the percentage of the semester completed. Generally, the student is required to repay a portion of the federal financial aid which has been paid to the student. This calculation is mandated and must be applied regardless of the circumstances for withdrawal. For more information, contact the Financial Aid Office by e‐mail at financialaid@guamcc.edu or call (671)735-5543 ext. 5545 or 5556.
DoD: Policy of Return of Unearned Military Tuition Assistance (TA) Funds
Military Tuition Assistance (TA) is awarded to a student under the assumption that the student will attend school for the entire period for which the assistance is awarded. When a student withdraws (officially or unofficially) on or before 60 percent of the course(s) meeting period has been completed, Guam Community College will comply with the Department of Defense policy to return unearned TA funds on a proportional basis through the 60 percent portion of the period for which the TA funds were provided. After a student completes 60 percent of the term, all TA funds are considered fully earned.
The return of unearned military TA funds will follow the same guidelines as the Department of Education Title IV funding, outlined in the Withdrawal Policy for Return of Title IV Funds policy. The calculation is completed for each course individually. Once the completion (earned) percentage is calculated, the College will multiply the percentage by the amount of TA funds awarded to determine the amount of TA funds earned. The unearned TA funds will be returned to the military service, not to the service member, within 45 days of the determination of withdrawal.
15 week course withdrawal
| Before or by the 1st day of class: | 100% returned to DoD |
| During Weeks 1 – 3: | 75% returned to DoD |
| During Weeks 4 – 5: | 50% returned to DoD |
| During Weeks 6 – 8: | 25% returned to DoD |
| During Weeks 9 -15: | 0% returned to DoD |
Students Called to Active Military Service
Recognizing the need to accommodate students who are asked to serve their country during wartime, the College will allow students called to active military duty, while enrolled in a given semester, to be provided a refund of tuition and fees. As an alternative to refunds, students may opt for credit against future enrollment. Students will be required to provide to the Admissions & Registration Office and the Business Office, written notice of active military status and indicate whether a refund or credit is preferred.
Returned Check Policy
If a student makes a payment for tuition and fees using a check and the check is returned, the student will be contacted by the GCC Business Office regarding the returned check. Once contacted, the student must pay the amount of the check in full by cash or cashier’s check within 48 hours of notice. Additionally, a $37 returned check fee is assessed. A $37 late fee may also be assessed. If a student fails to make payment, he or she will be dropped from courses and will be referred to a collection agency. Moreover, neither grades nor transcripts will be released until the full amount of the returned check plus the service charge is paid in full.
Outstanding Balances
Students who have an outstanding balance at the end of a semester will not be allowed to register until the amount is paid in full. In addition, neither grades nor transcripts will be released until the past due balance is paid in full. If a student fails to make payment by the required due date, he or she will be dropped from courses and will be referred to a collection agency.
AY 2025-2026
The College estimates the cost of attendance as a full-time student at the College during the 2025-2026 academic year (ten months, including fall, spring and summer semesters) to be as follows:
| Resident | Independent Student Cost (Off-Campus) | Dependent Student Cost (with Parent(s))
|
| Tuition and Fees | $3,414.00 | $3,414.00 |
| Room and Board | $11,325.00 | $3,000.00 |
| Transportation* | $1,600.00 | $1,600.00 |
| Personal Expenses | $2,200.00 | $2,200.00 |
| Books and Supplies | $1,800.00 | $1,800.00 |
| Total Estimated Cost of Attendance | $20,339.00 | $12,014.00 |
| Non-Resident | Independent Student Cost (Off-Campus) | Dependent Student Cost (with Parent(s)) |
| Tuition and Fees | $4,014.00 | $4,014.00 |
| Room and Board | $11,325.00 | $3,000.00 |
| Transportation* | $2,500.00 | $2,500.00 |
| Personal Expenses | $2,200.00 | $2,200.00 |
| Books and Supplies | $1,800.00 | $1,800.00 |
| Total Estimated Cost of Attendance | $21,839.00 | $13,014.00 |
*Plus round-trip airfare for off-island students.
NOTE: Students whose permanent residence is not Guam should add the cost of round-trip travel from their permanent residence to Guam and back again.
International students should contact the Admissions and Registration Office for more information regarding the cost of attendance.
These estimates of the cost of attendance as a full-time student are based on the following assumptions:
An independent student is sharing housing costs with one other student.
AY 2025-2026 is a ten (10) month period of class attendance.
The College believes that each individual should have the opportunity to develop his or her potential to the fullest extent possible. As part of the commitment to that principle, the College makes available financial aid programs which can provide students with money to pay for tuition, books, supplies, transportation and living expenses while they attend college.
Financial Aid
The Financial Aid Office provides information and advice on how students can gain financial assistance from various sources. Such assistance is available to students with financial need through the Federal Student Aid Programs that include Pell Grant, Federal Work Study, and Federal Supplemental Educational Opportunity Grant. The College is also approved to certify Veteran’s benefits. In addition, various independent scholarship programs are available based on a combination of factors such as merit, interest in certain degree programs, and in some cases, need. The College does not administer federal student loan programs. Students may receive complete financial aid counseling services at the College’s Financial Aid Office located on the 1st floor of the Student Services & Administration Building.
Financial Aid Application Deadlines
The College processes financial aid applications throughout the year. Most scholarship programs, however, have application deadlines established by the grantor. In the case of Federal Student Aid Programs, students must have completed both the government forms and the entire admissions process at the College in order to qualify. This process should be started well in advance of the semester to be attended in order to prevent delays in payment. Students should complete their applications early to ensure maximum awards. No applications will be accepted after the end of the school year. For further information, contact the Financial Aid Office at (671) 735-5543 ext. 5545 or 5556.
Pell Grant
This is a grant, which does not need to be repaid. It is based on financial need, and upon maintaining satisfactory progress at the College. Depending on income, students can be eligible for up to $7,395.00 per year for full-time enrollment during Academic Year 2025-2026.
Federal Work Study Program (FWSP)
Students who qualify for the Pell Grant and who still have remaining financial need may sign up for College Work Study as a means of earning income. These awards are made on a first-come, first-served basis until the funds are spent. Job placement is done by the Financial Aid Office. The awards usually range between $1,000 and $4,000 per year, depending on need.
Federal Supplemental Educational Opportunity Grant (FSEOG)
Students who qualify for the Pell Grant and who fall into the greatest need category may also receive FSEOG awards. Typical awards are around $500 per year.
Veterans Educational Benefits
The College is approved for Veteran’s benefits. Counseling regarding individual eligibility is available either at the Financial Aid Office or at the Veteran’s Administration Offices in Guam. Veterans must comply with established Financial Aid Office policies in order to receive benefits, and must meet established standards of progress.
Federated States of Micronesia Scholarship Programs
The neighboring island states have scholarship funds for their students. The island states have generally made the applications and information available to the College. Students who wish to apply may contact either their island’s scholarship program office, or the Financial Aid Office.
Scholarships
Various private groups and organizations provide scholarships for GCC students. Information about these scholarships is available at the Financial Aid Office and at https://guamcc.edu/FinancialAid.
Eligibility
Financial Aid, with the exception of gift aid and merit-based scholarships, is awarded on the basis of a student’s financial need. A student’s financial need is defined as the difference between the cost of the student’s education and the student’s resources to meet that cost. In general, a student may be eligible for financial aid under the following conditions:
- The student can demonstrate that a financial need exists;
- The student is making satisfactory progress toward a postsecondary educational goal;
- The student is enrolled as a Declared Student;
- The student is a U.S. Citizen, U.S. National, U.S. Permanent Resident, a permanent resident of the Federated States of Micronesia, or a permanent resident of the Commonwealth of the Northern Marianas Islands, or the Republic of the Marshall Islands and the Republic of Palau; and
- The student, if required by federal law, attests to his/her Selective Service Status.
Application Procedures
Students must complete the Free Application for Federal Student Aid (FAFSA) in order to be considered for any Federal assistance. These applications are available online at www.fafsa.ed.gov. Students must apply and qualify annually on the basis of demonstrated financial need. To apply, students should first create an FSA ID and then go to www.fafsa.ed.gov to fill out the form or click on the Financial Aid links at https://guamcc.edu/financialaid, then select the “Applying for Financial Aid” and follow the directions on that list. The Guam Community College school code is 015361. In addition to the FAFSA, students will need to complete an “Application for Admission” as a "Declared Student” which is available on the GCC website or at the Admissions desk in the Student Services and Administration building.
Awards
To be eligible for Title IV funds, a student must be a regular student as defined in 34 CFR§ 668.32 of the General Provisions regulations. A regular student is defined as: “A person who is enrolled or accepted for enrollment at an institution for the purpose of obtaining a degree, certificate or other recognized educational credential offered by that institution.” Therefore, students are not eligible to receive Title IV assistance for credit hours/coursework, which will not count towards the completion for that student’s degree program requirements. Pell grants are awarded by the Financial Aid Office and disbursed at mid-term. Students can view their account information on MyGCC at https://guamcc.edu.
Student Responsibilities
In order to receive any form of assistance from the Financial Aid Office, all applicants must:
- Complete all necessary application forms and pertinent documents on or before the established deadlines of each school year.
- Be admitted as a “Declared Student.”
- Enroll in a program of study leading towards a postsecondary degree or certificate program (Adult High School Diploma may be eligible for some financial assistance, e.g., VA Benefits).
- Enroll in courses required for the declared program of study.
- Satisfactorily meet progress standards for financial aid. For further explanation, please visit the Financial Aid website at https://guamcc.edu/financialaid.
- Inform the Financial Aid Office of any changes that may affect their financial assistance.
- Pick up award checks on the scheduled disbursement dates.
- Comply with all other policies established by the Financial Aid Office as described in the Student Handbook and Financial Aid website at https://guamcc.edu/financialaid.
- VA students must have previous education credits/military training evaluated. Submit an evaluation request form along with transcripts, DD-214’s etc. to the Registrar’s office.
Students who fail to comply with the above requirements may jeopardize their eligibility for assistance. Furthermore, students are urged to work closely with their program advisors and/or counselors in planning their course of study at GCC. For more information regarding Financial Aid, contact:
Financial Aid Office
Guam Community College
P.O. Box 23069
Barrigada, Guam 96921
(671) 735-5543 ext. 5545 or 5556
Email: financialaid@guamcc.edu
FAFSA website: https://studentaid.gov/h/apply-for-aid/fafsa
The ABE programs are instructional programs designed to help adult learners master the skills and content necessary to enhance their employability skills by improving their ability to speak, read, or write the English language and by increasing their ability to function effectively in society. These courses can help adult learners prepare to enroll in the Adult High School Diploma Program or prepare for an administration of the GED®.
For more information regarding Adult Basic Education, please call (671) 735-6010 ext. 5415 or email at gccadulteducation@guamcc.edu.
High School Equivalency
Adult High School Diploma Program (AHSDP) Guidelines
The mission of the Adult High School Diploma Program (AHSDP) is to assist students with the completion of a secondary high school diploma and transition into postsecondary education and/or the workforce.
GCC is mandated through Public Law 14-77 to provide adult education to individuals who are 16 years of age and not enrolled or required to be enrolled in a secondary school under Guam Law (P.L. 34-104; Compulsory Age 18 yrs. old). The AHSDP supports the College’s mission statement and the personal, academic, and career goals of adults on Guam who have not earned a high school diploma. The AHSDP offers adults the opportunity to earn credits toward their diploma while receiving education and training, in preparation for the workplace and/or postsecondary education. Students will be required to apply for admission to the College as a diploma student once they are determined eligible for the Adult High School Diploma Program.
Program Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs):
Upon successful completion of the Adult High School Diploma program, students will be able to:
- Demonstrate proficiency in basic skills areas, as necessary for entry level employment and/or postsecondary education.
- Analyze complex informational text independently.
- Apply technical knowledge and skills necessary for workplace productivity.
Eligibility
GCC is mandated through Public Law 14-77 to provide adult education to individuals who are 16 years of age and not enrolled or required to be enrolled in a secondary school under Guam Law (P.L. 34-104; Compulsory Age 18 yrs. old) and is :
- Basic skills deficient;
- Does not have a secondary school diploma or its recognized equivalent and has not achieved an equivalent of education; or
- An English language learner who has limited ability in reading, writing, speaking, or comprehending the English language and whose native language is a language other than English or lives in a family or community environment where a language other than English is the dominant language.
Upon completion of the Comprehensive Adult Student Assessment System (CASAS), individuals who score a 239 or higher in reading and a 236 or higher in math may enroll in the AHSDP.
Individuals scoring below 239 in the reading and 236 in the math portion of the CASAS will begin by taking courses to refresh basic skills until scores of 239 in reading and a 236 in math and above are met. Individuals who score above 239 in reading and 236 in math may go directly into the AHS Diploma Program or schedule to take the high school equivalency diploma (GED®). Additionally, students who score below a 236 will receive the following assistance while attending basic skills courses: Tutoring Services from the Reach for College Program.
Adult High School Diploma Requirements
Course Requirements:
Successful completion of courses in the following areas (either at GCC or through accepted transfer credit):
| General Education Requirements | ||
| Course | Course Name | Credits |
| EN068 | Language Arts Literacy | 3 |
| EN081 | Literature Survey | 3 |
| EN091 | Fundamentals of Communication | 3 |
| AEMA050 | Algebra I | 3 |
| AEMA060 | Geometry | 3 |
| AEMA070 | Algebra II | 3 |
| SI051 | Earth Science | 3 |
| SI061 | Biology | 3 |
| SS063 | American Government | 3 |
History (Choose 1) | ||
| SS081 | US History I | 3 |
| SS082 | US History II | |
Major Requirements | ||
| Course | Course Name | Credits |
| SO099 | Student-Centered Success in College | 3 |
| OA101 | Keyboarding | 3 |
Electives | ||
| Course | Course Name | Credits |
| Elective Choice 1 | 3 | |
| Elective Choice 2 | 3 | |
| Elective Choice 3 | 3 | |
Program Total | 45 | |
The AHSDP advisor/counselor must approve students’ enrollment into courses for the semester. Students will be limited to register in no more than 12 credit hours of adult high school courses (English, Mathematics, Science, Social Studies, and Student Success Workshop) and postsecondary career and technical (CTE)/elective courses.
AHS students shall adhere to the following guidelines in order to maintain eligibility to continue the AHS Diploma Program:
- Students must attend all registered courses. Students receiving more than five (5) absences in any registered course will receive a failure grade (F) or unsatisfactory completion (NC), whichever is applicable, for the course. If a student receives more than two (2) failure grades (F) and/or unsatisfactory completion (NC) resulting from absences, the student will no longer be eligible to continue with the AHS Diploma Program and will be referred by their advisor/counselor to the Adult Education Office for other program options.
- Students who receive a failure grade (F) or unsatisfactory completion (NC) will be allowed to retake the course only once. Students may retake no more than two (2) courses while enrolled in the AHS Diploma Program. After retaking two (2) courses and it is determined that the student will be unable to complete the requirements of the AHS Diploma Program, the student will be referred by his/her advisor/counselor to the Adult Education Office for other program options.
After the official add/drop dates posted in the Schedule of Classes, any student who withdraws (W), who has been technically withdrawn (TW), and/or who abandons any course he/she has registered in resulting in a failure grade (F) or a technical failure grade (TF) will not be eligible to continue to participate in the AHS Diploma Program.
Nine (9) credits of Career and Technical Education (CTE) electives should be from the same career area as part of the student's approved educational plan. Development of a Student Educational Plan with counselor or advisor is required.
Adult High School students must achieve a minimum cumulative GPA of 2.0 in order to earn an Adult High School Diploma.
High school credits completed elsewhere will be converted to credit hours to meet the requirements of the adult high school diploma using the following equivalency: one (1) Carnegie unit = three (3) credit hours on 050-099 level. Career and Technical Education (CTE) credits earned at GCC through the AHSDP articulate to GCC’s postsecondary programs.
Students will be loaned the required books for their registered courses with an obligation of returning all books to the Adult Education Office at the end of the semester. Outstanding obligations will result in a hold on grades, transcripts, or other processes.
High School Equivalency Diploma
Eligibility for Testing
Minimum Age:
18 years of age and not currently enrolled or required to be enrolled in high school.
Assessment
All applicants must take the free 2-hour CASAS Appraisal which is administered daily. An individual must score at least 239 in reading and 236 in math on the CASAS Appraisal in order to take the GED®.
Fees
There is no charge to take the CASAS Appraisal. GED® has four computer-based content areas (Reasoning through Language Arts, Reasoning through Mathematics, Science, and Social Studies); the cost to take each content area is $37.25 or $149 for all four content areas. Retake cost is $25.00 per content area. Payment must be made online at https://ged.com.
How to Apply
To apply for the CASAS Assessment, the applicant must present a valid driver’s license, passport, military ID or other form of government-issued identification that shows his/her name, address, date of birth, signature, and photograph to a staff member at the Adult Education Office.
Testing Schedule
Assessment Test: The CASAS Appraisal is administered every Tuesday to Friday at the Guam Community College campus (Adult Education Office), Bldg. 6000, Room 6215. There are two testing periods from 9:30am-12:00pm & 1:30pm-4:00pm, for Testing and Retesting; while the GED® Test has to be scheduled online at https://ged.com, at the Guam Community College Technology Center.
To Receive a Diploma
Individuals may apply for a diploma at the Guam Community College, Continuing Education and Workforce Development, Building 2000, Room 2137.
Minimum Test Scores
For the GED®, the minimum test score is 145 on each content area and a total of 600 on all four areas.
Residency
In order to take the GED®, a person must be a resident of Guam. You are considered a resident of Guam if your permanent home is on Guam and your most recent income tax forms were filed on Guam, or if you are a dependent of someone whose most recent income tax forms were filed on Guam. Active duty military personnel and their dependents are considered residents, as are citizens of the Freely Associated States of Micronesia. Please be prepared to submit a stamped copy of your income tax form as proof of residency.
*Adult Basic Education courses have been moved from the regular College Catalog to the Continuing Education Catalog. Courses are scheduled and maintained by the Office of Continuing Education and Workforce Development. For more information regarding these courses, please call (671) 735-5640 ext.5579.
These courses or series of courses are nationally and internationally recognized by industry and government as providing a significant body of information. These courses prepare students for industry specific licensure listed below.
- Nursing Assistant Industry Certification
- Cisco Certified Network Associate (CCNA) Industry Certification
- Cisco Certified Network Professional (CCNP) Industry Certification
- Industry Certification in Cosmetology
Many of these courses are offered through the Office of Continuing Education/Workforce Development, located on the 1st floor of the Student Services & Administration Building (Building 2000).
The courses listed below prepares students to function professionally and competently as Nursing Assistants under the supervision of the LPN, RN, or MD in such clinical areas as home health, community health, hospitals, clinics, private medical offices, and mental health. Graduates will be able to generate the knowledge and illustrate the skills required to pass the National Nurse Aide Assessment Program Exam which leads to becoming a Certified Nursing Assistant (CNA).
Prerequisite: Admission to the Certified Nursing Assistant Program.
Upon successful completion of this certification, students will be able to:
- Identify the principles of prevention, therapy and rehabilitation for patients of all ages.
- Distinguish the roles of a Nursing Assistant in a healthcare team.
- Apply the Nursing Assistant principals and skills learned in class/lab to the clinical setting.
- Demonstrate proficiency and knowledge of nursing assistant skills in preparation for the NNAAP (National Nurse Aide Assessment Program) written and practical exam.
Course Requirements | ||
| Course | Course Name | Credits |
| NU101 | Nursing Assistant | 4 |
HL131
| Basic Life Support for Health Care Providers | 1 |
| Total Requirements | 5 | |
The courses listed below will prepare students to take Cisco’s CCNA exam. These courses prepare the student for configuration of networks using routers, switches and hubs (Local Area Network). Continuing coursework prepares the student to understand Wide Area Networks (WAN). Next, a student focuses on Network Layers, Cisco Internetwork Operating System software user interface, router configuration, startup and setup configuration sources for Cisco IOS software TCP/IP, configuration router interfaces with IP and routing protocols. Other coursework involves LAN design and implementation. Final preparatory coursework includes fundamentals of Wide Area Networks. Coursework must be taken in sequence. After successful completion of the four networking courses, a student will be ready to take the Cisco CCNA exam.
| Course Requirements | ||
| Course | Course Name | Credits |
| IT265 | Computer Networking I | 5 |
| IT266 | Computer Networking II | 5 |
| IT267 | Computer Networking III | 5 |
| IT271 | Advanced Computer Networking I | 5 |
| Total Requirements | 20 | |
Successful completion of the program will prepare students to pass The National Interstate Council of State Boards of Cosmetology Practical Examination in order to obtain a Guam license to qualify for positions in the cosmetology field. Students will acquire skills required to pass the National-Interstate Council of State Boards of Cosmetology Practical Examination and the two-part Guam Board of Barbering and Cosmetology exam. Students will acquire skills needed to work in a variety of cosmetology-related occupations such as a cosmetologist, barber 1 (no chemical), barber stylist, esthetician, salon owner, nail technician, hair color specialist, and/or makeup artist. Students will also gain effective interpersonal skills and demonstrate ethical conduct in a lab and shop setting.
The Industry Certification in Cosmetology program offers students’ opportunities to develop the skill, knowledge, attitudes, and leadership qualities required to meet licensure standards of the Guam Board of Barbering and Cosmetology. Through lecture, demonstrations and lab practice, students will complete a minimum of 1600 hours in this four-semester program. Students may recover clock hours via a Continuing Education non-credit course. If a student is not present by the end of the second day of class, they may be dropped. A minimum grade of 75% is required to demonstrate competency in all courses.
Upon successful completion of this certification, students will be able to:
- Master the skills needed for entry-level work in a variety of cosmetology, barbering, and/or related occupations.
- Apply content knowledge and skills as indicated in the National-Interstate Council (NIC) of State Board of Cosmetology Practical Examination.
- Utilize effective interpersonal skills and practice professional ethics needed to succeed in the cosmetology and/or barbering profession.
Course Requirements | ||
| Course | Course Name | Credits |
| CM101 | Cosmetology I | 10 |
| CM102 | Cosmetology II | 10 |
| CM104A | Cosmetology III | 5 |
| CM104B | Cosmetology IV | 5 |
| Total Requirements | 30 | |
| Total Contact Hours Required | 1600 | |
The Registered Apprenticeship Program (RAP) consists of On-the-Job Training (OJT) and the Related Technical Instruction (RTI). The College is a provider of the Related Technical Instruction (RTI) as part of the Registered Apprenticeship Program (RAP) through the State Apprentice Agency (SAA) of the Guam Department of Labor, in partnership with the Guam Contractors Association and individual employers.
As for the On-the-Job Training (OJT), the Apprentice learns a trade or occupation through formal training under close supervision of a skilled worker or journeyman during his or her term of apprenticeship. In general, an Apprentice works at an actual job setting with an employer during the day and attends related classes at the College during the weekday and/or Saturdays.
In order for an Apprentice to be eligible to receive a Certificate of Completion of Apprenticeship, the Apprentice must satisfactorily complete a minimum of 144 hours of RTI per year plus a term of 2000, 4000, 6000 or 8000 hours of OJT, depending on his or her respective Apprenticeship Trade. Upon satisfactory completion of the required training, the Apprentice is issued a Certificate of Completion of Apprenticeship from the Office of Apprenticeship of the United States Department of Labor.
For more information on the Registered Apprenticeship Program, contact the Continuing Education and Workforce Development Office, Student Services and Administration (Building 2000), Rooms 2128 or 2129, or call (671) 735-5640 ext. 5571 or 5572, or the State Apprenticeship Agency of the Guam, Department of Labor, in the GCIC Building, Suite 300 (3rd Floor), or call (671) 300-4572.
The terms of apprenticeship are determined by the trade or occupation in which the Apprentice is registered and being trained under. Training is available in the following occupational trades:
| APPRENTICESHIP OCCUPATION | APPROXIMATE OJT HRS | CONTACT HOURS | APPRENTICESHIP OCCUPATION | APPROXIMATE OJT HRS | CONTACT HOURS |
| Accounting Technician | 4000 | 288 | Inspector, Quality Assurance | 6000 | 432 |
| Air-Conditioning and Refrigeration Mechanic | 6000 | 432 | Instrument Technician | 8000 | 576 |
| Automobile Body Repairer | 8000 | 576 | Insulation Worker | 8000 | 576 |
| Automobile Mechanic | 8000 | 576 | Internetworking Technician | 8000 | 576 |
| Automotive Technician Specialist | 8000 | 576 | IT Generalist | 2880 | 216 |
| Baker | 6000 | 432 | IT Project Manager | 2000 | 144 |
| Biomedical Technician | 8000 | 576 | Line Installer-Repairer | 8000 | 576 |
| Boiler Operator | 8000 | 576 | Line Maintainer (High Voltage Electrician) | 7000 | 504 |
| Cable Installer-Repairer | 6000 | 432 | Lineman | 8000 | 576 |
| Cable Splicer | 8000 | 576 | Load Dispatcher | 8000 | 576 |
| Carpenter | 8000 | 576 | Logistics Engineer | 8000 | 576 |
| Cement Mason | 4000 | 288 | Machinist, Marine Engine | 8000 | 576 |
| Chief of Party | 8000 | 576 | Machinist, Outside | 8000 | 576 |
| Child Care Development Specialist | 3500 | 288 | Maintenance Building Repairer | 4000 | 288 |
| Coach Operator | 2000 | 144 | Maintenance Mechanic | 8000 | 576 |
| Computer Operator | 6000 | 432 | Manager, Retail Store | 6000 | 432 |
| Computer Programmer | 4000 | 288 | Operating Engineer (Heavy Equipment Operator) | 6000 | 432 |
| Computer Support Specialist | 4000 | 288 | Painter, Shipyard | 6000 | 432 |
| Computer Systems Analyst | 4000 | 288 | Paralegal | 6000 | 432 |
| Construction Equipment Mechanic | 8000 | 576 | Paramedic | 4000 | 288 |
| Cook | 6000 | 432 | Pipe Fitter | 8000 | 576 |
| Correction Officer | 4000 | 288 | Pipe Fitter (Ship & Boat) | 8000 | 576 |
| Crime Scene Technician | 4000 | 288 | Plumber | 8000 | 576 |
| Customer Service Representative | 4000 | 288 | Police Officer | 4000 | 288 |
| Diesel Mechanic | 8000 | 576 | Power Plant Operator | 8000 | 576 |
| Drafter, Civil | 8000 | 576 | Powerhouse Mechanic | 8000 | 576 |
| Drafter, Structural | 6000 | 432 | Public Affairs | 2500 | 360 |
| Electrical Technician | 8000 | 576 | Pump Servicer | 6000 | 432 |
| Electrician | 8000 | 576 | Purchasing Agent | 8000 | 576 |
| Electrician, Maintenance | 8000 | 576 | Refrigeration Mechanic | 6000 | 432 |
| Electrician, Powerhouse | 8000 | 576 | Relay Technician | 4000 | 288 |
| Electrician (Ship & Boat) | 8000 | 576 | Rigger (Ship & Boat) | 6000 | 432 |
| Electrician, Substation | 6000 | 432 | Salesperson Parts | 4000 | 288 |
| Electronic Systems Technician | 8000 | 576 | Sheet Metal Worker | 8000 | 576 |
| Electronics Technician | 8000 | 576 | Ship Fitter | 8000 | 576 |
| Field Engineer | 8000 | 756 | Shipwright (Ship & Boat) | 8000 | 576 |
| Field Engineer Drafter, Civil | 8000 | 576 | Surveyor Assistant, Instrument | 4000 | 288 |
| Field Service Engineer | 8000 | 576 | Telecommunication Technician | 8000 | 576 |
| Financial Management | 2000 | 144 | Treatment Plant Mechanic | 6000 | 432 |
| Geospatial Specialist | 4000 | 288 | Truck Driver, Heavy | 2000 | 144 |
| Graphic Designer | 3000 | 216 | Water Treatment Plant Operator | 6000 | 432 |
| Heavy Mobile Equipment Mechanic | 8000 | 576 | Wastewater Treatment Plant Operator | 4000 | 288 |
| Information Management | 2000 | 144 | Welder | 8000 | 576 |
| Inspector Building | 6000 | 432 | Welder, Arc | 8000 | 576 |
| Marine Machinery Mechanic | 8000 | 576 | Welder, Combination | 8000 | 576 |
| Office Manager/Adm. Services | 4000 | 288 | Welder Fitter | 8000 | 576 |
Program Mission and Description
GCC’s Early Middle College is a program that provides secondary students the opportunity to obtain postsecondary education and accelerate their job training to become skilled workers. EMC students will take college courses identified in their career pathway with their required high school courses to earn stackable credentials. EMC students will participate in wraparound services to support their academic needs and to overcome social and economic barriers unique to their population. These wraparound services will also focus on EMC students’ transition into the college-level mindset and their employability after graduation. This program prepares EMC graduates to be skillful, ethical, and professional for entry-level positions with a certificate of mastery, program certificate or associate’s degree, and other certifications related to their identified career pathway.
For secondary students, a portion of the requirements will be provided by the Dual Credit Articulated Programs of Study [DCAPS] and the Dual Enrollment Accelerated Learning [DEAL] program. The DCAPS involves the (11) Career and Technical Education programs available in Guam’s six public high schools: Allied Health; Automotive; AutoCAD; Construction; Early Childhood Education; Information Technology; Hospitality & Tourism: Hospitality and Tourism Management Program; Marketing; ProStart (Culinary); Telecommunications, and Visual Communication. Under DCAPS, students enrolled in the GCC CTE program will earn from three (3) to 19 college credits in the corresponding GCC postsecondary program. Under the DEAL program, eligible students are allowed to enroll in college math and English courses concurrently with high school classes and to receive both high school and college credit simultaneously. Upon successful completion of these college course(s), the student will receive credit for the corresponding high school course AND receive college credit. The career pathway identified below addresses the community need for skilled workers in Guam’s construction industry as well as infrastructure technology (IT).
Program Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs):
Upon successful completion of this program, students will be able to:
- Transition into the postsecondary environment earning college credentials leading to employment.
- Utilize skills necessary for entry-level positions in the identified career pathway.
- Demonstrate soft skills to be marketable and employable in an ever-changing workforce setting.
| Certificate in Construction Technology Carpentry | |||
Semester Term | High School DCAPS | DCAPS Equivalency | After High School Courses |
| 10th Grade Fall | CTCT053-1A Introduction to Carpentry |
CT153 (3) + CT173 (3) + CT140 (3) | Reach for College Workshop + CT100 (3) Introduction to Construction Trades |
| 10th Grade Spring | CTCT053-1B Introduction to Carpentry | AE103 (3) Basic Blueprint Reading HL135 (1) Heartsaver First Aid CPR AED | |
| Summer | AE121 (2) Technical Engineering Drawing I
| ||
| 11th Grade Fall | CTCT073-2A Carpentry | CT183 (3) Finishing | |
| 11th Grade Spring | CTCT073-2B Carpentry | CT154A (3) Masonry | |
| Summer | Construction Elective (Any CE/AE/CT course not listed) | ||
| 12th Grade Fall | MA096 (6) Pre-Collegiate Mathematics | ||
| 12th Grade Spring | CT292 (3) Construction Practicum | ||
Certificate in Construction Technology Masonry | |||
Semester Term | High School DCAPS | DCAPS Equivalency | After High School Courses |
| 10th Grade Fall | CTCT053-1A Introduction to Carpentry |
CT153 (3) + CT173 (3) + CT140 (3) | Reach for College Workshop + CT100 (3) Introduction to Construction Trades |
| 10th Grade Spring | CTCT053-1B Introduction to Carpentry | AE103 (3) Basic Blueprint Reading HL135 (1) Heartsaver First Aid CPR AED | |
| 11th Grade Fall | CTCT073-2A Carpentry | CT154A (4) Masonry Level I | |
| 11th Grade Spring | CTCT073-2B Carpentry | CT154B (4) Masonry Level II | |
| Summer | Construction Elective (Any CE/AT/CT course not listed) | ||
| 12th Grade Fall | MA096 (6) Pre-Collegiate Mathematics | ||
| 12th Grade Spring | CT292 (3) Construction Practicum | ||
Certificate in Construction Technology Reinforcing Metal Worker | |||
Semester Term | High School DCAPS | DCAPS Equivalency | After High School Courses |
| 10th Grade Fall | CTCT053-1A Introduction to Carpentry |
CT153 (3) + CT173 (3) + CT140 (3) | Reach for College Workshop + CT100 (3) Introduction to Construction Trades |
| 10th Grade Spring | CTCT053-1B Introduction to Carpentry | AE103 (3) Basic Blueprint Reading HL135 (1) Heartsaver First Aid CPR AED | |
| 11th Grade Fall | CTCT073-2A Carpentry | CT154A (4) Masonry Level I | |
| 11th Grade Spring | CTCT073-2B Carpentry | CT196A (4) Fundamentals of Oxyacetylene Welding I | |
| Summer | Construction Elective (Any CE/AT/CT course not listed) | ||
| 12th Grade Fall | MA096 (6) Pre-Collegiate Mathematics | ||
| 12th Grade Spring | CT292 (3) Construction Practicum | ||
Certificate in Construction Technology Electricity | |||
Semester Term | High School DCAPS | DCAPS Equivalency | After High School Courses |
| 10th Grade Fall | CTCT053-1A Introduction to Carpentry |
CT153 (3) + CT173 (3) + CT140 (3) | Reach for College Workshop + CT100 (3) Introduction to Construction Trades |
| 10th Grade Spring | CTCT053-1B Introduction to Carpentry | AE103 (3) Basic Blueprint Reading HL135 (1) Heartsaver First Aid CPR AED | |
| Summer | CT165A(4) Electricity Level I | ||
| 11th Grade Fall | CTCT073-2A Carpentry | CT165B(4) Electricity Level II | |
| 11th Grade Spring | CTCT073-2B Carpentry | CT165C(4) Electricity Level III | |
| Summer | MA096 (6) Pre-Collegiate Mathematics | ||
| 12th Grade Fall | CT165D(4) Electricity Level IV | ||
| 12th Grade Spring | CT292 (3) Construction Practicum | ||
Certificate in Construction Technology Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning (HVAC) | |||
Semester Term | High School DCAPS | DCAPS Equivalency | After High School Courses |
| 10th Grade Fall | CTCT053-1A Introduction to Carpentry |
CT153 (3) + CT173 (3) + CT140 (3) | Reach for College Workshop + CT100 (3) Introduction to Construction Trades |
| 10th Grade Spring | CTCT053-1B Introduction to Carpentry | AE103 (3) Basic Blueprint Reading HL135 (1) Heartsaver First Aid CPR AED | |
| 11th Grade Fall | CTCT073-2A Carpentry | CT185A (5) Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Level I | |
| 11th Grade Spring | CTCT073-2B Carpentry | CT185B (5) Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Level II | |
| Summer | MA096 (6) Pre-Collegiate Mathematics | ||
| 12th Grade Fall | CT185C (5) Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Level III | ||
| 12th Grade Spring | CT292 (3) Construction Practicum | ||
Certificate in Construction Technology Plumbing | |||
Semester Term | High School DCAPS | DCAPS Equivalency | After High School Courses |
| 10th Grade Fall | CTCT053-1A Introduction to Carpentry |
CT153 (3) + CT173 (3) + CT140 (3) | Reach for College Workshop + CT100 (3) Introduction to Construction Trades |
| 10th Grade Spring | CTCT053-1B Introduction to Carpentry | AE103 (3) Basic Blueprint Reading HL135 (1) Heartsaver First Aid CPR AED | |
| 11th Grade Fall | CTCT073-2A Carpentry | CT152 (4) Fundamentals of Plumbing | |
| 11th Grade Spring | CTCT073-2B Carpentry | CT152A(4) Plumbing Level I | |
| Summer | MA096 (6) Pre-Collegiate Mathematics | ||
| 12th Grade Fall | CT182 (3) Uniform Plumbing Code | ||
| 12th Grade Spring | CT292 (3) Construction Practicum | ||
Certificate in Construction Technology Welding | |||
Semester Term | High School DCAPS | DCAPS Equivalency | After High School Courses |
| 10th Grade Fall | CTCT053-1A Introduction to Carpentry |
CT153 (3) + CT173 (3) + CT140 (3) | Reach for College Workshop + CT100 (3) Introduction to Construction Trades |
| 10th Grade Spring | CTCT053-1B Introduction to Carpentry | AE103 (3) Basic Blueprint Reading HL135 (1) Heartsaver First Aid CPR AED | |
| Summer | CT196A(4) Fundamentals of Oxyacetylene Welding I | ||
| 11th Grade Fall | CTCT073-2A Carpentry | CT196B(4) Fundamentals of Oxyacetylene Welding I | |
| 11th Grade Spring | CTCT073-2B Carpentry | CT197A(4) Shielded Metal Arc Welding I | |
| Summer | MA096 (6) Pre-Collegiate Mathematics | ||
| 12th Grade Fall | CT197B(5) Shielded Metal Arc Welding II | ||
| 12th Grade Spring | CT292 (3) Construction Practicum | ||
Certificate in Computer Science | |||
Semester Term | High School DCAPS | DCAPS Equivalency | After High School Courses |
| 10th Grade Fall | CTTE101 Intro to Comp Systems and Info Tech |
CS101 (3) CS112 (3) CS205 (4) CS206 (3) CS211 (3) CS212 (3)
*One of the extra classes will count as a technical elective | Reach for College Workshop +
|
| 10th Grade Spring | CTTE102 Javascript Programming | CS151 (3) Windows Application
| |
| Summer | SM108 (3) Introduction to Business | ||
| 11th Grade Fall | CTTE103 Java I | MA110A (3) Finite Mathematics | |
| 11th Grade Spring | CTTE104 Python Programming | EN110 (3) Freshman Composition | |
| Summer | OA211 (3) Business Communication | ||
| 12th Grade Fall | CTTE105 Intro to Linux | CS290/292 (3) Practicum/Project
| |
| 12th Grade Spring | CTTE106 Network Communications | ||
Associate of Science in Computer Science | |||
Semester Term | High School DCAPS | DCAPS Equivalency | After High School Courses |
| 10th Grade Fall | CTTE101 Intro to Comp Systems and Info Tech |
CS101 (3) CS112 (3) CS205 (4) CS206 (3) CS211 (3) CS212 (3)
*One of the extra classes will count as a technical elective | Reach for College Workshop +
PY100 (3) Personal Adjustment |
| 10th Grade Spring | CTTE102 Javascript Programming | CS104 (3) Visual Basic Programming | |
| Summer | CS151 (3) Windows Application Humanities & Fine Arts (3-4) | ||
| 11th Grade Fall | CTTE103 Java I | SM108 (3) Introduction to Business CS203 (3) Systems Analysis & Design | |
| 11th Grade Spring | CTTE104 Python Programming | MA110a (3) Finite Mathematics CS204 (3) C++ Programming | |
| Summer | EN110 (3) Freshman Composition | ||
| 12th Grade Fall | CTTE105 Intro to Linux | OA211 (3) Business Communication Natural & Physical Science (4) | |
| 12th Grade Spring | CTTE106 Network Communications | CS299 (4) Capstone CS213 (3) PHP Programming w/ MySQL | |
Certificate and Associate of Science in Computer Science | |||
Semester Term | High School DCAPS | DCAPS Equivalency | After High School Courses |
| 10th Grade Fall | CTTE101 Intro to Comp Systems and Info Tech |
CS101 (3) CS112 (3) CS205 (4) CS206 (3) CS211 (3) CS212 (3)
*One of the extra classes will count as an elective | Reach for College Workshop +
|
| 10th Grade Spring | CTTE102 Javascript Programming | CS151 (3) Windows Application | |
| Summer | SM108 (3) Introduction to Business | ||
| 11th Grade Fall | CTTE103 Java I | MA110A (3) Finite Mathematics | |
| 11th Grade Spring | CTTE104 Python Programming | EN110 (3) Freshman Composition | |
| Summer | OA211 (3) Business Communication | ||
| 12th Grade Fall | CTTE105 Intro to Linux | CS290/292 (3) Practicum/Project
| |
| 12th Grade Spring | CTTE106 Network Communications | ||
Fall Semester After HS Graduation | Spring Semester After HS Graduation | ||||
| CS104 | Visual Basic Programming | 3 | CS299 | Computer Science Capstone | 4 |
| CS203 | Systems Analysis & Design | 3 | PY100 | Social & Behavioral Science | 3 |
| CS204 | C++ Programming | 3 | Humanities & Fine Arts | 3-4 | |
| CS213 | PHP Programming with MySQL | 3 | Natural & Physical Science | 4 | |
Summer - Semester 1 | Fall - Semester 2 | Spring - Semester 3 |
| College Success Seminar to show students (but not limited to) how to study, take notes, fill out study packets, and manage time. This is to be taken before any college classes. |
|
|
Summer - Semester 4 | Fall - Semester 5 | Spring - Semester 6 |
|
| |
Summer - Semester 7 | Fall - Semester 8 | Spring - Semester 9 |
|
Paid Work Experience Program |
Upon successful completion of the requirements for graduation, the College will award the appropriate Certificate credential.
The student must indicate which year’s catalog requirements they choose to satisfy when submitting the Application for Degree, Certificate, or Diploma. It is the responsibility of the student to apply for any degree, certificate or diploma they have earned. Students qualify for graduation once the following requirements are met:
- Achieve a 2.0 cumulative GPA as an undergraduate student.
- Meet individual certificate requirements, including major GPA (if applicable).
- Fulfill residency requirements – at least 12-degree applicable credit hours of coursework completed at the College.
- Successfully complete the program pertaining to their certificate.
- Submit Application for Graduation to the Admissions & Registration Office by the applicable deadline and pay the graduation fee.
- Meet financial obligations to the school.
NOTE: A single course cannot be used to satisfy more than one course requirement in a program.
Effective fall Semester 2003, several academic policy changes were implemented to ensure that students are adequately prepared to meet business and industry standards. All Undeclared or newly declared students enrolled in regularly scheduled postsecondary courses must be enrolled in or must have completed developmental coursework for Math and English or have successfully placed into post-secondary Math and English (or equivalent).
Students must fulfill the English general education requirement by the time they have enrolled in 12 credits of classes. This means that students may take only nine (9) credits before they must begin meeting the general education requirements. All declared students in Certificate programs will be required to successfully complete minimum general education course requirements. For more information, refer to the Admissions Information, General Education Policy section of this catalog.
A. General Education Requirements
Students must demonstrate proficiency in reading, writing, understanding and speaking English as indicated by one of the following:
- Test out of the English Placement Test (or equivalent), or
- Satisfactory completion of EN097 courses and
- Test out of the Math Placement Test (or equivalent), or
- Satisfactory completion of MA098 course
*Students in the Certificate of Construction Technology program can successfully complete their math requirements with MA096 Pre-Collegiate Mathematics in lieu of MA098 Intermediate Algebra.
B. Major Requirements
- Total Major Requirements vary by program. Minimum Total Credits Required for a Certificate is 30 credits
* No course may be counted for both Major and General Education requirements.
** Placement testing is not mandatory for admission to the College. Completion of placement testing or equivalent, however, is required for enrollment into English and mathematics courses; therefore, students who plan to enroll full-time in a program should take the placement test to be eligible for a full load of courses.
A Statement on Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Program Student Learning Outcomes follow each program description in this catalog. SLOs intentionally describe the 3-5 central goals that students will have attained by the end of the program. In essence, SLOs encapsulate the knowledge, skills, and attitudes that students are expected to learn from their respective programs. The focus is on what students can do with what they have learned and this outcome should be evaluated in some way. Primarily, three questions essentially frame the articulation of SLOs:
- What do students know? (cognitive domain)
- What do they think and value? (affective domain)
- What can they do? (behavioral domain)
In this catalog, program SLOs describe the broadest goals for the program, particularly those that require higher-level thinking. They, therefore, require students to synthesize many discrete skills or areas of content. SLOs also ask students to produce artifacts such as term papers, projects, portfolios, demonstrations, exams or other student work. Most importantly, SLOs also need to be evaluated or assessed in some way so that accountability and improvement remain the hallmarks of a good program. A separate SLO Booklet is published and updated (as needed) to guide faculty in helping students achieve articulated course outcomes.
The College, in close collaboration with faculty and members of Advisory committees, continues to embark on an ongoing institutional effort to revise and update all its curriculum documents so that they remain responsive to industry and community needs through well-articulated student learning outcomes.
A second certificate and/or degree may be granted provided that a student completes all additional general education and major requirements. Some programs of study offer more than one track; a student may earn a degree, which includes more than one track so long as the student completes the requirements before the degree is conferred.
The Certificate program in Automotive Service Technology General and Master Service Technician Tracks offers students comprehensive advanced technical training in automotive systems to include: Brakes, Electrical/Electronics, Engine Performance, Suspension & Steering, Automatic Transmissions and Trans-Axles, Engine Repair, Manual Drive Trains & Axles, Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning (HVAC), and Advanced Engine Performance.
Upon completion students will be prepared for all content area certification examinations administered by the National Institute for Automotive Service Excellence (ASE).
General Service and Master Service Technician Tracks Program Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs):
Upon successful completion of the Certificate in Automotive Service Technology General Service Technician or Master Service Technician program, students will be able to:
- Identify the purpose and proper functioning of the core components of an automotive engine.
- Perform a cylinder compression cranking test and interpret results.
- Demonstrate the proper use of a digital multi-meter (DMM) during diagnosis of electrical circuit problems.
- Conduct a performance test of the heating, ventilation, and air conditioning system.
- Conduct failure analysis on automatic and manual transmissions and transaxles.
- Perform service and maintenance of components on the brake, steering, and suspension systems.
Hybrid Electric Vehicle Technician Track Program Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs):
Upon successful completion of the Certificate in Automotive Service Technology Hybrid Electric Vehicle Technician program, students will be able to:
- Perform high voltage disconnect procedure and reconnect/enable high voltage system.
- Describe the regenerative braking process.
- Diagnose problems caused by damaged or failed harnesses, connectors, and terminals.
- Explain the concept of an electric transaxle system.
General Service Technician Track | ||
Major Requirements | ||
Course | Course Name | Credits |
| AST100 | Introduction to Automotive Service | 3 |
| AST140 | Suspension and Steering | 6 |
| AST150 | Brakes | 6 |
| AST160 | Electrical/Electronic Systems | 5 |
| AST180 | Engine Performance | 8 |
| AST240 | Theory/Practicum: Suspension & Steering | 2 |
| AST250 | Theory/Practicum: Brakes | 2 |
| AST260 | Theory/Practicum: Electrical/Electronic Systems | 5 |
| AST280 | Theory/Practicum: Engine Performance | 8 |
Certificate Total | 45 | |
Master Service Technician Track (The Master Service Technician Certificate Track requires completion of all courses required for the General Service Technician Track, plus all of the following: | ||
Major Requirements | ||
Course | Course Name | Credits |
| AST110 | Engine Repair | 3 |
| AST120 | Automatic Transmission and Transaxle | 6 |
| AST130 | Manual Drive Train & Axles I | 6 |
| AST170 | Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning (HVAC) | 6 |
| AST210 | Theory/Practicum: Engine Repair | 3 |
| AST220 | Theory/Practicum: Automatic Transmission and Transaxle | 3 |
| AST230 | Theory/Practicum: Manual Drive Train and Axles | 2 |
| AST270 | Theory/Practicum: Heating and Air Conditioning | 2 |
Certificate Total | 76 | |
Hybrid Electric Vehicle Technician Track | ||
Major Requirements | ||
Course | Course Name | Credits |
| AST100 | Introduction to Automotive Service | 3 |
| AST110 | Engine Repair | 3 |
| AST113 | Hybrid Engines and Motor/Generators | 4 |
| AST120 | Automatic Transmission and Trans-Axle | 6 |
| AST123 | Hybrid Electric Vehicle Energy Management, Transaxles, and Batteries | 4 |
| AST133 | Belted Alternator Starter (BAS), Power Electronics, and Support Systems | 4 |
| AST160 | Electrical / Electronic Systems | 5 |
| AST180 | Engine Performance | 8 |
| AST260 | Theory/Practicum: Electrical/Electronic Systems | 5 |
Certificate Total | 42 | |
Computer Aided Design and Drafting (CADD) systems are used by drafters to prepare electronic drawings that can be viewed, printed, or programmed directly into automated manufacturing systems. Although this system is extensively used by drafters, they also need knowledge of traditional drafting techniques in order to fully understand and explain concepts. The Certificate in Computer Aided Design and Drafting (CADD) program is designed to provide knowledge and skills required for employment as an assistant draft craftsperson. The Certificate in CADD is an area emphasized in the Architecture & Construction Career cluster, one out of 16 career clusters in Career & Technical Education.
Program Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs):
Upon successful completion of the Certificate in Computer Aided Design & Drafting program, students will be able to:
- Demonstrate knowledge and skills needed to design and draft projects ranging from two to three dimensional designs for commercial and residential buildings.
- Demonstrate basic skills needed to view, print, edit, and create variations of two and three dimensional electronic designs.
- Develop a professional work ethic needed in the architectural engineering industry.
Major Requirements | ||
Course | Course Name | Credits |
English (Choose 1) | ||
| EN110 | Freshman Composition | 3 |
| EN110A | Freshman Composition with Instructional Lab | 4 |
Course | Course Name | Credits |
| AE103 | Basic Blueprint Reading | 3 |
| AE121 | Technical Engineering Drawing I | 3 |
| AE122 | Technical Engineering Drawing II | 3 |
| AE138 | Specifications, Building Codes, Specs & Construction Management | 3 |
| AE150 | Computer Aided Drafting I (CAD I) | 3 |
| AE160 | Computer Aided Drafting II (CAD II) | 3 |
| CE215 | Construction Procedures | 3 |
| CE225 | Construction Planning & Estimating | 3 |
| CS101 | Introduction to Computer Systems and Information Technology | 3 |
| MA110A | Finite Mathematics | 3 |
| MA161A | >College Algebra & Trigonometry I | 3 |
| AE170 | Revit Architecture Essentials | 3 |
Certificate Total | 39-40 | |
The Certificate in Computer Science will provide opportunities for students to work as entry-level programmers who provide technical support to systems analysts and coders. These computer skills are in high demand in the rapidly evolving information technology field.
Program Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs):
Upon successful completion of the Certificate in Computer Science program, students will be able to:
- Write codes using appropriate programming language to implement solutions.
- Diagnose computer-based glitches and derive possible solutions.
- Demonstrate a solid foundation in the core areas of computer science.
Major Requirements | ||
Course | Course Name | Credits |
| MA115 | Fundamentals of College Algebra | 3 |
| CS101 | Introduction to Computer Systems and Information Technology | 3 |
| CS104 | Visual Basic Programming | 3 |
| CS112 | Introduction to Linux | 3 |
| CS203 | System Analysis and Design | 3 |
| CS205 | Network Communications | 4 |
| CS206 | Java I | 3 |
| CS211 | JavaScript Programming | 3 |
| CS212 | Python Programming | 3 |
Choose one from the following: | ||
Course | Course Name | Credits |
| CS204 | C++Programming | 3-4 |
| CS213 | PHP Programming with MySQL | |
| OA211 | Business Communication | |
| OA210 | Database Management Systems | |
| IT211 | IT Essentials | |
Certificate Total | 31-32 | |
The Certificate in Construction Technology Program will prepare students for the current local and global job market with entry-level skills needed for any of the following fields: carpentry; electricity; heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC); masonry; plumbing; reinforcing metal worker; and welding. All students must successfully pass four (4) core courses (technical related requirements) with a “C” or better before enrolling in one (1) of the seven (7) concentration areas.
Program Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs):
Upon successful completion of the Certificate in Construction Technology program, students will be able to:
- Demonstrate basic skills needed to function as an entry-level worker in at least one construction trades concentration area in accordance with industry safety standards: carpentry; electricity; heating, ventilation, and air-conditioning (HVAC); masonry; plumbing; reinforcing metal worker; or welding.
- Exhibit entry-level knowledge in chosen construction trades concentration area.
- Demonstrate professionalism as related to the construction trades industry.
Carpentry Track | ||
Major Requirements | ||
Course | Course Name | Credits |
| AE103 | Basic Blueprint Reading | 3 |
| AE121 | Technical Engineering Drawing I | 3 |
| CT100 | Introduction to Construction Trades | 3 |
| CT140 | Industrial Safety | 3 |
| CT153 | Introduction to Carpentry | 3 |
| CT154A | Masonry Level I | 4 |
| CT173 | Rough Framing and Exterior Finishing | 3 |
| CT292 | Construction Practicum | 3 |
| HL135 | Heartsaver First Aid CPR AED | 1 |
| MA096 | Pre-Collegiate Mathematics | 6 |
| Certificate Total Minimum | 32 | |
Welding Track | ||
Major Requirements | ||
Course | Course Name | Credits |
| AE103 | Basic Blueprint Reading | 3 |
| CT100 | Introduction to Construction Trades | 3 |
| CT140 | Industrial Safety | 3 |
| CT196A | Fundamentals of Oxyacetylene Welding and Cutting I | 4 |
| CT196B | Fundamentals of Oxyacetylene Welding II | 4 |
| CT197A | Shielded Metal Arc Welding I | 5 |
| CT197B | Shielded Metal Arc Welding II | 5 |
| CT292 | Construction Practicum | 3 |
| HL135 | Heartsaver First Aid CPR AED | 1 |
| Certificate Total Minimum | 31 | |
Plumbing Track | ||
Major Requirements | ||
Course | Course Name | Credits |
| AE103 | Basic Blueprint Reading | 3 |
| CT100 | Introduction to Construction Trades | 3 |
| CT140 | Industrial Safety | 3 |
| CT152 | Fundamentals of Plumbing | 4 |
| CT152A | Plumbing Level I | 4 |
| CT182 | Uniform Plumbing Code | 3 |
| CE215 | Construction Procedures | 3 |
| CT292 | Construction Practicum | 3 |
| HL135 | Heartsaver First Aid CPR AED | 1 |
| MA096 | Pre-Collegiate Mathematics | 6 |
| Certificate Total Minimum | 33 | |
Electricity Track | ||
Major Requirements | ||
Course | Course Name | Credits |
| AE103 | Basic Blueprint Reading | 3 |
| CT100 | Introduction to Construction Trades | 3 |
| CT140 | Industrial Safety | 3 |
| CT165A | Electricity Level I | 5 |
| CT165B | Electricity Level II | 5 |
| CT165C | Electricity Level III | 5 |
| CT165D | Electricity Level IV | 5 |
| CT292 | Construction Practicum | 3 |
| HL135 | Heartsaver First Aid CPR AED | 1 |
| MA096 | Pre-Collegiate Mathematics | 6 |
| Certificate Total Minimum | 39 | |
Heating, Ventilation, and Air-Conditioning (HVAC) Track | ||
Major Requirements | ||
Course | Course Name | Credits |
| AE103 | Basic Blueprint Reading | 3 |
| CT100 | Introduction to Construction Trades | 3 |
| CT140 | Industrial Safety | 3 |
| CT185A | Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Level I | 5 |
| CT185B | Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Level II | 5 |
| CT185C | Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Level III | 5 |
| CT292 | Construction Practicum | 3 |
| HL135 | Heartsaver First Aid CPR AED | 1 |
| MA096 | Pre-Collegiate Mathematics | 6 |
| Certificate Total Minimum | 34 | |
Reinforcing Metal Worker Track | ||
Major Requirements | ||
Course | Course Name | Credits |
| AE103 | Basic Blueprint Reading | 3 |
| CT100 | Introduction to Construction Trades | 3 |
| CT140 | Industrial Safety | 3 |
| CT153 | Introduction to Carpentry | 3 |
| CT154A | Masonry Level I | 4 |
| CT196A | Fundamentals of Oxyacetylene Welding and Cutting I | 4 |
| CE215 | Construction Procedures | 3 |
| CT292 | Construction Practicum | 3 |
| HL135 | Heartsaver First Aid CPR AED | 1 |
| MA096 | Pre-Collegiate Mathematics | 6 |
| Certificate Total Minimum | 33 | |
Masonry Track | ||
Major Requirements | ||
Course | Course Name | Credits |
| AE103 | Basic Blueprint Reading | 3 |
| CT100 | Introduction to Construction Trades | 3 |
| CT140 | Industrial Safety | 3 |
| CT153 | Introduction to Carpentry | 3 |
| CT154A | Masonry Level I | 4 |
| CT 154B | Masonry Level II | 4 |
| CE215 | Construction Procedures | 3 |
| CT292 | Construction Practicum | 3 |
| HL135 | Heartsaver First Aid CPR AED | 1 |
| MA096 | Pre-Collegiate Mathematics | 6 |
| Certificate Total Minimum | 33 | |
The Certificate in Basic Law Enforcement was initially developed when Guam Community College was created by Public Law 14-77 and the responsibility for police basic training was transferred from the University of Guam to Guam Community College. Presently, it continues to be the required curriculum for all territorial law enforcement academy cycles.
The first substantive revision was made in February 2011, which was made upon the Criminal Justice Advisory Committee’s request to realign the Certificate Program and the Criminal Justice Associate Degree Program. It also addressed new general education core requirements to commence Fall Semester 2003.
This the second substantive revision that proposes to create a new area of concentration in Marine & Terrestrial Conservation Enforcement. Thus, students may now elect to graduate with a Certificate in Criminal Justice with an emphasis in either the Law Enforcement Track or Marine & Terrestrial Conservation Enforcement Track.
Program Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs):
Upon successful completion of the Certificate in Criminal Justice program, students will be able to:
- Identify the legal procedures for gathering information about crimes, criminal procedure, and defendants’ rights.
- Describe the process of the criminal justice system and the duties and responsibilities of the criminal justice professional.
- Demonstrate the ability to understand the interrelations, ethics, and role expectations of the criminal justice professional in society.
Law Enforcement Administration Track | ||
Major Requirements | ||
Course | Course Name | Credits |
| CJ100 | Introduction to Criminal Justice | 3 |
| CJ102 | First Responder | 3 |
| CJ126 | Officer Survival | 3 |
| CJ126L | Officer Survival Laboratory | 1 |
| CJ132 | Emergency Vehicle Operator Course (EVOC) | 3 |
| CJ135 | Firearms Use/Safety/Care | 3 |
| CJ150 | Criminal Procedure | 3 |
| CJ200 | Criminal Law | 3 |
| CJ205 | Report Writing for Law Enforcement | 3 |
| CJ225 | Criminal Investigation | 3 |
| PY125 | Interpersonal Relations | 3 |
| Certificate Total | 31 | |
Marine & Terrestrial Conservation Enforcement Track | ||
Major Requirements | ||
Course | Course Name | Credits |
| CJ100 | Introduction to Criminal Justice | 3 |
| CJ102 | First Responder | 3 |
| CJ122/SI122 | Introduction to Forensic Science | 4 |
| CJ126 | Officer Survival | 3 |
| CJ126L | Officer Survival Laboratory | 1 |
| CJ132 | Emergency Vehicle Operator Course (EVOC) | 3 |
| CJ135 | Firearms Use/Safety/Care | 3 |
| CJ150 | Criminal Procedure | 3 |
| CJ200 | Criminal Law | 3 |
| CJ205 | Report Writing for Law Enforcement | 3 |
| CJ225 | Criminal Investigation | 3 |
| CJ292 | Criminal Justice Practicum | 3 |
| Certificate Total | 35 | |
Early childhood educators and caregivers work in Head Start programs, childcare centers, family home care programs, elementary schools, social services programs, and health care services. These professionals plan and implement appropriate experiences for young children in areas such as language, health, movement, creativity, thinking, problem solving, self-concept and social behavior. They also supervise children's activities, care for their needs, keep records of their progress, and confer with parents and other professionals.
The Certificate in Early Childhood Education is closely aligned with national standards and meets Head Start requirements for classroom personnel. Only technical requirement courses that have a grade of "C" or better will be counted towards the Certificate.
Program Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs):
Upon successful completion of the Certificate in Early Childhood Education program, students will be able to:
- Model appropriate practices for children, professionalism, and demonstrate ethical conduct based on guidelines from the National Association for the Education of Young Children (NAEYC).
- Implement various developmentally and age-appropriate teaching, assessment and guidance strategies needed to effectively work with young children from birth to age eight.
- Reflect on practices, pedagogy and resources used in an early childhood setting that serves children ages birth through age eight years.
The Certificate in Early Childhood Education CDA Track is closely aligned with national standards and meets Head Start requirements for classroom personnel. As part of this program there is an option for students to earn a 'stackable' internationally recognized credential, the Child Development Associate (CDA) Credential.
Program Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs):
Upon successful completion of the Certificate in Early Childhood Education Child Development Associate (CDA) program, students will be able to:
- To advocate appropriate practices based on the National Association for the Education of Young Children (NAEYC).
- To effectively and respectfully communicate with children, staff and families from diverse backgrounds and special populations.
- To implement developmentally and age-appropriate teaching needed to effectively work with children birth to age five.
- To prepare students to obtain the nationally recognized Child Development Associate (CDA) credential.
Early Childhood Education Track | ||
Major Requirements | ||
Course | Course Name | Credits |
| CD110 OR ED150 | Introduction to Early Childhood Education OR Introduction to Teaching | 3 |
| CD140 | Nutrition and Physical Health | 3 |
| CD180 | Language Arts Development in Early Childhood | 3 |
| CD221 OR ED220 | Child Growth & Development OR Human Growth and Development | 3 |
| CD240 | Cognitive & Creative Development in Early Childhood | 3 |
| CD260 | Social and Emotional Development | 3 |
| CD292 | Early Childhood Education Practicum | 3 |
| ED231 | Introduction to Exceptionalities | 3 |
Electives | ||
| ED265 | Culture and Education in Guam | 3 |
| CD285 OR ED180A OR ASL100 OR CH110 OR JA110 | CD285 Childcare Management OR ED180A Educational Methods I OR American Sign Language I, OR CH110 CHamoru I, OR JA110 Japanese I | 3-4 |
Certificate Total | 30-31 | |
Early Childhood Education Child Development Associate (CDA) Track | ||
Major Requirements | ||
Course | Course Name | Credits |
| CD110 | Introduction to Early Childhood Education | 3 |
| CD140 | Nutrition and Physical Health | 3 |
| CD180 | Language Arts Development in Early Childhood | 3 |
| CD221 | Child Growth and Development | 3 |
| CD260 | Social and Emotional Development | 3 |
| CD285 | Childcare Management | 3 |
| CD293 | Early Childhood CDA Practicum | 12 |
Certificate Total | 30 | |
The Certificate in Education is designed to provide entry- level training for persons interested in working in educational settings. The program also serves as a career/educational ladder for those interested in pursuing an Associate degree in the field. Emphasis is placed on students learning skills that cover a broad range of educational areas. Only technical requirement courses that have a grade of “C” or better will be counted towards the Certificate degree.
Program Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs):
Upon successful completion of the Certificate in Education program, students will be able to:
- Demonstrate professional and ethical conduct and communication within educational environments.
- Create and implement diverse teaching strategies and materials which address the diversity of our student population and optimize learning for all students.
- Exhibit skills in critical thinking, collaboration, creativity, and reflective practice.
Major Requirements | ||
Course | Course Name | Credits |
ASL100 OR CH110 | American Sign Language I OR CHamoru I | 4 |
ASL110 OR CH111 | American Sign Language II OR CHamoru II | 4 |
| ED150 | Introduction to Teaching | 3 |
| ED180A | Educational Methods I | 3 |
| ED180B | Educational Methods II | 3 |
| ED180C | Educational Methods III | 3 |
| ED220 | Human Growth & Development | 3 |
| ED231 | Introduction to Exceptionalities | 3 |
| ED265 | Culture and Education in Guam | 3 |
| EN111 | Writing for Research | 3 |
| ED292 | Education Practicum | 3 |
Certificate Total | 35 | |
Emergency Management graduates will be able to apply basic emergency management skills in the event of natural and manmade disasters. Graduates will be able to implement the four major areas of emergency management, namely, mitigation, preparation, response, and recovery. The Emergency Management program utilizes the Emergency Management Institute’s Independent Study (IS) courses to prepare graduates to apply leadership skills, to communicate effectively, to solve problems, to plan, to work as a team, to operate within the legal system and governmental framework for emergency management, to analyze risks and hazards, and to manage resources efficiently.
Guam Community College is mirroring Frederick Community College’s model whereby college credits are granted upon successful completion of Emergency Management Institute’s (EMI) Independent Study (IS) courses online. Students who have completed these IS courses will need to request for an official transcript from EMI then apply for college credits at Guam Community College towards a Certificate in Emergency Management.
The Emergency Management Program’s Major Requirements are adopted and derived from EMI’s Independent Study program. These courses are subject to revision and new courses will be added to the program. GCC’s Emergency Management program will adhere to the latest IS offerings to ensure that students learn what is relevant and most up-to-date information and skills.
Program Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs):
Upon successful completion of the Certificate in Emergency Management program, students will be able to:
- State the government’s role in Emergency Management.
- Describe the function of the Emergency Operations Center and National Incident Management System.
- Evaluate hazards and risks in emergency situations.
- Make decisions, solve problems, and use critical thinking skills vis-a-vis the emergency planning process.
Major Requirements | ||
Course | Course Name | Credits |
English (Choose 1) | ||
| EN10 | Freshman Composition | 3 |
| EN110A | Freshman Composition with Instructional Lab | 4 |
Course | Course Name | Credits |
| PS140 | American Government | 3 |
| HL135 | Heartsaver First Aid CPR AED | 1 |
| EMI154 (ISO317.a) | Community Emergency Response Team | 1 |
| MA096 | Pre-Collegiate Mathematics | 6 |
Choose 19 courses from the following | ||
| EMI100 | Emergency Manager | 1 |
| EMI102 | Hazardous Materials | 1 |
| EMI104 | A Citizen’s Guide to Disaster Assistance | 1 |
| EMI106 | Building for the Earthquake of tomorrow | 1 |
| EMI108 | Orientation to Disaster Exercise | 1 |
| EMI110 | Exercise Design | 1 |
| EMI112 | State Disaster Management | 1 |
| EMI114 | Principles of Emergency Management | 1 |
| EMI116 | Emergency Planning | 1 |
| EMI118 | Leadership & Influence | 1 |
| EMI120 | Decision Making & Problem Solving | 1 |
| EMI122 | Effective Communication | 1 |
| EMI124 | Developing & Managing Volunteers | 1 |
| EMI126 | Anticipating Hazardous Weather | 1 |
| EMI128 | Emergency Operations Center Role | 1 |
| EMI130 | Volunteer Agencies in Emergency Management | 1 |
| EMI132 | Disaster Basics | 1 |
| EMI134 | Community Hurricane Preparedness | 1 |
| EMI136 | Hazardous Material Prevention | 1 |
| EMI138 | Multi-hazard Emergency Planning for Schools | 1 |
| EMI140 | Introduction to Mitigation | 1 |
| EMI142 | Protecting your Home and Small Business from Disaster | 1 |
| EMI144 | Introduction to Public Assistance | 1 |
| EMI146 | Debris Operation | 1 |
| EMI148 | Incident Command System | 1 |
| EMI150 | National Incident Management System | 1 |
| EMI152 | National Response Plan & Disaster Medical System | 1 |
Certificate Total | 33-34 | |
This Certificate in Environmental Technician is designed to provide entry-level training for those interested in supporting environmental services. Emphasis is placed on developing field skills as well as competencies in basic science and math content for technical work. The program will serve as a career or educational ladder for students interested in interdisciplinary environmental studies.
Program Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs):
Upon successful completion of the Certificate in Environmental Technician program, students will be able to:
- Demonstrate professionalism and ethical conduct within disciplines in the environmental field.
- Demonstrate interdisciplinary knowledge and skills needed to effectively work in the environmental field.
- Demonstrate proficiency in technical methods and data handling and processing methodology.
Major Requirements | ||
Course | Course Name | Credits |
Choose 1 course from the following | ||
EN___ | English Requirement | 3-4 |
Choose 1 course from the following | ||
MA110A | Finite Mathematics | 3 |
MA161A | College Algebra & Trigonometry I | |
MA161B | College Algebra & Trigonometry II | |
Course | Course Name | Credits |
SI101 | Introduction to Chemistry: Theory | 3 |
SI101L | Introduction to Chemistry: Laboratory | 1 |
SI105 | Introduction to Physical Geology | 3 |
SI105L | Introduction to Physical Geology Laboratory | 1 |
SI125 | Scientific Methods and Data Analysis | 3 |
SU250 | Introduction to Geographic Information Systems | 3 |
Biological Sciences (Choose 2 - Lecture and 2 respective Labs for 8 credits total) | ||
SI103 | Introduction to Marine Biology: Theory | 3 |
SI103L | Introduction to Marine Biology: Laboratory | 1 |
SI110 | Environmental Biology: Theory | 3 |
SI110L | Environmental Biology: Laboratory | 1 |
SI150 | Introduction to Microbiology: Theory | 3 |
SI150L | Introduction to Microbiology: Laboratory | 1 |
SI155 | Waste Site Worker Safety Hazardous Waste Operations and Emergency Response (HAZWOPER) | 3 |
| Certificate Total | 35-36 | |
The Certificate in Family Services program is designed to provide entry level training for paraprofessionals providing human services to families. Emphasis is placed on developing competencies for the effective delivery of human services.
Course requirements may identify Prerequisites that must be completed with a passing grade. Prerequisite course credits are not counted as credits earned towards the program unless they are certificate core course requirements. Prerequisites are identified in the course description section of this catalog and below with a + sign next to each course with a prerequisite.
Program Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs):
Upon successful completion of the Certificate in Family Services program, students will be able to:
- Demonstrate effective communication skills with clients and co-workers.
- Demonstrate appropriate competency needed in the effective delivery of human services.
- Demonstrate professionalism and ethical conduct within the field.
Major Requirements | ||
Course | Course Name | Credits |
English (Choose 1) | ||
EN110 | Freshman Composition | 3 |
EN110A | Freshman Composition with Instructional Lab | 4 |
Course | Course Name | Credits |
PY120 | General Psychology | 3 |
SO130 | Introduction to Sociology | 3 |
HM110 | Introduction to Community Services | 3 |
HM201 | Social Welfare & Development: Global Challenges | 3 |
HM292 OR FA192 | Human Services Practicum OR FA192 Family Services Practicum | 3 |
Choose 1 course from the following | ||
ED220 | Human Growth and Development | 3 |
CD221 | Child Growth and Development | |
Choose 3 Courses from the following | ||
ASL100 | American Sign Language I | 4 |
CH110 | CHamoru I | 4 |
CO125 | Introduction to Human Communication and Speech | 3 |
CS151 | Windows Applications | 3 |
PY125 | Interpersonal Relations | 3 |
HU120 | Pacific Cultures | 3 |
CJ100 | Introduction to Criminal Justice | 3 |
CJ101 | Juvenile Justice Process | 3 |
CJ104 | Dynamics of Substance Abuse | 3 |
ED231 | Introduction to Exceptionalities | 3 |
HL202 | Nutrition | 3 |
Certificate Total | 30-32 | |
It is the mission of the Fire Science Technology program to prepare, educate, and train students for a career in firefighting. The certificate program in Fire Science Technology is not open to the general public. It is a competency-based academy program designed to offer entry-level training for fire recruits. Students who wish to attend the GCC Fire Academy should first obtain employment with the Guam Fire Department or any other Pacific Basin fire department that sends recruits to the GCC Fire Academy for basic training.
Course requirements may identify prerequisites that must be completed with a passing grade. Prerequisite course credits are not counted as credits earned towards the program unless they are certificate core course requirements. Prerequisites are identified in the course description section of this catalog and below with a + sign next to each course with a prerequisite.
Program Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs):
Upon successful completion of the Certificate in Fire Science Technology, students will be able to:
- Understand the current tactics used by fire personnel for suppression and prevention of fires, the operations and role of fire personnel, and the functions of fire service within the community.
- Analyze and apply the theories, techniques, and methods of basic fire and rescue.
- Demonstrate the techniques required for fire safety and prevention, to work as a team, and to respond to a variety of emergency situations.
Major Requirements | ||
Course | Course Name | Credits |
FS100 | Fire Protection | 3 |
FS101 | Intro to Fire Suppression | 3 |
FS103 | Firefighter I | 8 |
FS104 | Firefighter II | 3 |
FS105 | Fire Prevention | 3 |
FS107 | Report Writing for The Fire Service | 3 |
| Elective Requirement |
|
CJ102 | First Responder | 3 |
EMS103 | Emergency Medical Technician (EMT)-Basic | 8 |
Certificate Total | 34 | |
Medical Assistants are the only allied health professionals specifically trained to work in ambulatory settings, such as physician’s offices, clinics, and group practices. These multi-skilled personnel can perform administrative and clinical procedures. Physicians value this unique versatility more and more, as managed care necessitates the need to contain costs and manage human resources efficiently. Medical Assistants are trained allied health professionals who work primarily in physicians’ offices, and outpatient clinics under the direct supervision of a physician. One portion of the training concentrates on administrative medical assisting, which provides a suitable background for employment in health maintenance organizations, home health care organizations, and nursing homes. Upon completion of the Medical Assisting Program, students will be prepared for the Registered Medical Assistant (RMA) national certification examination through the American Medical Technologists (AMT), an affiliated partner with Guam Community College.
- Note: The student must have a “C” or better in all courses to receive a Certificate in Medical Assisting. Students must pass each course with a “C” or better to continue toward the next course in the program. Those students who do not successfully complete a core technical of related technical requirement course will have to wait a minimum of one year for reentry.
Program Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs):
Upon successful completion of the Certificate in Medical Assisting program, students will be able to:
- Navigate through an electronic health record system and practice management software.
- Explain the need for Medical Law and Ethics.
- Examine the purpose of Healthcare Policy and Procedures.
Major Requirements | ||
Course | Course Name | Credits |
English (Choose 1) | ||
EN110 | Freshman Composition | 3 |
EN110A | Freshman Composition with Instructional Lab | 4 |
Mathematics | ||
MA108 | Introduction to College Algebra OR placement examination | 3 |
Course | Course Name | Credits |
HL120 | Medical Terminology | 2 |
HL131 | Basic Life Support for Healthcare Providers | 1 |
HL190 | Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology for Allied Health Professionals | 4 |
MS 125 | Clinical Medical Assisting: Clinical | 1 |
MS101 | Introduction to Medical Assisting | 3 |
MS120 | Clinical Medical Assisting: Theory | 3 |
MS121 | Clinical Medical Assisting: Laboratory | 2 |
MS140 | Administrative Medical Assisting: Theory | 2 |
MS141 | Administrative Medical Assisting: Laboratory | 2 |
MS145 | Administrative Medical Assisting: Clinical | 1 |
MS160 | Pharmacology: Dosage and Calculations | 2 |
MS161 | Administration of Medications Laboratory | 1 |
MS180 | Introduction to Clinical: Laboratory | 2 |
MS210 | Medical Assisting Critique | 1 |
MS292 | Medical Assisting Practicum | 5 |
Program Total | 38-39 | |
The Medium/Heavy Truck Diesel Technology program prepares graduates to work in the automotive field with special emphasis in diesel service. Graduates will be able to troubleshoot, maintain, and repair various types of diesel engines, trucks, boats, and other heavy equipment. Students will obtain knowledge and skills in Medium/Heavy Truck in a variety of areas to include: diesel engines; drive trains; brake systems; suspension and steering; heating, ventilation, and air conditioning; hydraulics; electrical/electronic systems; and preventive maintenance.
Students completing this program will have preparatory knowledge in the eight main areas of the Medium/Heavy Truck Diesel Technology and will prepare them for entry-level Assistant Technician positions. This program prepares graduates to pass the ASE National Certification Exams and enter the workforce as entry-level Junior Technicians.
Program Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs):
Upon successful completion of the Certificate in Medium/Heavy Truck Diesel Technology program, students will be able to:
- Seek employment as a Heavy/Medium Truck Technician, Fleet Mechanic, Heavy Marine Diesel Technician, Generator Repair, Heavy Equipment Repair or Parts Counter person.
- Troubleshoot, maintain, and repair various heavy trucks and mobile equipment, including bulldozers, boats, cranes, road graders, farm tractors, and combines.
Major Requirements | ||
Course | Course Name | Credits |
MA108 | Introduction to College Algebra I | 3 |
MHT100A | Introduction to Diesel Technology and Preventive Maintenance I | 3 |
MHT100B | Introduction to Diesel Technology and Preventive Maintenance II | 3 |
MHT110 | Diesel Engines Part I | 3 |
MHT120 | Medium/Heavy Truck Drive Trains Part I | 3 |
MHT130 | Medium/Heavy Truck Brake Systems Part I | 3 |
MHT140 | Medium/Heavy Truck Suspension & Steering I | 3 |
MHT150 | Medium/Heavy Truck Heating, Ventilation, & Air Conditioning | 3 |
MHT160 | Hydraulics | 3 |
MHT170 | Medium/Heavy Truck Electrical/Electronic Systems Part I | 3 |
MHT210 | Diesel Engines Part II | 3 |
MHT230 | Medium/Heavy Truck Brake Systems II | 3 |
MHT270 | Medium/Heavy Truck Electrical/Electronic Systems Part II | 3 |
Certificate Total | 39 | |
This program prepares students for entry- through mid-level positions as administrative assistants or may be used to update office technology knowledge and skills for job advancement in the field. Related job titles include clerk, typist, receptionist, and data entry operators.
Program Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs):
Upon successful completion of the Certificate in Office Technology program, students will be able to:
- Key at current speed and accuracy to meet industry requirements for keyboarding.
- Format, produce, and manage business documents such as memos, letters, databases, spreadsheets, presentations, and reports.
- Demonstrate effective written and oral business communication skills.
Major Requirements | ||
Course | Course Name | Credits |
English (Choose 1) | ||
EN110 | Freshman Composition | 3 |
EN110A | Freshman Composition with Instructional Lab | 4 |
Course | Course Name | Credits |
CS151 | Windows Applications | 3 |
OA101 | Keyboarding and Document Processing | 3 |
OA103 | Filing Systems | 3 |
OA130 | Information Processing | 3 |
OA210 | Database Management Systems | 3 |
OA211 | Business Communications | 3 |
OA220 | Spreadsheet Systems | 3 |
OA230 | Advanced Information Processing | 3 |
OA250 | Office Procedures | 3 |
PY125 | Interpersonal Relations | 3 |
Electives | ||
Choose 2 courses from the following: | ||
AC100 | Fundamentals of Bookkeeping and Accounting | 3 |
AC211 | Accounting Principles I | 4 |
OA109 | Business Math Using Excel | 3 |
SM108 | Introduction to Business | 3 |
Certificate Total | 39-41 | |
The Certificate in Sign Language Interpreting program is designed to prepare individuals who are pursuing a path in interpreting and becoming facilitators of communication for the Deaf. The program combines theoretical and practical learning experiences that will develop the students’ linguistic knowledge and understanding of American Sign Language (ASL), as well as their awareness of Deaf culture.
Program Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs):
Upon successful completion of the Certificate in Supervision and Management program, students will be able to:
- Demonstrate knowledge of historical, social, cultural and ideological constructions of deaf people and their communities on national and global scales.
- Introduce and present written projects related to the field of Deaf Culture using various media.
- Reflect and engage in critical inquiry relating to topics in Deaf Culture and sign languages.
Major Requirements | ||
Course | Course Name | Credits |
ASL100 | American Sign Language I | 4 |
ASL110 | American Sign Language II | 4 |
ASL120 | American Sign Language III | 4 |
ASL130 | American Sign Language IV | 4 |
IN145 | Vocabulary Development for Intercultural Development | 3 |
IN170 | Introduction to Interpreting | 3 |
IN180 | Ecology of Deafness | 3 |
IN220 | Voice to Sign/Sign to Voice Interpreting | 3 |
IN292 | Sign Language Interpreting Practicum | 3 |
Certificate Total | 31 | |
The Certificate in Supervision and Management program prepares students for entry-level and assistant management positions in supervision and management.
Program Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs):
Upon successful completion of the Certificate in Supervision and Management program, students will be able to:
- Describe theory and principles related to supervisory principles and procedures.
- Demonstrate entry-level supervisory and management skill techniques in business operations.
- Demonstrate practical leadership decision-making based on sound business practice, experience, and judgment.
Major Requirements | ||
Course | Course Name | Credits |
English (Choose 1) | ||
EN110 | Freshman Composition | 3 |
EN110A | Freshman Composition with Instructional Lab | 4 |
Mathematics (3-4 credits): | ||
MA098 | Intermediate Algebra or higher (placement and/or satisfactory completion of courses) | 4 |
Course | Course Name | Credits |
AC211 | Accounting Principles I | 4 |
EC110 | Principles of Economics | 3 |
SM108 | Introduction to Business | 3 |
SM208 | Personnel Supervision | 3 |
SM211 | E-Commerce Management | 3 |
SM220 | Management Skill Development | 3 |
SM225 | Leadership | 3 |
SM230 | Business Law Applications | 3 |
SM245 | Ethics & Stakeholder Management | 3 |
Electives | ||
Choose 1 course from the following | ||
CS151 | Windows Applications | 3 |
CS152 | Macintosh Applications | |
Certificate Total | 38-39 | |
The Surveying Technology program prepares the student for immediate employment as a surveying or Geographic Information Systems (GIS) technician and teaches the student knowledge and skills that will enable one to adapt to ever evolving technical and technological changes in geospatial field and office applications. The graduate will be prepared to face the challenge of modern Surveying and GIS practice. The program emphasizes applications-based approaches and provides an overview of the geospatial fields of surveying, mapping, and GIS and prepares the student for further study and for the Level 1 Certified Survey Technician examination prepared by the American Society on Surveying and Mapping National Society of Professional Surveyors (ACSM-NSPS).
Program Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs):
Upon successful completion of the Certificate in Surveying Technology program, students will be able to:
- Prepare to enter productive technical positions in the geospatial fields of surveying, mapping, and Geographic Information Systems.
- Pass the American Congress of Surveying and Mapping-National Society of Professional Surveyors (ACSM/NSPS) Level 3 Certified Survey Technician examination.
- Emulate a professional work ethic needed in the surveying industry.
- Utilize modern measurement technologies to acquire spatial data and employ industry-standard software to solve technical problems.
General Education Requirements | ||
Course | Course Name | Credits |
| EN110 OR EN110A | Freshman Composition OR Freshman Composition with Instructional Lab | 3-4 |
| MA110A | Finite Mathematics | 3 |
Major Requirements | ||
Course | Course Name | Credits |
AE103 | Basic Blueprint Reading | 3 |
AE121 | Technical Engineering Drawing I | 3 |
AE150 | Computer Aided Drafting I (CAD I) | 3 |
CE211 | Plane Surveying I | 3 |
CE222 | Plane Surveying II | 3 |
SU100 | Surveying Drafting | 3 |
SU101 | Surveying Problems I | 3 |
SU230 | Advanced Surveying | 3 |
SU250 | Introduction to Geographic Information Systems | 3 |
SU292 | Surveying Practicum | 3 |
Certificate Total | 36-37 | |
The student must indicate which year’s catalog requirements they choose to satisfy when submitting the Application for Degree, Certificate, or Diploma. It is the responsibility of the student to apply for any degree, certificate or diploma they have earned.
Students qualify for graduation once the following requirements are met:
- Achieve a 2.0 cumulative GPA as an undergraduate student.
- Meet individual program requirements, including major GPA (if applicable).
- Fulfill residency requirements – at least 12-degree applicable credit hours of coursework completed at the College.
- Successfully complete the program pertaining to their degree.
- Submit Application for Graduation to the Admissions & Registration Office by the applicable deadline and pay the graduation fee.
- Meet financial obligations to the school.
NOTE: A single course cannot be used to satisfy more than one course requirement in a program.
Effective fall Semester 2003, several academic policy changes were implemented to ensure that students are adequately prepared to meet business and industry standards. All Undeclared or newly Declared Students enrolled in regularly scheduled postsecondary courses must be enrolled in or have completed EN110 Freshman Composition general education requirement by the time they have enrolled in 12 credits of classes. They must also enroll in or have completed MA110A Finite Mathematics (or higher) general education requirement by the time they have enrolled in 15 credits. This means that students may take only nine to eleven (9-11) credits before they must begin meeting the general education requirements. All declared students in Associate Degree programs are required to successfully complete minimum standardized general education course requirements. For more information, refer to the Admissions Information and General Education Policy section of this catalog.
All candidates for an Associate Degree at the College must meet the general requirements listed above. Course requirements may identify prerequisites that must be completed with a passing grade. Prerequisite course credit is not counted as credit earned towards the program unless it is an Associate Degree core course requirement.
Recognizing the necessity for students to succeed in the complex and rapidly changing workplace, Guam Community College offers a general education curriculum that introduces students to major areas of knowledge and methods of inquiry. All degree programs require an interdisciplinary general education component that promotes the development of intellectual skills that enable students to become effective learners and informed citizens. Critical thinking, the use of language and computation, appropriate social skills, global awareness and respect for diverse opinions are among the learning outcomes provided in the general education requirements of each program.
Guam Community College believes that general education provides the academic foundation necessary for students to achieve their life goals. General education is intended to offer students a breadth of quality student learning experiences, encourage their respect for cultural heritage, promote their ethical and responsible social behavior and facilitate their life-long learning.
The General Education program strives to foster student learning and skill development in civic engagement, critical thinking, understanding of the relationship between the individual and society, information literacy, oral communication, quantitative reasoning, and written communication.
Guam Community College believes that high quality general education opportunities for all citizens are necessary for democratic principles and practices to exist and for a sound economy to flourish. The College continually scrutinizes the general education curriculum in order to assure that all degrees and certificates granted by the College support this vision of general education and that it serves as a means to inspire hope, opportunity and responsibility in all its constituencies.
Requirements for General Education follow the options described below. Students declared prior to fall 2010 will follow the requirements indicated in the applicable catalog in which they first declared their major program at the College.
Notes on General Education requirements
Students are advised to check the requirements for their specific programs before taking General Education courses.
Courses chosen to meet the general education requirements may not be used to meet the Major Requirements of a student’s specific degree program.
The list contains courses with prerequisites, so students should make their choices carefully and thoughtfully. Students may consult a counselor or an academic advisor for guidance in choosing any of the course options listed.
IMPORTANT NOTE: Some programs require different levels of coursework to meet General Education requirements, please review the individual programs for more information.
Minimum program length of 60 semester credit hours awarded for achievement of student learning for an Associate of Arts and an Associate of Science degree.
Program Student Learning Outcomes follow each program description in the following pages. SLOs intentionally describe the 3-5 central goals that students will have attained by the end of the program. In essence, SLOs encapsulate the knowledge, skills, and attitudes that students are expected to learn from their respective programs. The focus is on what students can do with what they have learned and this outcome should be evaluated in some way. Primarily, three questions essentially frame the articulation of SLOs:
- What do students know? (cognitive domain)
- What do they think and value? (affective domain)
- What can they do? (behavioral domain)
In this catalog, program SLOs describe the broadest goals for the program, particularly those that require higher-level thinking. They, therefore, require students to synthesize many discrete skills or areas of content. SLOs also ask students to produce artifacts such as term papers, projects, portfolios, demonstrations, exams or other student work. Most importantly, SLOs also need to be evaluated or assessed in some way so that accountability and improvement remain the hallmarks of a good program. A separate SLO Booklet is published and updated regularly to guide faculty in helping students achieve articulated course outcomes.
The College, in close collaboration with faculty and members of Advisory committees, continues to embark on an ongoing institutional effort to revise and update all its curriculum documents so that they remain responsive to industry and community needs.
SLO Mapping - ILO, PROGRAM, AND COURSE LEVELS
SLOs also align with collective program and institution level expectations for student learning translated into the curriculum and co-curriculum. Most importantly, these SLOs map to the curriculum, co-curriculum and other educational practices that provide students multiple opportunities for meaningful learning. SLO maps developed for three (3) different levels – ILOs, program, and course -- reflect the desired goals of learning experiences that the College continues to intentionally develop, structure, deliver, and evaluate on an ongoing basis.
GENERAL EDUCATION | ||
Scope 1: Skills for and Application of Lifelong Learning | ||
Freshman Composition (Choose one course from the following to meet the required 3-4 credits) | ||
Course # | Course Name | Credits |
EN110 | Freshman Composition | 3 |
EN110A | Freshman Composition with Instructional Lab | 4 |
EN111 | Writing for Research | 3 |
Mathematics (Choose one course from the following to meet the required 3-4 credits)* | ||
Course # | Course Name | Credits |
MA110A | Finite Mathematics | 3 |
MA115 | Fundamentals of College Algebra | 3 |
MA161A | College Algebra & Trigonometry I | 3 |
*Any college level math will be considered for the completion of this category | ||
Literacy for Life Skills (Choose one course from the following to meet the required 3 credits) | ||
Course # | Course Name | Credits |
CO110 | Critical Thinking for Civic Engagement | 3 |
CS151 | Windows Applications | |
CS152 | Macintosh Applications | |
Humanities & Fine Arts (Choose one course from the following to meet the required 3-4 credits)* | ||
Course # | Course Name | Credits |
ASL100 | American Sign Language I | 4 |
CH110 | CHamoru I | 4 |
ED265 | Culture and Education in Guam | 3 |
CO125 | Introduction to Human Communication and Speech | 3 |
EN210 | Introduction to Literature | 3 |
HI121 | History of World Civilization I | 3 |
HI122 | History of World Civilization II | 3 |
HI176 | Guam History | 3 |
HM110 | Introduction to Community Services | 3 |
HM201 | Social Welfare & Development: Global Challenges | 3 |
HU120 | Pacific Cultures | 3 |
HU220 | Guam Cultures and Legends | 3 |
JA110 | Japanese I | 4 |
KE110 | Korean I | 4 |
MU110 | Chorale I | 3 |
PI101 | Introduction to Philosophy | 3 |
TH101 | Introduction to Theatre | 3 |
VC101 | Introduction to Visual Communications | 3 |
*Any foreign language, humanities, or fine arts course will be considered for the completion of this category | ||
Scope 2: Broad Comprehension of the Development of Knowledge, Practice and Interpretation Natural & Physical Sciences (Choose one course and the corresponding lab from the following to meet the required 4 credits)** | ||
Course # | Course Name | Credits |
SI101/101L | Introduction to Chemistry: Theory (3) & Introduction to Chemistry Laboratory (1) | 4 |
SI103/103L | Introduction to Marine Biology: Theory (3) & Introduction to Marine Biology Laboratory (1) | |
SI105/105L | Introduction to Physical Geology (3) & Introduction to Physical Geology Laboratory (1) | |
SI110/110L | Environmental Biology: Theory (3) & Environmental Biology: Laboratory (1) | |
SI141 | Applied Physics I | |
SI150/150L | Introduction to Microbiology: Theory (3) & Introduction to Microbiology: Laboratory (1) | |
SI131/131L | Human Anatomy & Physiology I: Theory (3) & Human Anatomy & Physiology I: Laboratory (1) | |
SI132/132L | Human Anatomy & Physiology II: Theory (3) & Human Anatomy & Physiology II: Laboratory (1) | |
**The exception to this would be SI141 which does not include a laboratory requirement | ||
Scope 3: Preparation for and Acceptance of Responsible Participation in Civil Society | ||
Social & Behavioral Sciences (Choose one course from the following to meet the required 3 credits) | ||
Course # | Course Name | Credits |
EC110 | Principles of Economics | 3 |
PS140 | American Government | 3 |
PY100 | Personal Adjustment | 3 |
PY120 | General Psychology | 3 |
PY125 | Interpersonal Relations | 3 |
SO130 | Introduction to Sociology | 3 |
CJ100 | Introduction to Criminal Justice | 3 |
WG101 | Introduction to Women and Gender Studies | 3 |
*Any social and behavioral science course will be considered for the completion of this category | ||
Minimum General Education Requirements | 19 | |
The Accounting program will train individuals for employment in accounting fields and provide employees working in accounting-related fields the knowledge to upgrade job skills. Students are offered opportunities to experience learning environments through service learning that educate, empower, and enable students to be civically engaged—gaining skills that lead to participatory leadership, effective citizenship, and increased volunteerism.
Program Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs):
Upon successful completion of the AS in Accounting program, students will be able to:
- Describe the steps of the accounting cycle using a computer based program.
- Perform necessary procedures at each step of the accounting cycle for various types of business.
- Discuss skills needed to sustain careers in accounting.
General Education Requirements | ||
Course | Course Name | Credits |
English (Choose 1) | ||
EN110 | Freshman Composition | 3 |
EN110A | Freshman Composition with Instructional Lab | 4 |
Course | Course Name | Credits |
MA____ | MA110A or higher | 3 |
CS151 | Windows Applications | 3 |
| Humanities & Fine Arts | 3 |
| Social & Behavioral Science | 3 |
SI____ | Natural & Physical Science | 4 |
Related General Education & Technical Requirements | ||
Course | Course Name | Credits |
AC110 | Payroll Accounting | 3 |
AC150 | Federal Income Tax I | 3 |
AC210 | Introduction to Financial Management | 3 |
AC211 | Accounting Principles I | 4 |
AC212 | Accounting Principles II | 4 |
AC233 | Accounting on the Computer Using QuickBooks | 3 |
EC110 | Principles of Economics | 3 |
EN111 OR OA211 | Writing for Research OR Business Communication | 3 |
OA220 | Spreadsheet Systems | 3 |
SM108 | Introduction to Business | 3 |
SM230 | Business Law Applications | 3 |
Technical Requirements (Continued) | ||
Course | Course Name | Credits |
Accounting Electives (choose 2 courses from the following) | ||
AC225 | Hospitality Industry Accounting | 6 |
AC240 | Certified Bookkeeper Review | |
AC250 | Federal Income Tax II | |
AC280 | Personal Finance | |
AC292 | Accounting Practicum | |
Program Total | 60-61 | |
Course Sequence by Semester
Year 1 | |||||
Semester 1 | Semester 2 | ||||
Course # | Course Name | Credits | Course # | Course Name | Credits |
| EN___ | English Composition Requirement | 3-4 | Humanities & Fine Arts | 3 | |
| MA_ | Mathematics Requirement | 3 | AC212 | Accounting Principles II | 4 |
| AC211 | Accounting Principles I | 4 | AC110 | Payroll Accounting | 3 |
| AC150 | Federal Taxation I | 3 | Social & Behavioral Sciences | 3 | |
| CS151 | Windows Application | 3 | AC200+ Accounting Elective | 3 | |
Total | 16-17 | Total | 16 | ||
Year 2 | |||||
Semester 3 | Semester 4 | ||||
Course # | Course Name | Credits | Course # | Course Name | Credits |
| Natural & Physical Sciences | 4 | AC210 | Introduction to Financial Management | 3 | |
| AC200+ Accounting Elective | 3 | OA211 OR EN111 | Business Communication OR Writing for Research | 3 | |
| AC233 | Accounting Using QuickBooks | 3 | OA220 | Spreadsheet Systems | 3 |
| EC110 | Principles of Economics | 3 | SM230 | Business Law | 3 |
| SM108 | Introduction to Business | 3 | |||
| Total | 16 | Total | 12 | |
PROGRAM TOTAL | 60-61 | ||||
The Associate of Science program in Automotive Service Technology General and Master Service Technician Tracks offers students both a comprehensive general education as well as advanced technical training in all automotive systems to include: Brakes, Electrical/Electronics, Engine Performance, Suspension & Steering, Automatic Transmissions and Transaxles, Engine Repair, Manual Drive Trains & Axles, Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning (HVAC), and Advanced Engine Performance.
Upon completion students will be prepared for all eight content area certification examinations
administered by the National Institute for Automotive Service Excellence (ASE).
Program Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs):
Upon successful completion of the AS in Automotive Service Technology program, students will be able to:
- Identify the purpose and proper functioning of the core components of an automotive engine.
- Perform a cylinder compression cranking test and interpret results.
- Demonstrate the proper use of a digital multimeter (DMM) during diagnosis of electrical circuit problems.
- Conduct a performance test of the heating, ventilation, and air conditioning system.
- Conduct failure analysis on automatic and/or manual transmissions and/or transaxles.
- Perform service and maintenance of components on the brake, steering, and suspension systems.
General Education Requirements – General Service Technician Track | ||
Course | Course Name | Credits |
EN___ | English Requirement | 3-4 |
MA___ | Mathematics Requirement | 3 |
SI___ | Natural & Physical Sciences Requirement | 4 |
Computer Literacy (Choose 1) | ||
CS151 | Windows Applications | 3 |
CS152 | Macintosh Applications | |
Social & Behavioral Sciences Requirement (Choose 1) | ||
PY 100 | Personal Adjustment | 3 |
PY 125 | Interpersonal Relations | |
PY 120 | General Psychology | |
Humanities & Fine Arts Requirement (Choose 1) | ||
ASL100 | American Sign Language I | 3-4 |
JA110 | Japanese I | |
CH110 | CHamoru I | |
Major Requirements – General Service Technician Track | ||
Course | Course Name | Credits |
AST100 | Introduction to Automotive Service | 3 |
AST110 | Engine Repair | 6 |
AST120 | Automatic Transmission and Trans-Axle | 6 |
AST140 | Suspension and Steering | 6 |
AST150 | Brake Systems I | 6 |
AST160 | Electrical/Electronic Systems | 5 |
AST180 | Engine Performance | 8 |
AST 260 | Theory/Practicum: Electrical/Electronic Systems | 5 |
Program Total | 64-66 | |
General Education Requirements – Master Service Technician Track | ||
Course | Course Name | Credits |
EN___ | English Requirement | 3-4 |
MA___ | Mathematics Requirement | 3 |
SI___ | Natural & Physical Sciences Requirement | 4 |
| Social & Behavioral Sciences Requirement | 3 |
Computer Literacy (Choose 1) | ||
CS151 | Windows Applications | 3 |
CS152 | Macintosh Applications | |
Humanities & Fine Arts Requirement (Choose 1) | ||
ASL100 | American Sign Language I | 3-4 |
JA110 | Japanese I | |
CH110 | CHamoru I | |
Major Requirements – Master Service Technician Track | ||
Course | Course Name | Credits |
AST100 | Introduction to Automotive Service | 3 |
AST110 | Engine Repair | 6 |
AST120 | Automatic Transmission and Trans-Axle | 6 |
AST140 | Suspension and Steering | 6 |
AST150 | Brake Systems | 6 |
AST160 | Electrical/Electronic Systems | 5 |
AST180 | Engine Performance | 8 |
AST260 | Theory/Practicum: Electrical/Electronic Systems | 5 |
Program Total | 45 | |
Course Sequence by Semester General Service Technician Track
Year 1 | |||||
Semester 1 | Semester 2 | ||||
Course # | Course Name | Credits | Course # | Course Name | Credits |
EN___ | English Composition Requirement | 3-4 | AST140 | Suspension and Steering | 6 |
AST100 | Introduction to Automotive Service | 3 | AST150 | Brake Systems I | 6 |
AST110 | Engine Repair | 6 | AST260 | Theory/Practicum: Electrical/Electronic Systems | 5 |
AST160 | Electrical/Electronic Systems | 5 |
| ||
Total | 17-18 |
| Total | 17 | |
Year 2 | |||||
Semester 3 | Semester 4 | ||||
Course # | Course Name | Credits | Course # | Course Name | Credits |
MA___ | Math | 3 | PY___ | PY100 OR PY125 OR PY120 | 3 |
AST120 | Automatic Transmissions & Transmissions | 6 | Science | 4 | |
AST180 | Engine Performance | 8 | Humanities & Fine Arts Requirement | 3-4 | |
| CS___ | CS151 OR CS152 | 3 | ||
| Total | 17 |
| Total | 13-14 |
Program Total | 64-66 | ||||
Course Sequence by Semester Master Service Technician Track
Year 1 | |||||
Semester 1 | Semester 2 | ||||
Course # | Course Name | Credits | Course # | Course Name | Credits |
| EN___ | Freshman Composition | 3-4 | AST140 | Suspension and Steering | 6 |
| AST100 | Introduction to Automotive Service | 3 | AST150 | Brake Systems I | 6 |
| AST110 | Engine Repair | 6 | AST260 | Theory/Practicum: Electrical/Electronic Systems | 5 |
| AST160 | Electrical/Electronic Systems | 5 | |||
Total | 17-18 |
| Total | 17 | |
Year 2 | |||||
Semester 3 | Semester 4 | ||||
Course # | Course Name | Credits | Course # | Course Name | Credits |
| MA___ | Math Requirements | 3 | AST120 | Automatic Transmission/Transaxles | 6 |
| AST180 | Engine Performance | 8 | AST130 | Manual Drive Train & Axles I | 6 |
| AST280 | Advanced Engine Performance | 8 | AST170 | Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning | 6 |
| Total | 19 |
| Total | 18 |
Year 3 | |||||
Semester 5 |
| ||||
Course # | Course Name | Credits | Course # | Course Name | Credits |
| SI___ | Science | 4 | |||
| Humanities and Fine Arts | 3-4 | ||||
| PY___ | PY100 OR PY125 OR PY120 | 3 | |||
| CS___ | Literacy for Life Skills | 3 | |||
| Total | 13-14 | |||
Program Total | 84-86 | ||||
The Associate of Science in Civil Engineering Technology is a course of study that prepares students to analyze construction sites, use and maintain equipment, draft plans, and write reports. Technical requirement classes are designed to provide students with fundamentals in surveying, analyzing material strength, and structural drafting and design. This course of study will provide students with an overview of technical drawing, construction management and procedures, planning, and estimating. The student learning outcomes meet the professional standards of technicians in this field.
Program Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs):
Upon successful completion of the AS in Civil Engineering Technology program, students will be able to:
Properly use surveying equipment and tools and perform applications accordingly.
Create a construction drawing set consisting of at least six sheets from a design.
Perform basic techniques and skills using modern engineering tools in the current civil engineering industry.
Sequence the steps related to the construction process in chronological order.
General Education Requirements | ||
Course | Course Name | Credits |
EN110 OR EN110A | Freshman Composition OR Freshman Composition with Instructional Lab | 3 OR 4 |
MA161A | College Algebra & Trigonometry I | 3 |
SI141 | Applied Physics I | 4 |
CO110 | Critical Thinking for Civic Engagement | 3 |
Social & Behavioral Science Requirement (Choose 1) | ||
CJ100 | Introduction to Criminal Justice | 3 |
EC110 | Principles of Economics | 3 |
PS140 | American Government | 3 |
PY100 | Personal Adjustment | 3 |
PY120 | General Psychology | 3 |
PY125 | Interpersonal Relations | 3 |
SO130 | Introduction to Sociology | 3 |
WG101 | Introduction to Women and Gender Studies | 3 |
Humanities & Fine Arts Requirement (Choose 1) | ||
ASL100 | American Sign Language I | 4 |
CH110 | CHamoru I | 4 |
CO125 | Introduction to Human Communication and Speech | 3 |
ED265 | Culture and Education in Guam | 3 |
EN210 | Introduction to Literature | 3 |
HI121 | History of World Civilization I | 3 |
HI122 | History of World Civilization II | 3 |
HI176 | Guam History | 3 |
HM110 | Introduction to Community Services | 3 |
HM201 | Social Welfare & Development: Global Challenges | 3 |
HU120 | Pacific Cultures | 3 |
HU220 | Guam Cultures and Legends | 3 |
JA110 | Japanese I | 4 |
KE110 | Korean I | 4 |
PI101 | Introduction to Philosophy | 3 |
TH101 | Introduction to the Theatre | 3 |
VC101 | Introduction to Visual Communications | 3 |
TOTAL | 19-21 | |
Major Requirements | ||
Course | Course Name | Credits |
CT100 OR SU100 | Introduction to Construction Trades (CT100) OR Surveying Drafting (SU100) | 3 |
AE103 | Basic Blueprint Reading | 3 |
AE121 | Technical Engineering Drawing I | 3 |
AE122 | Technical Engineering Drawing II | 3 |
AE138 | Building Codes, Specifications & Construction Management | 3 |
AE150 | Computer Aided Drafting I (CADD 1) | 3 |
AE160 | Computer Aided Drafting II (CADD II) | 3 |
CE210 | Statics | 3 |
CE211 | Plane Surveying I | 3 |
CE215 | Construction Procedures | 3 |
CE225 | Construction Planning & Estimating | 3 |
MA161B | College Algebra & Trigonometry II | 3 |
EN194 | Technical Communication | 3 |
SU250 | Introduction to Geographic Information Systems | 3 |
Total | 42 | |
PROGRAM TOTAL | 61-63 | |
Course Sequence by Semester
Year 1 | |||||
Semester 1 | Semester 2 | ||||
Course # | Course Name | Credits | Course # | Course Name | Credits |
EN___ | English Composition Requirement | 3-4 | AE121 | Technical Engineering Drawing I | 3 |
MA161A | College Algebra & Trigonometry I | 3 | AE150 | Computer Aided Drafting I | 3 |
AE103 | Basic Blueprint Reading | 3 | EN194 | Technical Communication | 3 |
CT100 OR SU100 | Introduction to Construction Trades OR Surveying Drafting | 3 | MA161B | College Algebra & Trigonometry II | 3 |
CO110 | Critical Thinking for Civic Engagement | 3 | SI141 | Applied Physics I | 4 |
Total | 15-16 |
| Total | 16 | |
Year 2 | |||||
Semester 3 | Semester 4 | ||||
Course # | Course Name | Credits | Course # | Course Name | Credits |
AE138 | Building Codes, Specifications & Construction Management | 3 | AE122 | Technical Engineering Drawing II | 3 |
AE160 | Computer Aided Drafting II | 3 | CE225 | Construction Planning & Estimating | 3 |
CE210 | Statics | 3 |
| Humanities & Fine Arts | 3-4 |
CE211 | Plane Surveying I | 3 |
| Social & Behavioral Sciences | 3 |
CE215 | Construction Procedures | 3 |
|
| |
SU250 | Introduction to Geographic Information Systems | 3 |
|
| |
Total | 18 |
| Total | 12-13 | |
PROGRAM TOTAL | 61-63 | ||||
The Associate of Science in Information Technology is a program of study that prepares students for entry-level employment in the field of Information Technology (IT). Technical requirement classes are designed to give students a firm foundation in the basics of computer operations, repair, network medium design and installation, enterprise networking, security and cybersecurity operations. Elective courses allow the students to further specialize.
This program of study will provide students with a practical overview of Information Technology, including hands-on experience with configuring networking devices, network management, network security, and cybersecurity operations. Students who complete the Associate Degree program are prepared to take various certifications and licensing exams, including the Cisco Certified Networking Associates (CCNA) exam. Cisco Cyber Ops Associate, ETA Fiber Optic Installer and Data Cabling Installer Certifications, CompTIA’s A+, Security+, Project Management and Server Certifications.
Program Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs):
Upon successful completion of the AS in Information Technology program, students will be able to:
- Install, configure, and repair computer systems.
- Apply concepts and knowledge in the core areas of computer networking.
- Apply concepts and knowledge in the core areas of computer network security and cybersecurity operations.
General Education Requirements | ||
Course | Course Name | Credits |
| EN110 | Freshman Composition | 3 |
| MA___ | Mathematics Requirement | 3 |
| SI___ | Natural & Physical Sciences Requirement | 4 |
| Social & Behavioral Sciences Requirement | 3 | |
| Humanities & Fine Arts Requirement | 3-4 | |
| Literacy for Life Requirement | 3 | |
Total | 19-20 | |
Major Requirements | ||
Course | Course Name | Credits |
| IT130 | Project Management for IT | 3 |
| IT211 | IT Essentials | 4 |
| IT242 | Principles of Voice and Data Cabling | 3 |
| IT243 | Fiber Optics Installation | 3 |
| IT265 | Computer Networking I | 5 |
| IT266 | Computer Networking II | 5 |
| IT267 | Computer Networking III | 5 |
| IT283 | Network Security + | 3 |
| IT285 | Cybersecurity Operations | 5 |
Total | 36 | |
Computer Networking Electives (Choose 2) | ||
Course | Course Name | Credits |
| CS112 | Introduction to Linux | 3 |
| IT131 | Server Technology | 3 |
| IT292 | Information Technology Practicum | 3 |
Total | 6 | |
Program Total | 61-62 | |
Course Sequence by Semester
Year 1 | |||||
Semester 1 | Semester 2 | ||||
Course # | Course Name | Credits | Course # | Course Name | Credits |
| EN___ | English Composition Requirement | 3-4 | IT130 | Project Management | 3 |
| MA___ | Mathematics Requirements | 3-4 | SI____ | Natural & Physical Sciences | 4 |
| IT242 | Principles of Voice and Data Cabling | 3 | IT283 | Network Security + | 3 |
| IT243 | Fiber Optics Installation | 3 | Elective | 3 | |
| IT211 | IT Essentials | 4 |
| ||
Total | 16-18 |
| Total | 13 | |
Year 2 | |||||
Semester 3 | Semester 4 | ||||
Course # | Course Name | Credits | Course # | Course Name | Credits |
| IT265 | Computer Networking I | 5 | IT267 | Computer Networking III | 5 |
| IT266 | Computer Networking II | 5 | IT285 | Cybersecurity Operations | 5 |
| Humanities & Fine Arts Requirement | 3-4 | Elective – See elective list | 3 | ||
| Literacy for Life | 3 | Social & Behavioral Sciences Requirement | 3 | ||
| Total | 16-17 |
| Total | 16 |
Program Total | 61-62 | ||||
The Associate of Science in Computer Science program will provide opportunities for students to work as programmers who write instructions and translate them into a machine-readable language, as system analysts who design computer systems for processing information, computer operators who monitor and control computer systems and retrieve results, data entry personnel who enter information and instructions into the computers, etc.
The Associate of Science in Computer Science UOG Track will provide the foundational knowledge and hands-on skills to prepare students to further their education at the University of Guam with a goal of earning a Bachelor of Science in Computer Science. Students will learn to design computer systems for processing information; work as programmers who write instructions and translate them into a machine readable language, computer operators who monitor and control computer systems and retrieve results, and data entry personnel who enter information and instructions into the computer.
Program Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs):
Upon successful completion of the AS in Computer Science program, students will be able to:
- Apply concepts and knowledge in the core areas of computer science.
- Distinguish among basic networking systems, operating systems, and database structures.
- Write code using programming languages, to include Java, Python, C++, PHP with MySQL and JavaScript.
Computer Science Track | ||
General Education Requirements | ||
Course | Course Name | Credits |
English (Choose 1) | ||
| EN110 | Freshman Composition | 3 |
| EN110A | Freshman Composition with Instructional Lab | 4 |
Course | Course Name | Credits |
| MA___ | Mathematics Requirement | 3 |
| CO110 | Critical Thinking for Civic Engagement | 3 |
| Social & Behavioral Sciences Requirement | 3 | |
| CO125 | Introduction to Human Communication and Speech | 3 |
| SI___ | Natural & Physical Sciences Requirement | 4 |
Total | 19-20 | |
Major Requirements | ||
Course | Course Name | Credits |
| CS101 | Introduction to Computer Systems and Information Technology | 3 |
| CS104 | Visual Basic Programming | 3 |
| CS112 | Introduction to Linux | 3 |
| CS203 | Systems Analysis and Design | 3 |
| CS204 | C ++ Programming | 3 |
| CS205 | Network Communications | 4 |
| CS206 | Java I | 3 |
| CS211 | JavaScript Programming | 3 |
| CS212 | Python Programming | 3 |
| CS213 | PHP Programming with MySQL | 3 |
| CS266 | Advanced Java | 4 |
| OA211 | Business Communication | 3 |
Computer Science Elective (Choose 1) | ||
| OA210 | Database Management Systems | 3-4 |
| IT211 | IT Essentials | |
| OA101 | Keyboarding and Document Processing | |
Total | 41-42 | |
Program Total | 60-62 | |
Computer Science UOG Track | ||
General Education Requirements | ||
Course | Course Name | Credits |
English (Choose 1) | ||
| EN110 | Freshman Composition | 3 |
| EN110A | Freshman Composition with Instructional Lab | 4 |
Course | Course Name | Credits |
| MA165 OR MA203 | Precalculus OR Calculus | 5 |
| CO110 | Critical Thinking for Civic Engagement | 3 |
| Social & Behavioral Sciences Requirement | 3 | |
| CO125 | Introduction to Human Communication and Speech | 3 |
| SI___ | Natural & Physical Sciences Requirement | 4 |
Total | 21-22 | |
Major Requirements | ||
Course | Course Name | Credits |
| CS101 | Introduction to Computer Systems and Information Technology | 3 |
| CS104 | Visual Basic Programming | 3 |
| CS112 | Introduction to Linux | 3 |
| CS203 | Systems Analysis and Design | 3 |
| CS204 | C ++ Programming | 3 |
| CS205 | Network Communications | 4 |
| CS206 | Java I | 3 |
| CS211 | JavaScript Programming | 3 |
| CS212 | Python Programming | 3 |
| CS213 | PHP Programming with MySQL | 3 |
| CS266 | Advanced Java | 4 |
| EN111 | Writing for Research | 3 |
| OA211 | Business Communication | 3 |
Total | 41 | |
Program Total | 62-63 | |
Associate of Science in Computer Science – Course Sequence by Semester
Year 1 | |||||
Semester 1 | Semester 2 | ||||
Course # | Course Name | Credits | Course # | Course Name | Credits |
| EN___ | English Composition Requirement | 3-4 | CO110 | Critical Thinking for Civic Engagement | 3 |
| MA___ | Mathematics Requirement | 3 | CS212 | Python Programming | 3 |
| CS101 | Introduction to Computer Systems and Information Technology | 3 | CS213 | PHP Programming with MySQL | 3 |
| CS211 | JavaScript Programming | 3 | CS205 | Network Communications | 4 |
| OA101 | Keyboarding and Document Processing | 3 | Social & Behavioral Science requirement | 3 | |
Total | 15-16 |
| Total | 16 | |
Year 2 | |||||
Semester 3 | Semester 4 | ||||
Course # | Course Name | Credits | Course # | Course Name | Credits |
| CS206 | Java I | 3 | CS266 | Advanced Java | 4 |
| CS112 | Introduction to Linux | 3 | OA211 | Business Communications | 3 |
| CS104 | Visual Basic Programming | 3 | Humanities and Fine Arts | 3-4 | |
| CS204 | C++ Programming | 3 | Natural and Physical Sciences | 4 | |
| CS203 | Systems Analysis and Design | 3 |
| ||
| Total | 15 | Total | 14-15 | |
Program Total | 60-62 | ||||
Associate of Science in Computer Science UOG Track – Course Sequence by Semester
Year 1 | |||||
Semester 1 | Semester 2 | ||||
Course # | Course Name | Credits | Course # | Course Name | Credits |
| CS101 | Intro to Computer Systems and Information Technology | 3 | CS104 | Visual Basic Programming | 3 |
| CS211 | JavaScript Programming | 3 | CS212 | Python Programming | 3 |
| MA165 OR MA203 | Precalculus OR Calculus | 5 | CS203 | Systems Analysis and Design | 3 |
| EN110 OR EN110A | Freshman Composition OR Freshman Composition with Instructional Lab | 3-4 | CO110 | Critical Thinking for Civic Engagement | 3 |
| SI___ | Natural & Physical Science | 4 | |||
Total | 14-15 |
| Total | 16 | |
Year 2 | |||||
Semester 3 | Semester 4 | ||||
Course # | Course Name | Credits | Course # | Course Name | Credits |
| CS112 | Introduction to Linux | 3 | CO125 | Introduction to Human Communication and Speech | 3 |
| CS204 | C++ Programming | 3 | CS266 | Advanced Java | 4 |
| CS205 | Network Communications | 4 | EN111 | Writing for Research | 3 |
| CS206 | Java I | 3 | OA210 | Database Management Systems | 3 |
| CS213 | PHP Programming with MySQL | 3 | Social & Behavioral Requirement | 3 | |
Total | 16 | Total | 16 | ||
Program Total | 62-63 | ||||
This program is designed to address training requirements for students seeking employment as police officers, marshals, conservation officers, Guam Customs officers, investigators, corrections officers, forensic computer examiners, forensic lab technicians, and other public safety employees. Students may choose an emphasis in one of four areas of concentration:
- Administration of Criminal Justice
- Law Enforcement Administration
- Forensic Lab Technician
- Forensic Computer Examiner
Program Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs):
Upon successful completion of the AS in Criminal Justice program, students will be able to:
- Identify the legal procedures for gathering information about crimes, criminal procedure, and defendants’ rights.
- Describe the process of the criminal justice system including the duties and responsibilities of the criminal justice professional as it pertains to one of the chosen concentration areas: Administration of Criminal Justice, Law Enforcement Administration, Forensic Lab Technician, or Forensic Computer Examiner.
- Demonstrate the ability to understand the interrelations, ethics, and role expectations of the criminal justice professional in society.
Administration of Criminal Justice Track | ||
General Education Requirements | ||
Course | Course Name | Credits |
English (Choose 1) | ||
| EN110 OR EN110A | Freshman Composition OR Freshman Composition with Instructional Lab | 3-4 |
Natural & Physical Science Requirement (Choose 1) | ||
| SI 103/103L | Introduction to Marine Biology: Theory (3) & Introduction to Marine Biology Laboratory (1) | 4 |
| SI 110/110L | Environmental Biology: Theory (3) & Environmental Biology: Laboratory (1) | |
Course | Course Name | Credits |
| MA110A | Finite Mathematics | 3 |
| CS151 | Windows Applications | 3 |
| HU120 | Pacific Cultures | 3 |
| PS140 | American Government | 3 |
TOTAL | 19 | |
Major Requirements | ||
Course | Course Name | Credits |
| CJ100 | Introduction to Criminal Justice | 3 |
| CJ101 | Juvenile Justice Process | 3 |
| CJ107 | Introduction to Corrections | 3 |
| CJ150 | Criminal Procedure | 3 |
| CJ200 | Criminal Law | 3 |
| CJ204 | Introduction to Criminology | 3 |
| CJ206 | Social Values & the Criminal Justice Process | 3 |
| CJ209 | Concept of Police Operations | 3 |
| CJ292 | Criminal Justice Practicum | 3 |
| PY125 | Interpersonal Relations | 3 |
| SO130 | Introduction to Sociology | 3 |
Electives | ||
Course | Course Name | Credits |
| Related Major Course | 3 | |
| Related Major Course | 3 | |
| Related Major Course | 3 | |
Total | 42 | |
Program Total | 61-62 | |
Course Sequence by Semester – Administration of Criminal Justice Track
Year 1 | |||||
Semester 1 | Semester 2 | ||||
Course # | Course Name | Credits | Course # | Course Name | Credits |
| EN__ | Freshman Composition OR Freshman Composition with Instructional Lab | 3-4 | CJ101 | Juvenile Justice Process | 3 |
| MA110A | Finite Mathematics | 3 | CJ150 | Criminal Procedure | 3 |
| PS125 | Interpersonal Relations | 3 | CJ200 | Criminal Law | 3 |
| CJ100 | Introduction to Criminal Justice | 3 | PS140 | American Government | 3 |
| CJ107 | Introduction to Corrections | 3 | SO130 | Introduction to Sociology | 3 |
Total | 15-16 |
| Total | 15 | |
Year 2 | |||||
Semester 3 | Semester 4 | ||||
Course # | Course Name | Credits | Course # | Course Name | Credits |
| CJ204 | Introduction to Criminology | 3 | CJ292 | Criminal Justice Practicum | 3 |
| CJ206 | Social Values & the Criminal Justice Process | 3 | HU120 | Pacific Cultures | 3 |
| CJ209 | Concept of Police Operations | 3 | Electives | 3 | |
| CS151 | Windows Applications | 3 | Electives | 3 | |
SI103/103L OR SI110/110L | Introduction to Marine Biology: Theory (3) & Introduction to Marine Biology Laboratory (1) OR Environmental Biology: Theory (3) & Environmental Biology: Laboratory (1) | 4 | Electives | 3 | |
Total | 16 | Total | 15 | ||
Program Total | 61-62 | ||||
Law Enforcement Administration Track | ||
General Education Requirements | ||
Course | Course Name | Credits |
English (Choose 1) | ||
| EN110 | Freshman Composition | 3 |
| EN110A | Freshman Composition with Instructional Lab | 4 |
Course | Course Name | Credits |
| MA110A | Finite Mathematics | 3 |
| HU120 | Pacific Cultures | 3 |
| PS140 | American Government | 3 |
| CS151 | Windows Applications | 3 |
Natural & Physical Science Requirement (Choose 1) | ||
| SI 103/103L | Introduction to Marine Biology: Theory (3) & Introduction to Marine Biology: Laboratory (1) | 4 |
| SI 110/110L | Environmental Biology: Theory (3) & Environmental Biology Laboratory (1) | |
Total | 19 | |
Major Requirements | ||
Course | Course Name | Credits |
| CJ100 | Introduction to Criminal Justice | 3 |
| CJ150 | Criminal Procedure | 3 |
| CJ200 | Criminal Law | 3 |
| CJ205 | Report Writing for Law Enforcement | 3 |
| CJ206 | Social Values & the Criminal Justice Process | 3 |
| CJ209 | Concept of Police Operations | 3 |
| CJ225 | Criminal Investigation | 3 |
| CJ250 | Police Organizational Theory | 3 |
| CJ292 | Criminal Justice Practicum | 3 |
| PY125 | Interpersonal Relations | 3 |
| SO130 | Introduction to Sociology | 3 |
Electives | ||
Course | Course Name | Credits |
| Related Major Course | 3 | |
| Related Major Course | 3 | |
| Related Major Course | 3 | |
Total | 42 | |
Program Total | 61-62 | |
Course Sequence by Semester – Law Enforcement Administration Track
Year 1 | |||||
Semester 1 | Semester 2 | ||||
Course # | Course Name | Credits | Course # | Course Name | Credits |
| EN110 OR EN110A | Freshman Composition OR Freshman Composition with Instructional Lab | 3-4 | CJ150 | Criminal Procedure | 3 |
| MA110A | Finite Mathematics | 3 | CJ200 | Criminal Law | 3 |
| PY125 | Interpersonal Relations | 3 | CJ225 | Criminal Investigation | 3 |
| CJ100 | Introduction to Criminal Justice | 3 | PS140 | American Government | 3 |
| CJ205 | Report Writing for Law Enforcement | 3 | SO130 | Introduction to Sociology | 3 |
Total | 15-16 |
| Total | 15 | |
Year 2 | |||||
Semester 3 | Semester 4 | ||||
Course # | Course Name | Credits | Course # | Course Name | Credits |
| CJ206 | Social Values & The Criminal Justice Process | 3 | CJ292 | Criminal Justice Practicum | 3 |
| CJ209 | Concept of Police Operations | 3 | HU120 | Pacific Cultures | 3 |
| CJ250 | Police Organizational Theory | 3 | Electives | 3 | |
| CS151 | Windows Applications | 3 | Electives | 3 | |
SI103/103L OR SI110/110L | Introduction to Marine Biology: Theory (3) & Introduction to Marine Biology Laboratory (1) OR Environmental Biology: Theory (3) & Environmental Biology: Laboratory (1) | 4 | Electives | 3 | |
| Total | 16 |
| Total | 15 |
Program Total | 61-62 | ||||
Forensic Lab Technician Track | ||
General Education Requirements | ||
Course | Course Name | Credits |
English | ||
| EN110 | Freshman Composition | 3 |
Course | Course Name | Credits |
| MA115 | Fundamentals of College Algebra | 3 |
| SI131/SI131L | Human Anatomy and Physiology I: Theory & Human Anatomy & Physiology I: Laboratory | 4 |
| PS140 | American Government | 3 |
| HU120 | Pacific Cultures | 3 |
| CS151 | Windows Applications | 3 |
Total | 19 | |
Major Requirements | ||
Course | Course Name | Credits |
| PY125 | Interpersonal Relations | 3 |
| SO130 | Introduction to Sociology | 3 |
| CJ100 | Introduction to Criminal Justice | 3 |
| CJ122 | Introduction to Forensic Science | 4 |
| CJ150 | Criminal Procedure | 3 |
| CJ200 | Criminal Law | 3 |
| CJ206 | Social Values & the Criminal Justice Process | 3 |
| CJ225 | Criminal Investigation | 3 |
| CJ292 | Criminal Justice Practicum | 3 |
| MA161A & MA161B | College Algebra & Trigonometry I & College Algebra & Trigonometry II (Students can opt to take MA161A & MA161B OR MA165) | 6 OR |
| MA165 | Precalculus (Students can opt to take MA161A & MA161B OR MA165) | 5 |
| SI141 | Applied Physics I | 4 |
| SI101/101L | Introduction to Chemistry: Theory (3) & Introduction to Chemistry: Laboratory (1) | 4 |
| SI150/150L | Introduction to Microbiology: Theory (3) & Introduction to Microbiology: Laboratory (1) | 4 |
Total | 45-46 | |
Program Total | 64-65 | |
*MA161A College Algebra & Trigonometry I should be taken summer after year 1
Course Sequence by Semester – Forensic Lab Technician Track
Year 1 | |||||
Semester 1 | Semester 2 | ||||
Course # | Course Name | Credits | Course # | Course Name | Credits |
| EN110 | Freshman Composition | 3 | CJ122 | Introduction to Forensic Science | 4 |
| MA115 | Fundamentals of College Algebra | 3 | CJ150 | Criminal Procedure | 3 |
| PY125 | Interpersonal Relations | 3 | CJ200 | Criminal Law | 3 |
| CJ100 | Introduction to Criminal Justice | 3 | PS140 | American Government | 3 |
| HU120 | Pacific Cultures | 3 | SO130 | Introduction to Sociology | 3 |
Total | 15 |
| Total | 16 | |
Year 2 | |||||
Summer |
| ||||
| MA161A & MA161B OR MA165 | College Algebra & Trigonometry I OR Pre-Calculus | 5-6 | |||
Total | 5-6 |
| |||
Semester 3 | Semester 4 | ||||
Course # | Course Name | Credits | Course # | Course Name | Credits |
| CJ206 | Social Values & The Criminal Justice Process | 3 | CJ292 | Criminal Justice Practicum | 3 |
| SI131/SI131L | Human Anatomy & Physiology I: Theory & Human Anatomy & Physiology I: Laboratory | 4 | SI141 | Applied Physics I | 4 |
| CS151 | Windows Applications | 3 | SI101/101L | Introduction to Chemistry: Theory/Introduction to Chemistry: Laboratory | 4 |
| CJ225 | Criminal Investigation | 3 | SI150/150L | Introduction to Microbiology: Theory/Introduction to Microbiology: Laboratory | 4 |
| Total | 13 |
| Total | 15 |
Program Total | 64-65 | ||||
Forensic Computer Examiner Track | ||
General Education Requirements | ||
Course | Course Name | Credits |
English | ||
| EN110 | Freshman Composition | 3 |
Course | Course Name | Credits |
| MA110A | Finite Mathematics | 3 |
| SI110/SI110L OR SI103/SI103L | Environmental Biology: Theory (3) & Environmental Biology: Laboratory (1) OR Introduction to Marine Biology: Theory (3) and Introduction to Marine Biology: Laboratory (1) | 4 |
| SI141 | Applied Physics I | 4 |
| HU120 | Pacific Cultures | 3 |
| PS140 | American Government | 3 |
| CS151 | Windows Applications | 3 |
Total | 23 | |
Major Requirements | ||
Course | Course Name | Credits |
| PY125 | Interpersonal Relations | 3 |
| SO130 | Introduction to Sociology | 3 |
| CJ100 | Introduction to Criminal Justice | 3 |
| CJ122 | Introduction to Forensic Science | 4 |
| CJ150 | Criminal Procedure | 3 |
| CJ200 | Criminal Law | 3 |
| CJ205 | Report Writing for Law Enforcement | 3 |
| CJ206 | Social Values & the Criminal Justice Process | 3 |
| CJ225 | Criminal Investigation | 3 |
| CJ292 | Criminal Justice Practicum | 3 |
| IT211 | IT Essentials | 4 |
| CS101 | Introduction to Computer Systems & Information Technology | 3 |
Approved Computer Science Courses | ||
Course | Course Name | Credits |
| CS___ | Computer Science Course 1 | 3 |
| CS___ | Computer Science Course 2 | 3 |
| CS___ | Computer Science Course 3 | 3 |
Total | 47 | |
Program Total | 70 | |
Course Sequence by Semester – Forensic Computer Examiner Track
Year 1 | |||||
Semester 1 | Semester 2 | ||||
Course # | Course Name | Credits | Course # | Course Name | Credits |
| EN__ | Freshman Composition Requirement | 3 | CJ122 | Introduction to Forensic Science | 4 |
| CJ205 | Report Writing for Law Enforcement | 3 | CJ150 | Criminal Procedure | 3 |
| CS101 | Introduction to Computer Systems & Information Technology | 3 | CJ200 | Criminal Law | 3 |
| CJ100 | Introduction to Criminal Justice | 3 | MA110A | Finite Mathematics | 3 |
| HU120 | Pacific Cultures | 3 | PY125 | Interpersonal Relations | 3 |
Total | 15 | Total | 16 | ||
Year 2 | |||||
Summer | |||||
| SI141 | Applied Physics | 4 | |||
| CJ225 | Criminal Investigation | 3 | |||
Total | 7 |
|
| ||
Semester 3 | Semester 4 | ||||
Course # | Course Name | Credits | Course # | Course Name | Credits |
| CS_____ | Computer Science Course | 3 | CJ292 | Criminal Justice Practicum | 3 |
| SI110/SI110L OR SI103/SI103L | Environmental Biology: Theory (3) & Environmental Biology: Laboratory (1) OR Introduction to Marine Biology: Theory (3) and Introduction to Marine Biology: Laboratory (1) | 4 | CJ206 | Social Values & the Criminal Justice Process | 3 |
| SO130 | Introduction to Sociology | 3 | CS_____ | Computer Science Course | 3 |
| CS151 | Windows Applications | 3 | IT211 | IT Essentials I | 4 |
| CS_____ | Computer Science Course | 3 | PS140 | American Government | 3 |
| Total | 16 |
| Total | 16 |
Program Total | 70 | ||||
Early childhood pertains to children age eight and below. Early childhood educators work in Head Start programs, childcare centers, family home care programs, elementary schools, social services programs, and health care services. These professionals plan and implement appropriate experiences for young children in areas such as language, health, movement, creativity, cognitive, self-concept and social behavior. They also supervise children’s activities, care for their needs, keep records of their progress, and confer with parents and other professionals.
The Associate of Science in Early Childhood Education is closely aligned with national standards and meets the education requirements for Basic Educator Preschool Certification from the Guam Commission for Educator Certification. The National Association for the Education of Young Children encourages a minimal educational level of an associate degree in early childhood education for early childhood program teachers. A grade of “C” or higher must be achieved for the Program’s “Major” courses.
Program Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs):
Upon successful completion of the AS in Early Childhood, students will be able to:
- Model appropriate practices for children, professionalism, and demonstrate ethical conduct based on guidelines from the National Association for the Education of Young Children (NAEYC).
- Implement various developmentally and age-appropriate teaching, assessment and guidance strategies needed to work with young children from birth to age eight.
- Reflect on practices, pedagogy and resources used in early childhood settings that serve children ages birth through eight years.
Early Childhood Education | ||
General Education Requirements | ||
Course | Course Name | Credits |
English (Choose 1) | ||
EN110 | Freshman Composition | 3 |
EN110A | Freshman Composition with Instructional Lab | 4 |
Course | Mathematics (Choose One) | Credits |
MA110A | Finite Mathematics | 3 |
MA115 | Fundamentals of College Algebra | 3 |
MA161A | College Algebra & Trigonometry I | 3 |
Course | Literacy for Life (Choose One) | Credits |
CO110 | Critical Thinking for Civic Engagement | 3 |
CS151 | Windows Applications | 3 |
CS152 | Macintosh Applications | 3 |
Course | Humanities & Fine Arts (Choose One) | Credits |
ASL100 | American Sign Language I | 4 |
CH110 | CHamoru I | 4 |
CO125 | Introduction to Human Communication and Speech | 3 |
EN210 | Introduction to Literature | 3 |
HI121 | History of World Civilization I | 3 |
HI122 | History of World Civilization II | 3 |
HI176 | Guam History | 3 |
HU120 | Pacific Cultures | 3 |
HU220 | Guam Cultures and Legends | 3 |
JA110 | Japanese I | 4 |
KE110 | Korean I | 4 |
PI101 | Introduction to Philosophy | 3 |
TH101 | Introduction to Theatre | 3 |
VC101 | Introduction to Visual Communications | 3 |
Course | Natural & Physical Sciences (all options are 4 credits): (Choose One) | Credits |
SI101/101L | Introduction to Chemistry & Introduction to Chemistry Laboratory | 4 |
SI103/103L | Introduction to Marine Biology & Introduction to Marine Biology Laboratory | 4 |
SI105/105L | Introduction to Physical Geology & Introduction to Physical Geology Laboratory | 4 |
SI110/110L | Environmental Biology: Theory & Environmental Biology Laboratory | 4 |
SI131/131L | Human anatomy & Physiology I; Theory & Human Anatomy & Physiology I Laboratory | 4 |
Course | Social & Behavioral Sciences: (Choose One) | Credits |
EC110 | Principles of Economics | 3 |
PS140 | American Government | 3 |
PY100 | Personal Adjustment | 3 |
PY120 | General Psychology | 3 |
PY125 | Interpersonal Relations | 3 |
SO130 | Introduction to Sociology | 3 |
WG101 | Introduction to Women and Gender Studies | 3 |
List Major Requirements (alpha/number/title/credits) this includes any General Education courses in addition to what is required under General Education Requirements. Include total number of credits:
CD110 OR ED150 | Introduction to Early Childhood Education OR Introduction to Teaching | 3 |
CD140 | Nutrition and Physical Health | 3 |
CD180 | Language Arts Development in Early Childhood | 3 |
CD221 OR ED220 | Child Growth & Development OR Human Growth & Development | 3 |
CD240 | Cognitive & Creative Development in Early Childhood | 3 |
CD260 | Social & Emotional Development | 3 |
CD292 OR CD293 | Early Childhood Education Practicum (3) OR Early Childhood CDA Practicum (12) | 3-12 |
ED231 | Introduction to Exceptionalities | 3 |
ED265 | Culture and Education on Guam | 3 |
List Elective Courses (or provide category, optional) include total: (5-14) **Important Note: Students who choose CD293 need (5) elective credits; students who choose CD292 need (14) elective credits.
ASL100 | American Sign Language I | 4 |
ASL110 | American Sign Language II | 4 |
ASL120 | American Sign Language III | 4 |
ASL130 | American Sign Language IV | 4 |
CD285 | Childcare Management | 3 |
CH110 | CHamoru I | 4 |
CH111 | CHamoru II | 4 |
CH200 | Immersion Method for CHamoru Language Teaching I | 3 |
CH220 | CHamoru Composition | 3 |
ED150 | Introduction to Teaching | 3 |
ED180A | Educational Methods I | 3 |
ED220 | Human Growth and Development | 3 |
ED292 | Education Practicum | 3 |
CTE299A | PRAXIS I Review Part A | 2 |
CTE299B | PRAXIS I Review Part B | 1 |
HL135 | Heartsaver First Aid CPR AED | 1 |
Program Total | 61-62 | |
Course Sequence by Semester - Early Childhood Education
Year 1 | |||||
Semester 1 | Semester 2 | ||||
Course # | Course Name | Credits | Course # | Course Name | Credits |
| EN110 OR EN111 | Freshman Composition OR Writing for Research | 3 | CD110 OR ED150 | Introduction to Early Childhood Education OR Introduction to Teaching | 3 |
MA110A OR MA115 OR MA161A | Finite Mathematics OR Fundamentals of College Algebra OR College Algebra & Trigonometry I | 3 | CD221 OR ED220 | Child Growth & Development OR Human Growth and Development | 3 |
| Humanities or Fine Arts | 3-4 | CD140 | Nutrition and Physical Health | 3 | |
| Elective | 3-4 | Social/Behavioral Science | 3 | ||
Total | 12-14 | Total | 12 | ||
Year 2 | |||||
Semester 3 | Semester 4 | ||||
Course # | Course Name | Credits | Course # | Course Name | Credits |
| CD240 | Cognitive & Creative Development in Early Childhood | 3 | ED265 | Culture and Education in Guam | 3 |
| CD180 | Language Arts Development in Early Childhood | 3 | ED231 | Introduction to Exceptionalities | 3 |
| Literacy for Life | 3 | CD260 | Social and Emotional Development | 3 | |
| Science with Lab | 4 | Elective (Only for students who are taking CD292) | 3-4 | ||
| Elective | 3-4 | Elective (Only for students who are taking CD292) | 3-4 | ||
| Total | 16-17 |
| Total | 15-17 |
Year 3 | |||||
Semester 5 |
| ||||
Course # | Course Name | Credits |
|
|
|
| CD292 OR CD293 | Early Childhood Education Practicum OR Early Childhood CDA Practicum | 3 OR 12 | |||
| Elective (Only for students who are taking CD292) | 3 | ||||
| Total | 6-12 |
|
|
|
PROGRAM TOTAL | 61-62 | ||||
Emergency Management graduates will be able to apply basic emergency management skills in the event of natural and manmade disasters. Graduates will be able to implement the four major areas of emergency, namely, mitigation, preparation, response, and recovery. The Emergency Management program utilizes the Emergency Management Institute’s Independent Study (IS) courses to prepare graduates to apply leadership skills, to communicate effectively, to solve problems, to plan, to work as a team, to operate within the legal system and governmental framework for emergency management, to analyze risks and hazards, and to manage resources efficiently.
The Emergency Management program’s major requirements are adopted and derived from EMI’s Independent Study program. GCC’s Emergency Management program will adhere to the latest IS offerings to ensure that students learn what is relevant and most up-to-date information and skills.
Approved college credits must be an approved EMI course and subject to the approval by the academic advisor or department chair. As such, Certificate and/or Associate degree students in EM must obtain prior approval by EM academic or department chair.
Program Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs):
Upon successful completion of the AS in Emergency Management program, students will be able to:
- Coordinate functions between local and federal law enforcement in response to disaster events.
- Analyze the functions of the Emergency Operations Center and National Incident Management System.
- Evaluate hazards and risks of emergency situations.
- Apply critical thinking skills during table top exercises.
General Education Requirements | ||
Course | Course Name | Credits |
English (Choose 1) | ||
| EN110 OR EN110A | Freshman Composition OR Freshman Composition with Instructional Lab | 3-4 |
| MA____ | Mathematics Requirement | 3 |
| Literacy for Life Requirement | 3 | |
| Humanities & Fine Arts Requirement | 3-4 | |
| Social & Behavioral Sciences Requirement | 3 | |
| Natural & Physical Sciences Requirement | 4 | |
Total | 19-21 | |
Major Requirements | ||
Course | Course Name | Credits |
| EMI approved courses | 29 | |
| CJ102 | First Responder | 3 |
| CJ104 | Dynamics of Substance Abuse | 3 |
| CJ206 | Social Values & the Criminal Justice Process | 3 |
| CJ292 | Criminal Justice Practicum | 3 |
Total | 41 | |
Program Total | 60-62 | |
Course Sequence by Semester
Year 1 | |||||
Semester 1 | Semester 2 | ||||
Course # | Course Name | Credits | Course # | Course Name | Credits |
EN110 OR EN110A | English Composition Requirement OR Freshman Composition with Instructional Lab | 3-4 | Humanities & Fine Arts Requirement | 3-4 | |
MA____ | Mathematics Requirement | 3 | Social Science Requirement | 3 | |
CJ102 | First Responder | 3 | CJ104 | Dynamics of Substance Abuse | 3 |
Total | 9-10 |
| Total | 9-10 | |
Year 2 | |||||
Semester 3 | Semester 4 | ||||
Course # | Course Name | Credits | Course # | Course Name | Credits |
| Natural & Physical Science Requirement | 4 | CJ292 | Criminal Justice Practicum | 3 | |
| Literacy for Life | 3 | EMI approved courses | 29 | ||
CJ206 | Social Values & the Criminal Justice Process | 3 |
| ||
Total | 10 | Total | 32 | ||
PROGRAM TOTAL | 60-62 | ||||
The Foodservice Management Program aligns with the National Restaurant Association (NRA) ManageFirst - a curriculum that is framed around a set of knowledge and skills identified by the restaurant industry as important for a successful career in the foodservice industry. By completing the NRA required 800-hour work experience, graduates have the option to earn the NRA ManageFirst Professional (MFP) or the Foodservice Management Professional (FMP) credential.
Program Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs):
Upon successful completion of the AS in Foodservice Management program, students will be able to:
- Perform foodservice manager tasks within a complex work environment.
- Manage resources to maintain fiscal responsibility as it relates to the foodservice industry.
- Model a customer-oriented work ethic.
General Education Requirements | ||
Course | Course Name | Credits |
EN___ | English Composition Requirement | 3-4 |
FSM145 | Culinary and Business Math | 3 |
| Literacy for Life Requirement | 3 |
CO125 | Introduction to Human Communication and Speech | 3 |
SI___ | Natural & Physical Sciences Requirement | 4 |
PY125 | Interpersonal Relations | 3 |
Total | 19-20 | |
Major Requirements | ||
Course | Course Name | Credits |
FSM100 | Introduction to the Foodservice Profession | 2 |
FSM110 | Professional Dining Room Service: Theory | 2 |
FSM110L | Professional Dining Room Service: Laboratory | 1 |
FSM115 | Purchasing and Receiving | 2 |
FSM120 | Food Safety & Sanitation | 2 |
FSM130 | Professional Bar and Alcohol Management | 3 |
FSM154 | Foodservice Nutrition | 3 |
FSM155 | Foodservice Accounting | 3 |
FSM222 | Foodservice Cost | 3 |
FSM240 | Menu Planning | 3 |
FSM254 | Foodservice Marketing | 3 |
FSM270 | Foodservice Human Resource Management | 3 |
FSM292 | Foodservice Practicum | 4 |
FSM299 | Foodservice Management Capstone | 3 |
CUL140 | Culinary Foundation I | 2 |
CUL160 | Culinary Foundations II | 2 |
Total | 41 | |
Program Total | 60-61 | |
Course Sequence by Semester
Year 1 | |||||
Semester 1 | Semester 2 | ||||
Course # | Course Name | Credits | Course # | Course Name | Credits |
EN___ | English Composition Requirement | 3-4 | FSM145 | Culinary and Business Math | 3 |
PY125 | Interpersonal Relations | 3 |
| Natural & Physical Science Requirement | 4 |
FSM100 | Introduction to the Foodservice Profession | 2 | FSM115 | Purchasing and Receiving | 2 |
FSM110 | Professional Dining Room Service: Theory | 2 | FSM154 | Foodservice Nutrition | 3 |
FSM110L | Professional Dining Room Service: Laboratory | 1 | FSM155 | Foodservice Accounting | 3 |
FSM120 | Food Safety & Sanitation | 2 |
|
| |
FSM130 | Professional Bar and Alcohol Management | 3 |
|
| |
Total | 16-17 |
| Total | 15 | |
Year 2 | |||||
Semester 3 | Semester 4 | ||||
Course # | Course Name | Credits | Course # | Course Name | Credits |
CO125 | Introduction to Human Communication and Speech | 3 | Literacy for Life | 3 | |
FSM222 | Foodservice Cost | 3 | FSM254 | Foodservice Marketing | 3 |
FSM240 | Menu Planning | 3 | CUL160 | Culinary Foundations II | 2 |
FSM270 | Foodservice Human Resource Management | 3 | FSM292 | Foodservice Practicum | 4 |
CUL140 | Culinary Foundation I | 2 | FSM299 | Foodservice Management Capstone | 3 |
Total | 14 | Total | 15 | ||
PROGRAM TOTAL | 60-61 | ||||
The Associate of Science in Human Services program provides a multi-disciplinary, culturally diverse curriculum as the foundation for entry-level career pathway in the human services field. The ASHS program prepares students with the knowledge and skills required for employment at entry level paraprofessional positions in human services, assisting social workers and other allied health professionals like counselors, psychologists, nurses and medical doctors.
Program Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs):
Upon successful completion of the AS in Human Services program, students will be able to:
- Explain and apply human service practice concepts and principles within a multidisciplinary, culturally diverse setting.
- Demonstrate entry level human services skills in human service settings.
- Describe and differentiate between personal values, professional values, and ethical responsibility pertaining to the human service worker.
General Education Requirements | ||
Course | Course Name | Credits |
English (Choose 1) | ||
| EN110A | Freshman Composition with Instructional Lab | 4 |
| EN110 | Freshman Composition | 3 |
Course | Course Name | Credits |
| MA110A | Finite Mathematics | 3 |
| SO130 | Introduction to Sociology | 3 |
| CS151 | Windows Applications | 3 |
| SI103/SI103L OR SI110/110L OR SI131/131L | Introduction to Marine Biology: Theory/ Introduction to Marine Biology: Laboratory OR Environmental Biology: Theory/ Environmental Biology: Laboratory OR Human Anatomy & Physiology I: Theory/ Human Anatomy & Physiology I: Laboratory | 4 |
Choose One | ||
| ASL100 | American Sign Language I | 4 |
| CH110 | CHamoru I | |
Total | 20-21 | |
Major Requirements | ||
Course | Course Name | Credits |
| HM110 | Introduction to Community Services | 3 |
| HM150 | Diversity in Human Services | 3 |
| HM180 | Human Services Practicum Orientation | 3 |
| HM201 | Social Welfare & Development: Global Challenges | 3 |
| HM205 | Foundations of Case Management | 3 |
| HM225 | Substance Misuse Prevention: Program Planning and Implementation | 3 |
| HM250 | Ethics and Values in Human Services | 3 |
| HM292 | Human Services Practicum | 3 |
| CD221 OR ED220 | Child Growth & Development OR Human Growth and Development | 3 |
| PY120 | General Psychology | 3 |
Electives (Complete 12 credits from the list below) | ||
Course | Course Name | Credits |
AC280 | Personal Finance | 3 |
CJ100 | Introduction to Criminal Justice | 3 |
CJ104 | Dynamics of Substance Abuse | 3 |
CO110 | Critical Thinking for Civic Engagement | 3 |
CO125 | Introduction to Human Communication and Speech | 3 |
EC110 | Principles of Economics | 3 |
VC101 | Introduction to Visual Communications | 3 |
TH101 | Introduction to Theatre | 3 |
EN111 | Writing for Research | 3 |
EN194 | Technical Communication | 3 |
MA151 | Introductory Statistics | 3 |
PY100 | Personal Adjustment | 3 |
PY125 | Interpersonal Relations | 3 |
HU120 | Pacific Cultures | 3 |
Total | 42 | |
Program Total | 62-63 | |
Course Sequence by Semester
Year 1 | |||||
Semester 1 | Semester 2 | ||||
Course # | Course Name | Credits | Course # | Course Name | Credits |
EN___ | English Composition Requirement | 3-4 | CS151 | Windows Applications | 3 |
MA110A | Finite Mathematics | 3 | PY120 | General Psychology | 3 |
CD221 OR ED220 | Child Growth & Development OR Human Growth and Development | 3 | SI103/SI103L OR SI110/110L OR SI131/131L | Introduction to Marine Biology: Theory/Introduction to Marine Biology: Laboratory OR Environmental Biology: Theory/Environmental Biology: Laboratory OR Human Anatomy & Physiology I: Theory/ Human Anatomy & Physiology I: Laboratory | 4 |
SO130 | Introduction to Sociology | 3 | HM201 | Social Welfare & Development: Global Challenges | 3 |
HM110 | Introduction to Community Services | 3 |
| Electives | 3 |
Total | 15-16 |
| Total | 16 | |
Year 2 | |||||
Semester 3 | Semester 4 | ||||
Course # | Course Name | Credits | Course # | Course Name | Credits |
HM150 | Diversity in Human Services | 3 | HM225 | Substance Misuse Prevention: Program Planning and Implementation | 3 |
HM180 | Human Services Practicum Orientation | 3 | HM250 | Ethics in Human Services | 3 |
ASL100 OR CH110 | American Sign Language I OR CHamoru I | 4 | HM292 | Human Services Practicum | 3 |
HM205 | Foundations of Case Management | 3 |
| Elective | 3 |
| Elective | 3 |
| Elective | 3 |
| Total | 16 |
| Total | 15 |
PROGRAM TOTAL | 62-63 | ||||
This program develops students' leadership capacity in hotel operational departments, emphasizing customer service, communication, problem solving, and organizational skills. Other key areas of focus include rooms division; Meetings, Incentives, Conventions, Exhibitions (MICE); human resources; marketing; international hotels; and hospitality technology in hotels. The program includes practicum for hands-on experience, and world language courses such as Korean or Japanese to enhance cultural competencies for success in the international hospitality sector.
Note: Effective Academic Year 2022-2023, the International Hotel Management Program is now a Distance Education Program. All the courses listed under the “Major Requirements” for this program are offered online.
Program Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs):
Upon successful completion of the AS in International Hotel Management program, students will be able to:
- Display various supervisory skills within the hospitality industry.
- Exhibit applicable customer service and hotel operations skills based on the situation.
- Evaluate the importance of communications skills within the hotel management.
General Education Requirements | ||
Course | Course Name | Credits |
EN___ | English Requirement | 3 |
| Social & Behavioral Sciences Requirement | 3 |
MA___ | Mathematics Requirement | 3-4 |
| Literacy for Life Requirement | 3 |
KE110, KE111, JA110 OR JA111 | Korean I, Korean II, Japanese I, OR Japanese II | 4 |
SI___ | Natural & Physical Sciences Requirement | 4 |
Total | 20-21 | |
Major Requirements | ||
Course | Course Name | Credits |
HS150 | Welcome to Hospitality | 3 |
HS152 | Customer Service | 3 |
HS155 | Basic Hotel and Restaurant Accounting OR AC211 Accounting Principles I | 3-4 |
HS158 | Introduction to MICE | 3 |
HS160 | Hospitality Supervision | 3 |
HS211 | Managing Front Office Operations | 3 |
HS215 | Managing Housekeeping Operations | 3 |
HS216 | Human Resources Management | 3 |
HS254 | Hospitality and Travel Marketing | 3 |
HS266 | International Hotels: Development & Management | 3 |
HS268 | Managing Technology in the Hospitality Industry | 3 |
HS292 | Hospitality and Tourism Practicum | 3 |
Choose One | ||
KE110 | Korean I | 4 |
KE111 | Korean II | |
JA110 | Japanese I | |
JA111 | Japanese II | |
Total | 40-41 | |
Program Total | 60-62 | |
Course Sequence by Semester
Year 1 | |||||
Semester 1 | Semester 2 | ||||
Course # | Course Name | Credits | Course # | Course Name | Credits |
EN___ | English Composition Requirement | 3-4 | MA___ | Mathematics Requirement | 3 |
| Social & Behavioral Requirement | 3 | KE110, KE111, JA110 OR JA111 | Korean I, Korean II, Japanese I, OR Japanese II | 4 |
HS150 | Welcome to Hospitality | 3 | HS158 | Introduction to MICE | 3 |
HS152 | Customer Service | 3 | HS160 | Hospitality Supervision | 3 |
| Computer Literacy Requirement | 3 | HS211 | Managing Front Office Operations | 3 |
Total | 15-16 |
| Total | 16 | |
Year 2 | |||||
Semester 3 | Semester 4 | ||||
Course # | Course Name | Credits | Course # | Course Name | Credits |
KE110, KE111, JA110 OR JA111 | Korean I, Korean II, Japanese I, OR Japanese II | 4 |
| Natural & Physical Sciences Requirement | 4 |
HS215 | Managing Housekeeping Operations | 3 | HS254 | Hospitality and Travel Marketing | 3 |
HS216 | Human Resources Management | 3 | HS266 | International Hotels: Development & Management | 3 |
HS155 OR AC211 | Basic Hotel and Restaurant Accounting OR Accounting Principles I | 3-4 | HS268 | Managing Technology in the Hospitality Industry | 3 |
| HS292 | Hospitality and Tourism Practicum | 3 | ||
| Total | 13-14 |
| Total | 16 |
PROGRAM TOTAL | 60-62 | ||||
The Associate of Science Degree in Marketing provides students with the knowledge and skills required to obtain career-sustaining employment in a marketing profession. Among the many career opportunities in marketing are account executive, buyer, merchandiser, brand manager, retail supervisor, advertising assistant, market researcher, and social media marketing coordinator. The marketing program will equip students with the experience and technical skills necessary for rapid progression into mid-management positions.
Program Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs):
Upon successful completion of the AS in Marketing program, students will be able to:
- Assess which marketing communication platforms will most effectively meet the needs of the marketplace.
- Design a strategic marketing plan for a new or existing business.
- Apply technical skills required to obtain career-sustaining marketing positions.
General Education Requirements | ||
Course | ENGLISH REQUIREMENT (Choose One) | Credits |
EN110 | Fresh Composition | 3 |
EN110A | Freshman Composition with Instructional Lab | 4 |
EN111 | Writing for Research | 3 |
Course Name | ||
MA110A | Finite Mathematics or higher | 3 |
CS152 | Macintosh Applications | 3 |
VC101 | Introduction to Visual Communications | 3 |
SI___ | Natural & Physical Sciences Requirement | 4 |
Social & Behavioral Science (Choose One) | ||
SO130 | Introduction to Sociology | 3 |
PY120 | General Psychology | |
PY125 | Interpersonal Relations | |
Total | 19-20 | |
Major Requirements | ||
Course | Course Name | Credits |
MK123 | Principles of Marketing | 3 |
MK124 | Selling | 3 |
MK125 | Social Media Marketing | 3 |
MK205 | Entrepreneurship | 3 |
MK206 | Retailing | 3 |
MK208 | International Marketing | 3 |
MK224 | Advertising | 3 |
MK292 | Marketing Practicum | 3 |
VC125 | Digital Graphics: Raster | 3 |
VC126 | Digital Graphics: Vector | 3 |
VC128 | Design Principles and Elements | 3 |
Course | Elective Courses (Choose 3) | Credits |
OA211 | Business Communication | 3 |
SM205 | Purchasing | 3 |
SM220 | Management Skill Development | 3 |
VC211 | Design Studio I | 3 |
VC212 | Design Studio II | 3 |
Total | 42 | |
Program Total | 61-62 | |
Course Sequence by Semester
Year 1 | |||||
Semester 1 | Semester 2 | ||||
Course # | Course Name | Credits | Course # | Course Name | Credits |
EN110, EN110A, OR EN111 | Freshman Composition, Freshman Composition with Instructional Lab OR Writing for Research | 3-4 | MK124 | Selling | 3 |
MK123 | Principles of Marketing | 3 | MK206 | Retailing | 3 |
CS152 | Macintosh Applications | 3 | MA110A | Finite Mathematics | 3 |
VC125 | Digital Graphics: Raster | 3 | VC101 | Introduction to Visual Communications | 3 |
VC126 | Digital Graphics: Vector | 3 | VC128 | Design Principles and Elements | 3 |
Total | 15-16 |
| Total | 15 | |
Year 2 | |||||
Semester 3 | Semester 4 | ||||
Course # | Course Name | Credits | Course # | Course Name | Credits |
MK125 | Social Media Marketing | 3 | PY120 OR PY125 OR SO130 | General Psychology OR Interpersonal Relations OR Introduction to Sociology | 3 |
MK208 | International Marketing | 3 |
| Elective | 3 |
MK224 | Advertising | 3 |
| Elective | 3 |
| Elective | 3 | MK205 | Entrepreneurship | 3 |
| Natural & Physical Science Requirement | 4 | MK292 | Marketing Practicum | 3 |
| Total | 16 |
| Total | 15 |
PROGRAM TOTAL | 61-62 | ||||
Medical Assistants are the only allied health professionals specifically trained to work in ambulatory settings, such as physicians’ offices, clinics, and group practices. These multi-skilled personnel can perform administrative and clinical procedures. Physicians value this unique versatility more and more, as managed care necessitates the need to contain costs and manage human resources efficiently. Medical Assistants are trained allied health professionals who work primarily in physicians’ offices, outpatient clinics, but also in hospitals, and other healthcare facilities. Medical Assistants are trained to perform clinical back office procedures and administrative tasks. In contrast to most other allied health professionals who work in inpatient hospital settings, Medical Assistants, work primarily in outpatient clinics under the direct supervision of a physician. One portion of his or her training that concentrates on administrative medical assisting provides suitable background for employment in health maintenance organizations, home health care organizations, and nursing homes. Their training as clinical medical assistants creates a well-rounded Medical Assistant that can perform a variety of tasks both administrative and clinical. The most common task performed by the medical assistant is recording patient history and personal information, measuring vital signs (such as blood pressure), helping the physician with patient examinations, giving patients injections or medications as directed by the physician, scheduling patient appointments, drawing and preparing blood samples for laboratory tests, and entering patient information into medical records. Once a student has successfully completed the Medical Assisting Program, he or she will be prepared to take the Registered Medical Assistant (RMA) national certification examination through American Medical Technologists (AMT). The Guam Community College is an affiliated partner with the American Medical Technologist (AMT).
10700 West Higgins Rd, Suite 150
Rosemont, IL 60018
Phone: 847.823.5169
Fax: 847.823.0458
With the exception of enrollment in MS101 Introduction to Medical Assisting, admission to the Medical Assisting program is required before enrollment in any Medical Assisting technical requirement course. Admission to the Medical Assisting program includes:
- Advisement from Allied Health faculty.
- Completion of English and mathematics placement tests with minimum scores or completion of English and mathematics development courses and attainment of passing scores.
- Health Clearance, which includes physical immunization (PPD, Hep B, 1, 2, 3).
Note: The student must have a “C” or better in all courses to receive a certificate in Medical Assisting. Students must pass each course with a “C” or better to continue toward the next course in the program. Those students who do not successfully complete a core technical or related technical requirement course will have to wait a minimum of one year for reentry. For further information, please refer to the Medical Assistant Program Handbook.
Pre-requisite courses are not required for program entry, but must be completed for approval for entry into the program learning group or cohort. When the student enters the learning group, he/she will begin the Medical Assisting Program.
Other Prerequisite:
- Health clearance to include physical and immunizations- PPD, with the addition of a Hepatitis B vaccine or declination form.
- Police and court clearance will be required for acceptance into Medical Assistant cohort.
Program Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs):
Upon successful completion of the AS in Medical Assisting program, students will be able to:
- Describe legal and ethical principles that affect the role of a medical assistant.
- Demonstrate proficiency in administrative medical office procedures.
- Demonstrate proficiency in clinical procedures.
- Perform medical laboratory procedures.
General Education Requirements | ||
Course | Course Name | Credits |
English (Choose 1) | ||
EN110A | Freshman Composition with Instructional Lab | 4 |
EN110 | Freshman Composition | 3 |
Course | Course Name | Credits |
MA___ | Mathematics Requirement | 3-4 |
| Literacy for Life Requirement | 3 |
| Humanities & Fine Arts Requirement | 3-4 |
| Social & Behavioral Sciences Requirement | 3 |
HL190 | Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology for Allied Health Professionals | 4 |
Total | 19-22 | |
Major Requirements | ||
Course | Course Name | Credits |
HL120 | Medical Terminology | 2 |
HL131 | Basic Life Support for Healthcare Providers | 1 |
HL150 | Study of Disease | 3 |
HL201 | Medical Law and Ethics | 3 |
HL202 | Nutrition | 3 |
HL252 | Pathology for Health Professions | 3 |
MS125 | Clinical Medical Assisting: Clinical | 1 |
MS101 | Introduction to Medical Assisting | 3 |
MS120 | Clinical Medical Assisting: Theory | 3 |
MS121 | Clinical Medical Assisting Laboratory | 2 |
MS140 | Administrative Medical Assisting: Theory | 2 |
MS141 | Administrative Medical Assisting: Laboratory | 2 |
MS145 | Administrative Medical Assisting: Clinical | 1 |
MS160 | Pharmacology: Dosage and Calculations | 2 |
MS161 | Administration of Medications Laboratory | 1 |
MS180 | Introduction to Clinical Laboratory | 2 |
MS210 | Medical Assisting Critique | 1 |
MS220 | Medical Assisting Specialties | 3 |
MS225 | Medical Assisting Specialties Clinical | 1 |
MS292 | Medical Assisting Practicum | 5 |
Total | 44 | |
Program Total | 63-66 | |
Course Sequence by Semester
Year 1 | |||||
Semester 1 | Semester 2 | ||||
Course # | Course Name | Credits | Course # | Course Name | Credits |
EN110 OR EN110A | Freshman Composition OR Freshman Composition with Instructional Lab | 3-4 | MS101 | Introduction to Medical Assisting | 3 |
MA___ | Mathematics Requirement | 3-4 | MS140 | Administrative Medical Assisting: Theory | 2 |
HL150 | Study of Disease | 3 | MS141 | Administrative Medical Assisting: Laboratory | 2 |
CS___ | Literacy for Life Requirement | 3 | MS145 | Administrative Medical Assisting Clinical | 1 |
HL190 | Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology for Allied Health Professionals | 4 | HL131 | Basic Life Support for Health Care Providers | 1 |
|
| HL120 | Medical Terminology | 2 | |
|
| HL202 | Nutrition | 3 | |
Total | 16-18 | Total | 14 | ||
Year 2 | |||||
Semester 3 | Semester 4 | ||||
Course # | Course Name | Credits | Course # | Course Name | Credits |
HL201 | Medical Law & Ethics | 3 | MS120 | Clinical Medical Assisting: Theory | 3 |
MS160 | Pharmacology: Dosage and Calculations | 2 | MS121 | Clinical Medical Assisting Laboratory | 2 |
MS161 | Administration of Medications Laboratory | 1 | MS 125 | Clinical Medical Assisting: Clinical | 1 |
| Humanities & Fine Arts Requirement | 3-4 | MS220 | Medical Assisting Specialties | 3 |
| Social & Behavioral Sciences Requirement | 3 | MS225 | Medical Assisting Specialties Clinical | 1 |
Total | 12-13 | Total | 10 | ||
Year 3 | |||||
Semester 5 |
| ||||
Course # | Course Name | Credits | Course # | Course Name | Credits |
MS180 | Introduction to Clinical Laboratory | 2 | |||
MS210 | Medical Assisting Critique | 1 | |||
MS292 | Medical Assisting Practicum | 5 | |||
HL252 | Pathology for Health Professions | 3 | |||
Total | 11 | Total |
| ||
Program Total | 63-66 | ||||
The mission of the Nursing and Allied Health Department is to generate locally educated and licensed nurses to work in the various health care provider agencies on Guam and the Pacific region. The Guam Community College Nursing Program is committed to providing career guidance and education in nursing to those students from Guam and the Pacific region who desire to become nurses. Upon completion of program requirements, students will earn an Associate of Science in Nursing (ADN) and will be eligible to apply and take the National Council Licensure Examination for Registered Nurses (NCLEX-RN). Licensure is granted through the Guam Board of Nurse Examiners.
Program Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs):
Upon successful completion of the AS in Practical Nursing program, students will be able to:
- Communicate therapeutically with clients & the interdisciplinary team in the practice of nursing.
- Integrate culture and diversity in the provision of holistic care across the lifespan.
- Demonstrate clinical reasoning skills in the provision of safe and competent care utilizing the nursing process in a variety of clinical situations.
- Analyze research to provide evidence-based practice in the care of the client.
General Education Requirements | ||
Course | Course Name | Credits |
EN110 | Freshman Composition | 3 |
MA151 | Introductory Statistics | 3 |
SI131/131L | Human Anatomy & Physiology I: Theory (3) and Human Anatomy & Physiology I: Laboratory (1) | 4 |
| Literacy for Life | 3 |
CO125 | Introduction to Human Communication and Speech | 3 |
PY120 | General Psychology | 3 |
Total | 19 | |
Major Requirements | ||
Course | Course Name | Credits |
ED220 | Human Growth and Development | 3 |
HL202 | Nutrition | 3 |
NU205 | Adult Medical Surgical Nursing I & Clinical Skills | 6 |
NU210 | Pharmacology | 2 |
NU212 | Health Assessment | 4 |
NU215 | Pathophysiology | 3 |
NU225 | Adult Medical Surgical Nursing II & Clinical Skills | 8 |
NU235 | Advanced Maternal Newborn Concepts & Clinical Skills | 3 |
NU245 | Advanced Pediatric Nursing Concepts & Clinical Skills | 3 |
NU252 | Mental Health Concepts & Communications | 4 |
NU295 | Professional Nursing Practicum | 6 |
SI102 | General Chemistry with Laboratory | 4 |
SI106 | Dosage Calculations for Practical Nursing | 1 |
SI132/132L | Human Anatomy & Physiology: Theory II (3)/Human Anatomy & Physiology II Laboratory (1) | 4 |
SI150/150L | Introduction to Microbiology: Theory (3) / Introduction to Microbiology: Laboratory (1) | 4 |
Total | 58 | |
Program Total | 77 | |
Course Sequence by Semester
Year 1 | |||||
Semester 1 | Semester 2 | ||||
Course # | Course Name | Credits | Course # | Course Name | Credits |
EN110 | Freshman Composition | 3 | SI106 | Drug Calculations for Practical Nursing | 1 |
MA151 | Introductory Statistics | 3 | HL202 | Nutrition | 3 |
SI131/SI131L | Human Anatomy & Physiology I: Theory/Human Anatomy & Physiology I: Laboratory | 4 | SI132/SI132L | Human Anatomy & Physiology: Theory II/Human Anatomy & Physiology II: Laboratory | 4 |
SI102 | General Chemistry with Laboratory | 4 | ED220 | Human Growth & Development | 3 |
PY120 | General Psychology | 3 | SI150/SI150L | Introduction to Microbiology: Theory/Introduction to Microbiology: Laboratory | 4 |
Total | 17 |
| Total | 15 | |
Year 2 | |||||
Semester 3 | Semester 4 | ||||
Course # | Course Name | Credits | Course # | Course Name | Credits |
| NU205 | Adult Medical Surgical Nursing I & Clinical Skills | 6 | NU225 | Adult Medical Surgical Nursing II & Clinical Skills | 8 |
| NU210 | Pharmacology | 2 | NU215 | Pathophysiology | 3 |
| NU212 | Health Assessment | 4 | NU252 | Mental Health Concepts & Communications | 4 |
| CO125 | Introduction to Human Communication and Speech | 3 |
|
| |
| Literacy for Life | 3 |
|
| ||
Total | 18 |
| Total | 15 | |
Semester 5 |
| ||||
Course # | Course Name | Credits |
|
|
|
NU295 | Professional Nursing Practicum | 6 |
|
| |
NU235 | Advanced Maternal Newborn Concepts & Clinical Skills | 3 |
|
| |
NU245 | Advanced Pediatric Nursing Concepts & Clinical Skills | 3 |
|
| |
Total | 12 |
|
| ||
PROGRAM TOTAL | 77 | ||||
This program provides training in skills used within the business office such as business correspondences, Microsoft Office applications, office procedures, basic accounting, customer service, and business communications. Upon completion, students will be trained to perform as a future office manager. Related job titles include executive administrative assistant, clerk, customer service support, and executive secretary.
Program Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs):
Upon successful completion of the AS in Office Technology program, students will be able to:
- Perform office management procedures.
- Format, produce, and manage business documents such as memos, letters, databases, spreadsheets, financial documents, presentations, and reports.
- Demonstrate effective written and oral business communication skills.
General Education Requirements | ||
Course | Course Name | Credits |
| EN___ | English Requirement | 3-4 |
| MA___ | Mathematics Requirement (MA110A OR MA115 OR MA161A) | 3-4 |
| CS151 | Windows Applications | 3 |
| Humanities & Fine Arts Requirement | 3-4 | |
| Natural & Physical Sciences Requirement | 4 | |
| PY125 | Interpersonal Relations | 3 |
Total | 19-22 | |
Major Requirements | ||
Course | Course Name | Credits |
| OA101 | Keyboarding and Document Processing | 3 |
| OA103 | Filing Systems | 3 |
| OA109 | Business Math Using Excel | 3 |
| OA130 | Information Processing | 3 |
| OA210 | Database Management Systems | 3 |
| OA211 | Business Communication | 3 |
| OA220 | Spreadsheet Systems | 3 |
| OA230 | Advanced Information Processing | 3 |
| OA250 | Office Procedures | 3 |
| SM108 | Introduction to Business | 3 |
| SM208 | Personnel Supervision | 3 |
Electives (Complete 9 credits) | ||
Course | Course Name | Credits |
| AC100 | Fundamentals of Bookkeeping and Accounting | 3 |
| AC211 | Accounting Principles I | 4 |
| MK125 | Social Media Marketing | 3 |
| OA240 | Machine Transcription | 3 |
| OA292 | Office Technology Practicum | 3 |
Total | 42 | |
Program Total | 61-64 | |
Course Sequence by Semester
Year 1 | |||||
Semester 1 | Semester 2 | ||||
Course # | Course Name | Credits | Course # | Course Name | Credits |
| EN___ | English Composition Requirement | 3-4 | SM108 | Introduction to Business | 3 |
| OA101 | Keyboarding and Document Processing | 3 | MA___ | Mathematics Requirement | 3-4 |
| OA103 | Filing Systems | 3 | OA230 | Advanced Information Processing | 3 |
| OA109 | Business Math Using Excel | 3 | CS151 | Windows Application | 3 |
| OA130 | Information Processing | 3 |
| Elective | 3 |
Total | 15-16 |
| Total | 15-16 | |
Year 2 | |||||
Semester 3 | Semester 4 | ||||
Course # | Course Name | Credits | Course # | Course Name | Credits |
| OA210 | Database Management Systems | 3 | OA220 | Spreadsheet Systems | 3 |
| SM208 | Personnel Supervision | 3 | OA211 | Business Communication | 3 |
| Humanities & Fine Arts Requirement | 3-4 | OA250 | Office Procedures | 3 | |
| PY125 | Interpersonal Relations | 3 |
| Natural and Physical Sciences Requirement | 4 |
| Elective | 3 |
| Elective | 3 | |
| Total | 15-16 |
| Total | 16 |
PROGRAM TOTAL | 61-64 | ||||
The mission of the Nursing and Allied Health Department is to generate locally educated and licensed nurses to work in the various health care provider agencies on Guam and the Pacific region. The Guam Community College Nursing Program is committed to providing career guidance and education in nursing to those students from Guam and the Pacific region who desire to become Practical Nurses. Upon completion of program requirements, students will earn an Associate’s Degree in Practical Nursing and will be eligible to apply and take the National Council Licensure Examination for Practical Nurses (NCLEX-PN). Licensure is granted through the Guam Board of Nurse Examiners.
Program Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs):
Upon successful completion of the AS in Practical Nursing program, students will be able to:
- Utilize established standards and practice guidelines to help clients restore, promote and maintain physical and mental health throughout their lifespan.
- Apply therapeutic communication with patients, patient support-persons and members of the health-care team.
- Employ evidence-based decision making to deliver safe and effective client care and to evaluate client outcomes.
General Education Requirements | ||
Course | Course Name | Credits |
English (Choose 1) | ||
EN110 | Freshman Composition | 3 |
EN110A | Freshman Composition with Instructional Lab | 4 |
Course | Course Name | Credits |
MA110A | Finite Mathematics | 3 |
SI131/131L | Human Anatomy & Physiology I: Theory (3) and Human Anatomy & Physiology I: Laboratory (1) | 4 |
CS151 | Windows Applications | 3 |
CO125 | Introduction to Human Communication and Speech | 3 |
PY120 | General Psychology | 3 |
Total | 19-20 | |
Major Requirements | ||
Course | Course Name | Credits |
ED220 | Human Growth and Development | 3 |
HL120 | Medical Terminology | 2 |
HL131 | Basic Life Support for Healthcare Providers | 1 |
HL202 | Nutrition | 3 |
NU160 | Pathophysiology & Pharmacology for Practical Nurses | 5 |
NU220 | Adult Medical Surgical Nursing | 8 |
NU230 | Maternal and Newborn Concepts & Skills | 3 |
NU240 | Pediatric Nursing Concepts & Skills | 3 |
NU250 | Mental Health Nursing | 3 |
NU280 | Nursing Trends | 1 |
NU281 | NCLEX-PN Review & Transition | 2 |
NU292 | Nursing Practicum | 6 |
SI106 | Drug Calculations for Practical Nursing | 1 |
SI132/132L | Human Anatomy & Physiology: Theory II (3)/Human Anatomy & Physiology II: Laboratory (1) | 4 |
SI150/150L | Introduction to Microbiology: Theory (3)/Introduction to Microbiology: Laboratory (1) | 4 |
Total | 49 | |
Program Total | 68-69 | |
Course Sequence by Semester
Year 1 | |||||
Semester 1 | Semester 2 | ||||
Course # | Course Name | Credits | Course # | Course Name | Credits |
| EN110 OR EN110A | Freshman Composition OR Freshman Composition with Instructional Lab | 3-4 | SI150/SI150L | Introduction to Microbiology: Theory/Introduction to Microbiology: Laboratory | 4 |
| MA110A | Finite Mathematics | 3 | HL131 | Basic Life Support for Healthcare Providers | 1 |
| SI131/SI131L | Human Anatomy & Physiology I: Theory/Human Anatomy & Physiology I: Laboratory | 4 | SI132/SI132L | Human Anatomy & Physiology: Theory II: Theory/Human Anatomy & Physiology II: Laboratory | 4 |
| HL120 | Medical Terminology | 2 | PY120 | General Psychology | 3 |
| HL202 | Nutrition | 3 | ED220 | Human Growth and Development | 3 |
Total | 15-16 |
| Total | 15 | |
Year 2 | |||||
Semester 3 | Semester 4 | ||||
Course # | Course Name | Credits | Course # | Course Name | Credits |
CS151 | Windows Application | 3 | NU220 | Adult Medical Surgical Nursing | 8 |
NU160 | Pathophysiology & Pharmacology for Practical Nurses | 5 | NU230 | Maternal and Newborn Concepts & Skills | 3 |
SI106 | Drug Calculations for Practical Nursing | 1 | NU240 | Pediatric Nursing Concepts & Skills | 3 |
CO125 | Introduction to Human Communications and Speech | 3 | |||
| Total | 12 |
| Total | 14 |
Year 2 | |||||
Semester 5 | Semester 4 | ||||
Course # | Course Name | Credits | Course # | Course Name | Credits |
NU250 | Mental Health Nursing | 3 | |||
NU292 | Nursing Practicum | 6 | |||
NU280 | Nursing Trends | 1 | |||
NU281 | NCLEX-PN Review & Transition | 2 | |||
Total | 12 |
|
|
| |
PROGRAM TOTAL | 68-69 | ||||
The A.S. in Pre-Architectural Drafting covers pre-architecture, building materials and properties, technical drafting, basic Computer Aided Drafting (CAD), architectural computer modeling, and an introductory engineering course. This program prepares students for entry-level employment as CADD operators, draftsmen/women, architect assistants, or as a bridge to enter a career as an Architect. Graduates are prepared for the professional workforce with sound theoretical knowledge, relevant computer technology, and hands-on experience.
Program Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs):
Upon successful completion of the AS in Pre-Architectural Drafting program, students will be able to:
- Design and draft projects ranging from two to three dimensional designs for commercial and residential buildings.
- View, print, edit, and create variations of two and three dimensional electronic designs.
- Emulate a professional work ethic needed in the architectural engineering industry.
- Create an electronic portfolio that represents proficiency in the development of two and three dimensional computer aided designs.
General Education Requirements | ||
Course | Course Name | Credits |
EN110 OR EN110A | Freshman Composition OR Freshman Composition with Instructional Lab | 3-4 |
MA161A | College Algebra & Trigonometry I | 3 |
SI141 | Applied Physics I | 4 |
CS151 | Windows Application | 3 |
Social & Behavioral Science Requirement (Choose 1) | ||
CJ100 | Introduction to Criminal Justice | 3 |
EC110 | Principles of Economics | 3 |
PS140 | American Government | 3 |
PY100 | Personal Adjustment | 3 |
PY120 | General Psychology | 3 |
PY125 | Interpersonal Relations | 3 |
SO130 | Introduction to Sociology | 3 |
WG101 | Introduction to Women and Gender Studies | 3 |
Humanities & Fine Arts Requirement (Choose 1) | ||
ASL100 | American Sign Language I | 4 |
CH110 | CHamoru I | 4 |
CO125 | Introduction to Human Communication and Speech | 3 |
ED265 | Culture and Education in Guam | 3 |
EN210 | Introduction to Literature | 3 |
HI121 | History of World Civilization I | 3 |
HI122 | History of World Civilization II | 3 |
HI176 | Guam History | 3 |
HM110 | Introduction to Community Services | 3 |
HM201 | Social Welfare & Development: Global Challenges | 3 |
HU120 | Pacific Cultures | 3 |
HU220 | Guam Cultures and Legends | 3 |
JA110 | Japanese I | 4 |
KE110 | Korean I | 4 |
PI101 | Introduction to Philosophy | 3 |
TH101 | Introduction to Theatre | 3 |
VC101 | Introduction to Visual Communications | 3 |
TOTAL | 19-21 | |
Major Requirements | ||
Course | Course Name | Credits |
| CT100 OR SU100 | Introduction to Construction Trades OR Surveying Drafting | 3 |
| AE103 | Basic Blueprint Reading | 3 |
| AE121 | Technical Engineering Drawing I | 3 |
| AE122 | Technical Engineering Drawing II | 3 |
| AE138 | Building Codes, Specifications & Construction Management | 3 |
| AE150 | Computer Aided Drafting I | 3 |
| AE160 | Comp Aided Drafting II | 3 |
| AE170 | Revit Architecture Essentials | 3 |
| CE211 | Plane Surveying I | 3 |
| CE215 | Construction Procedures | 3 |
| CE225 | Construction Planning & Estimating | 3 |
| MA161B | College Algebra & Trigonometry II | 3 |
| EN194 | Technical Communication | 3 |
| OR101 OR CS101 | Introduction to Engineering Technology OR Introduction to Computer Systems & Information Technology | 3 |
Total | 42 | |
PROGRAM TOTAL | 61-63 | |
Course Sequence by Semester
Year 1 | |||||
Semester 1 | Semester 2 | ||||
Course # | Course Name | Credits | Course # | Course Name | Credits |
| EN110 OR EN110A | Freshman Composition OR Freshman Composition with Instructional Laboratory | 3-4 | AE121 | Technical Engineering Drawing I | 3 |
| MA161A | College Algebra & Trigonometry I | 3 | AE150 | Comp. Aided Drafting I | 3 |
| AE103 | Basic Blueprint Reading | 3 | MA161B | College Algebra & Trigonometry II | 3 |
| CT100 OR SU100 | Introduction to Construction Trades OR Surveying Drafting | 3 | SI141 | Applied Physics I | 4 |
| CS151 | Windows Application | 3 | OR101 OR CS101 | Introduction to Engineering Technology OR Introduction to Computer Systems & Information Technology | 3 |
Total | 15-16 |
| Total | 16 | |
Year 2 | |||||
Semester 3 | Semester 4 | ||||
Course # | Course Name | Credits | Course # | Course Name | Credits |
AE138 | Building Codes, Specifications & Construction Management | 3 | AE122 | Technical Engineering Drawing II | 3 |
AE160 | Comp. Aided Drafting II | 3 | AE170 | Revit Architecture Essentials | 3 |
EN194 | Technical Communication | 3 | CE225 | Construction Planning & Estimating | 3 |
CE211 | Plane Surveying I | 3 |
| Social & Behavioral Sciences | 3 |
CE215 | Construction Procedures | 3 |
| Humanities & Fine Arts | 3-4 |
| Total | 15 |
| Total | 15-16 |
PROGRAM TOTAL | 61-63 | ||||
The Supervision and Management program prepares students for entry-level positions and employment in the field of supervision and management. The program is designed for students who want to learn, update and augment existing knowledge and skills and/or acquire cutting-edge technical and managerial skills; it is also designed for current and future leaders, supervisors, and managers who desire that their entry level employees have the latest skills to be effective and productive in their respective fields.
Program Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs):
Upon successful completion of the AS in Supervision & Management program, students will be able to:
- Apply supervisory techniques to manage people and projects.
- Explain planning, organizing, staffing, leading, and controlling functions of an organization.
- Discuss ethical behavior required in businesses.
A “cooperative 2 + 2” degree program is established between the GCC Associate of Science in Supervision & Management (AS&M) degree and the UOG Bachelor of Business Administration (BBA) degree. The “cooperative 2 + 2” degree program will consist of students earning their Associate of Science in Supervision & Management degree in the first 2 years and then earning their Bachelor of Business Administration degree in the second 2 years.
General Education Requirements | ||
Course | Course Name | Credits |
EN110 OR EN110A | English Composition OR English Composition with Instructional Lab | 3-4 |
MA___ | Mathematics Requirement | 3 |
| Literacy for Life Requirement | 3 |
| Humanities & Fine Arts Requirement | 3-4 |
| Natural & Physical Sciences Requirement | 4 |
| Social & Behavioral Sciences Requirement | 3 |
Total | 19-21 | |
Major Requirements | ||
Course | Course Name | Credits |
AC211 | Accounting Principles I | 4 |
EC110 | Principles of Economics | 3 |
SM108 | Introduction to Business | 3 |
SM208 | Personnel Supervision | 3 |
SM211 | E-Commerce Management | 3 |
SM215 | International Management | 3 |
SM220 | Management Skill Development | 3 |
SM225 | Leadership | 3 |
SM230 | Business Law Applications | 3 |
SM240 | Employment and Labor Law | 3 |
SM245 | Ethics & Stakeholder Management | 3 |
Electives (Complete 9 Credits) | ||
Course | Course Name | Credits |
EN111 | Writing for Research | 3 |
MK123 | Principles of Marketing | 3 |
MK205 | Entrepreneurship | 3 |
OA211 | Business Communication | 3 |
| Memorandum of Agreement between the University of Guam and the Guam Community College – Cooperative 2 + 2 degree program, Supervision & Management degree and the UOG Bachelor of Administration degree. | ||
OA250 | Office Procedures | 3 |
PY125 | Interpersonal Relations | 3 |
SM205 | Purchasing | 3 |
SM292 | Supervision & Management Practicum | 3-6 |
Total | 43 | |
Program Total | 62-64 | |
Course Sequence by Semester
Year 1 | |||||
Semester 1 | Semester 2 | ||||
Course # | Course Name | Credits | Course # | Course Name | Credits |
| EN110 OR EN110A | Freshman Composition OR Freshman Composition with Instructional Lab | 3-4 | AC211 | Accounting Principles I | 4 |
| MA___ | Mathematics | 3 |
| Literacy for Life Skills | 3 |
| Social & Behavioral Science Requirement | 3 |
| Humanities & Fine Arts Requirement | 3 | |
| SM108 | Introduction to Business | 3 | SM215 | International Management | 3 |
| SM208 | Personnel Supervision | 3 | SM220 | Management Skill Development | 3 |
Total | 15-16 |
| Total | 16 | |
Year 2 | |||||
Semester 3 | Semester 4 | ||||
Course # | Course Name | Credits | Course # | Course Name | Credits |
| EC110 | Principles of Economics | 3 | MK205 | Entrepreneurship (or any SM Elective) | 3 |
| Natural & Physical Sciences Requirement | 4 | SM211 | E-Commerce Management | 3 | |
| SM225 | Leadership | 3 | SM240 | Employment and Labor Law | 3 |
| SM230 | Business Law Applications | 3 | SM245 | Ethics & Stakeholder Management | 3 |
| MK123 | Principles of Marketing (or any SM elective) | 3 | SM292 | Supervision & Management Practicum (or any SM elective) | 3 |
| Total | 16 |
| Total | 15 |
PROGRAM TOTAL | 62-64 | ||||
The Surveying Technology program prepares the student for immediate employment as a surveying or Geographic Information Systems (GIS) technician and teaches the student knowledge and skills that will enable one to adapt to ever evolving technical and technological changes in geospatial field and office applications. The graduate will be prepared to face the challenge of modern Surveying and GIS practice. The program emphasizes applications-based approaches and provides an overview of the geospatial fields of surveying, mapping, and GIS and prepares the student for further study and for the Level 3 Certified Survey Technician examination prepared by the American Congress of Surveying and Mapping-National Society of Professional Surveyors (ACSM/NSPS).
Program Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs):
Upon successful completion of the AS in Surveying Technology program, students will be able to:
- Prepare to enter a productive technical position in the geospatial fields of surveying, mapping, and Geographic Information Systems.
- Successfully pass the American Congress of Surveying and Mapping-National Society of Professional Surveyors (ACSM/NSPS) Level 3 Certified Survey Technician examination.
- Emulate a professional work ethic needed in the surveying industry.
- Utilize modern measurement technologies to acquire spatial data and employ industry-standard software to solve technical problems.
General Education Requirements | ||
Course | Course Name | Credits |
EN110 OR EN110A | Freshman Composition OR Freshman Composition with Instructional Lab | 3-4 |
MA161A | College Algebra & Trigonometry I | 3 |
SI110/110L | Environmental Biology: Theory & Environmental Biology Laboratory | 4 |
CS151 | Windows Applications | 3 |
Social & Behavioral Science Requirement (Choose 1) | ||
CJ100 | Introduction to Criminal Justice | 3 |
EC110 | Principles of Economics | 3 |
PS140 | American Government | 3 |
PY100 | Personal Adjustment | 3 |
PY120 | General Psychology | 3 |
PY125 | Interpersonal Relations | 3 |
SO130 | Introduction to Sociology | 3 |
WG101 | Introduction to Women and Gender Studies | 3 |
Humanities & Fine Arts Requirement (Choose 1) | ||
ASL100 | American Sign Language I | 4 |
CH110 | CHamoru I | 4 |
CO125 | Introduction to Human Communication and Speech | 3 |
ED265 | Culture and Education in Guam | 3 |
EN210 | Introduction to Literature | 3 |
HI121 | History of World Civilization I | 3 |
HI122 | History of World Civilization II | 3 |
HI176 | Guam History | 3 |
HM110 | Introduction to Community Services | 3 |
HM201 | Social Welfare & Development: Global Challenges | 3 |
HU120 | Pacific Cultures | 3 |
HU220 | Guam Cultures and Legends | 3 |
JA110 | Japanese I | 4 |
KE110 | Korean I | 4 |
PI101 | Introduction to Philosophy | 3 |
TH101 | Introduction to Theatre | 3 |
VC101 | Introduction to Visual Communications | 3 |
TOTAL | 19-21 | |
Major Requirements | ||
Course | Course Name | Credits |
CT100 OR SU100 | Introduction to Construction Trades OR Surveying Drafting | 3 |
AE103 | Basic Blueprint Reading | 3 |
AE121 | Technical Engineering Drawing I | 3 |
AE150 | Computer Aided Drafting I (CAD I) | 3 |
CE211 | Plane Surveying I | 3 |
CE222 | Plane Surveying II | 3 |
MA161B | College Algebra & Trigonometry II | 3 |
SU101 | Surveying Problems | 3 |
SU230 | Advanced Surveying | 3 |
SU240 | Boundary Law I | 3 |
SU241 | Boundary Law II | 3 |
SU250 | Introduction to Geographic Information Systems | 3 |
SU251 | Advanced Geographic Information Systems | 3 |
SU280 | Special Topics in Geographic Information Systems | 3 |
SU292 | Surveying Practicum | 1 |
Total | 43 | |
PROGRAM TOTAL | 62-64 | |
Course Sequence by Semester
Year 1 | |||||
Semester 1 | Semester 2 | ||||
Course # | Course Name | Credits | Course # | Course Name | Credits |
SU101 | Surveying Problems I | 3 | AE121 | Technical Engineering Drawing I | 3 |
MA161A | College Algebra & Trigonometry I | 3 | AE150 | Computer Aided Drafting I (CAD I) | 3 |
AE103 | Basic Blueprint Reading | 3 | MA161B | College Algebra & Trigonometry II | 3 |
CT100 OR SU100 | Introduction to Construction Trades OR Surveying Drafting | 3 | EN___ | English Requirement | 3-4 |
CS151 | Windows Applications | 3 | SI110/SI110L | Environmental Biology: Theory/ Environmental Biology Laboratory | 4 |
Total | 15 | Total | 16-17 | ||
Year 2 | |||||
Semester 3 | Semester 4 | ||||
Course # | Course Name | Credits | Course # | Course Name | Credits |
CE211 | Plane Surveying I | 3 | SU230 | Advanced Surveying | 3 |
SU240 | Boundary Law I | 3 | SU251 | Advanced Geographic Information Systems | 3 |
SU250 | Introduction to Geographic Information Systems | 3 | CE222 | Plane Surveying II | 3 |
| Humanities & Fine Arts | 3-4 | SU241 | Boundary Law II | 3 |
| Social & Behavioral Sciences | 3 | SU280 | Special Topics in Geographic Information Systems | 3 |
|
| SU292 | Surveying Practicum | 1 | |
Total | 15-16 | Total | 16 | ||
PROGRAM TOTAL | 62-64 | ||||
The Tourism and Travel Management program is designed for individuals who aspire to begin a career in the tourism and travel industry. Students are introduced to management and operating principles of different sectors of the industry to prepare them for a meaningful career, leadership roles, or entrepreneurial opportunities.
Program Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs):
Upon successful completion of the AS in Tourism & Travel Management program, students will be able to:
- Exhibit professionalism and work ethic as it relates to the tourism and travel industry.
- Explain the inter-relationship among component parts of the tourism system.
- Create a career plan identifying additional training needed for professional success.
General Education Requirements | ||
Course | Course Name | Credits |
EN110 OR EN110A | Freshman Composition OR Freshman Composition with Instructional Lab | 3-4 |
MA___ | Mathematics Requirement | 3 |
| Literacy for Life Requirement | 3 |
| Humanities & Fine Arts Requirement (CH110 CHamoru I, JA110 Japanese I, KE110 Korean I | 4 | |
SI___ | Natural & Physical Sciences Requirement | 4 |
| Social & Behavioral Sciences Requirement | 3 | |
Total | 20-21 | |
Major Requirements | ||
Course | Course Name | Credits |
AC211 | Accounting Principles I | 4 |
HS150 | Welcome to Hospitality | 3 |
HS152 | Customer Service | 3 |
HS157 | Tourism Planning and Development | 3 |
HS158 | Introduction to MICE | 3 |
HS160 | Hospitality Supervision | 3 |
HS254 | Hospitality and Travel Marketing | 3 |
HS255 | Introduction to Air Transportation Industry | 3 |
HS257 | Principles of Tour Guiding | 3 |
HS265 | Sustainable Tourism | 3 |
HS292 | Hospitality and Tourism Practicum | 3 |
CHOOSE ONE | JA110 Japanese I; JA111, Japanese II; KE110 Korean I; KE111, Korean II; CH110 CHamoru I; CH111 CHamoru II | 4 |
Choose One | ||
KE110 | Korean I | 3-4 |
KE111 | Korean II | |
JA110 | Japanese I | |
JA111 | Japanese II | |
CH110 | CHamoru I | |
CH111 | CHamoru II | |
MK123 | Principles of Marketing (3) (Students who choose to take this course must take HL131) | |
SM108 | Introduction to Business (3) (Students who choose to take this course must take HL131) | |
Total | 41-42 | |
Program Total | 61-63 | |
Course Sequence by Semester
Year 1 | |||||
Semester 1 | Semester 2 | ||||
Course # | Course Name | Credits | Course # | Course Name | Credits |
EN___ | English Composition Requirement | 3-4 | MA___ | Mathematics Requirement | 3 |
| Humanities & Fine Arts Choose One: Japanese I OR Korean I OR CHamoru I | 4 | Literacy for Life | 3 | |
HS150 | Welcome to Hospitality | 3 | Choose One: Japanese I, OR Japanese II, Korean I, OR Korean II, OR CHamoru I, OR CHamoru II | 4 | |
HS152 | Customer Service | 3 | HS257 | Principles of Tour Guiding | 3 |
HS158 | Introduction to MICE | 3 | HS265 | Sustainable Tourism | 3 |
Total | 16-17 | Total | 16 | ||
Year 2 | |||||
Semester 3 | Semester 4 | ||||
Course # | Course Name | Credits | Course # | Course Name | Credits |
HS160 | Hospitality Supervision | 3 | HS157 | Tourism Planning and Development | 3 |
HS254 | Hospitality and Travel Marketing | 3 | AC211 | Accounting Principles I | 4 |
HS255 | Introduction to Air Transportation Industry | 3 | HS292 | Hospitality and Tourism Practicum | 3 |
| Natural & Physical Sciences Requirement | 4 |
| Social & Behavioral Sciences | 3 |
|
|
| Electives | 3-4 | |
| Total | 13 |
| Total | 16-17 |
Program Total | 61-63 | ||||
The Associate of Science in Visual Communications (VisCom) provides students with the knowledge and experience necessary for employment in a Visual Communication profession. Students will learn the fundamental concepts, skills, and workflow techniques to design and execute effective media products. Career opportunities in Visual Communications may include graphic designer, photographer, video producer, website developer, and digital media producer.
Program Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs):
Upon successful completion of the AS in Visual Communications program, students will be able to:
- Apply critical thinking skills in the practice of media production.
- Use different techniques in the creation and development of media solutions.
- Develop effective communication solutions using theories, tools, and best practices in media production.
General Education Requirements | ||
Course | Course Name | Credits |
EN___ | English Requirement | 3-4 |
MA110A | Finite Mathematics or higher | 3 |
| Literacy for Life Requirement | 3 |
VC101 | Introduction to Visual Communications | 3 |
SI___ | Natural & Physical Sciences Requirement | 4 |
PY125 | Interpersonal Relations | 3 |
Total GE | 19-20 | |
Major Requirements | ||
Course | Course Name | Credits |
VC125 | Digital Graphics: Raster | 3 |
VC126 | Digital Graphics: Vector | 3 |
VC127 | Digital Photography | 3 |
VC128 | Design Principles and Elements | 3 |
VC211 | Design Studio I | 3 |
VC212 | Design Studio II | 3 |
VC221 | Interactive Studio I | 3 |
VC222 | Interactive Studio II | 3 |
VC231 | Video Production I | 3 |
VC232 | Video Production II | 3 |
VC291 | Project Management & Marketing Solutions | 3 |
VC292 | Visual Communication Practicum | 3 |
MK123 | Principles of Marketing | 3 |
MK224 | Advertising | 3 |
Total | 42 | |
Program Total | 61-62 | |
Course Sequence by Semester
Year 1 | |||||
Semester 1 | Semester 2 | ||||
Course # | Course Name | Credits | Course # | Course Name | Credits |
EN___ | English Composition Requirement | 3-4 | VC101 | Introduction to Visual Communications | 3 |
MA__ | Mathematics Requirement | 3 | MK123 | Principles of Marketing | 3 |
| Literacy for Life Requirement | 3 | VC127 | Digital Photography | 3 |
VC125 | Digital Graphics: Raster | 3 | VC128 | Design Principles and Elements | 3 |
VC126 | Digital Graphics: Vector | 3 | PY125 | Interpersonal Relations | 3 |
Total | 15-16 | Total | 15 | ||
Year 2 | |||||
Semester 3 | Semester 4 | ||||
Course # | Course Name | Credits | Course # | Course Name | Credits |
VC211 | Design Studio I | 3 | VC291 | Project Management & Marketing Solutions | 3 |
VC212 | Design Studio II | 3 | MK224 | Advertising | 3 |
VC221 | Interactive Studio I | 3 | VC231 | Video Production I | 3 |
VC222 | Interactive Studio II | 3 | VC232 | Video Production II | 3 |
SI___ | Natural & Physical Sciences Requirement | 4 | VC292 | Visual Communication Practicum | 3 |
Total | 16 | Total | 15 | ||
PROGRAM TOTAL | 61-62 | ||||
Culinary Arts Program
The Hospitality industry is one of the fastest-growing segments of our economy and employs over 10 million food service workers in the U.S. The continued expansion of hotels, restaurants and related services has created vast career opportunities in the culinary arts field. The GCC Culinary Arts program is THE PROGRAM that Guam’s top chefs turn to for culinary personnel. Our Associate of Arts in Culinary Arts degree is accredited by the American Culinary Federation (ACF). Program completers earn the ACF Certified Culinarian certification upon graduation.
Program Mission
The mission of the Culinary Arts Program is to provide students with practical culinary, baking and pastry skills, a strong business foundation to prepare students for high-wage employment and to meet industry demands for trained culinarians and pastry culinarians.
Program Learning Outcomes
- Demonstrate the attributes of a professional culinarian.
- Apply culinary and baking & pastry fundamentals in the preparation of a variety of food products.
- Use quantitative techniques in business decision-making processes in a culinary and bakery setting.
- Manage resources in a commercial culinary and bakery environment.
- specialize in the following concentration areas:
- Cookery
- Baking & Pastry
Student Job Placement Rate:
- 79% of graduates (or 15 of 19) who received an A.A. Culinary Arts degree in 2021 were employed in a job-related field.
- 88% of graduates (or 14 of 16) who received an A.A. Culinary Arts degree in 2022 were employed in a job-related field.
- 84% of graduates (or 11 of 13) who received an A.A. Culinary Arts degree in 2023 were employed in a job-related field.
- 100% of graduates (or 33 of 33) who received an A.A. Culinary Arts degree in 2024 were employed in a job-related field.
- 89% of graduates (or 17 of 19) who received an A.A. Culinary Arts degree in 2025 were employed in a job-related field.

Program Accreditation
The American Culinary Federation has awarded the Seven–Year Exemplary status to the Guam Community College Culinary Arts Program for their Associate of Arts in Culinary Arts and as such, program completers earn the ACF Certified Culinarian designation upon graduation. The program is now ACFEF-accredited through 2029.
ACEF Required Program Outcomes
Baking & Pastry Track | ||
General Education Requirements | ||
Course | Course Name | Credits |
English (Choose 1) | ||
EN110A | Freshman Composition with Instructional Lab | 4 |
EN110 | Freshman Composition | 3 |
Course | Course Name | Credits |
FSM145 | Culinary and Business Math | 3 |
CS151 | Windows Applications | 3 |
PY125 | Interpersonal Relations | 3 |
CO125 | Introduction to Human Communication and Speech | 3 |
SI110 /110L | Environmental Biology: Theory/Environmental Biology: Laboratory | 4 |
TOTAL | 19-20 | |
Major Requirements | ||
Course | Course Name | Credits |
FSM100 | Introduction to the Foodservice Profession | 2 |
FSM105 | Foodservice Sustainability | 2 |
FSM110/FSM110L | Professional Dining Room Service: Theory / Professional Dining Room Service: Laboratory (1) | 3 |
FSM115 | Purchasing and Receiving | 2 |
FSM120 | Food Safety and Sanitation | 2 |
FSM130 | Professional Bar and Alcohol Management | 3 |
FSM154 | Foodservice Nutrition | 3 |
FSM240 | Menu Planning | 3 |
FSM270 | Foodservice Human Resource Management | 3 |
CUL140 | Culinary Foundation I | 2 |
CUL160 | Culinary Foundations II | 2 |
BAK200 | Foundations of Baking and Pastry | 2 |
BAK220 | Intermediate Baking and Pastry | 2 |
BAK240 | Boulangerie: Advanced Bread Techniques | 2 |
BAK250 | Cakes & Desserts Presentation | 2 |
BAK293A | Restaurant Desserts & Pastries Practicum | 3 |
BAK293B | Breads and Cakes Practicum | 3 |
BAK299 | Baking & Pastry Capstone | 2 |
TOTAL | 43 | |
PROGRAM TOTAL | 62-63 | |
Cookery Track | ||
General Education Requirements | ||
Course | Course Name | Credits |
English (Choose 1) | ||
EN110A | Freshman Composition with Instructional Lab | 4 |
EN110 | Freshman Composition | 3 |
Course | Course Name | Credits |
FSM145 | Culinary and Business Math | 3 |
CS151 | Windows Applications | 3 |
PY125 | Interpersonal Relations | 3 |
CO125 | Introduction to Human Communication and Speech | 3 |
SI110 /SI110L | Environmental Biology: Theory/Environmental Biology: Laboratory | 4 |
TOTAL | 19-20 | |
Major Requirements | ||
Course | Course Name | Credits |
FSM100 | Introduction to the Foodservice Profession | 2 |
FSM105 | Foodservice Sustainability | 2 |
FSM110/FSM110L | Professional Dining Room Service: Theory / Professional Dining Room Service: Laboratory (1) | 3 |
FSM115 | Purchasing and Receiving | 2 |
FSM120 | Food Safety & Sanitation | 2 |
FSM130 | Professional Bar and Alcohol Management | 3 |
FSM154 | Foodservice Nutrition | 3 |
FSM240 | Menu Planning | 3 |
FSM270 | Foodservice Human Resource Management | 3 |
CUL140 | Culinary Foundation I | 2 |
CUL160 | Culinary Foundations II | 2 |
BAK200 | Foundations of Baking & Pastry | 2 |
BAK220 | Intermediate Baking and Pastry | 2 |
CUL180 | Garde Manger | 2 |
CUL240 | Pacific Asian Cuisine | 2 |
CUL299 | Culinary Capstone | 2 |
CUL293A | Culinary Practicum Part I | 2 |
CUL293B | Culinary Practicum Part II | 3 |
TOTAL | 42 | |
PROGRAM TOTAL | 61-62 | |
Course Sequence by Semester
Year 1 | |||||
Semester 1 | Semester 2 | ||||
Course # | Course Name | Credits | Course # | Course Name | Credits |
EN___ | English Composition Requirement | 3-4 | CO125 | Introduction to Human Communication and Speech | 3 |
FSM145 | Culinary and Business Math | 3 | PY125 | Interpersonal Relations | 3 |
FSM100 | Introduction to the Foodservice Profession | 2 | CS151 | Windows Application | 3 |
FSM105 | Foodservice Sustainability | 2 | CUL140 | Culinary Foundation I | 2 |
FSM110 | Professional Dining Room Service: Theory | 2 | CUL160 | Culinary Foundations II | 2 |
FSM110L | Professional Dining Room Service: Laboratory | 1 | FSM115 | Purchasing and Receiving | 2 |
FSM120 | Food Safety & Sanitation | 2 |
|
| |
Total | 15-16 | Total | 15 | ||
Year 2 | |||||
Semester 3 | Semester 4 | ||||
Course # | Course Name | Credits | Course # | Course Name | Credits |
SI110/110L | Environmental Biology: Theory/Environmental Biology: Laboratory | 4 | FSM130 | Professional Bar and Alcohol Management | 3 |
FSM154 | Foodservice Nutrition | 3 | FSM240 | Menu Planning | 3 |
BAK200 | Foundations of Baking & Pastry | 2 | Baking & Pastry Track | ||
BAK220 | Intermediate Baking and Pastry | 2 | BAK240 | Boulangerie: Advanced Bread Techniques | 2 |
Baking & Pastry Track | BAK250 | Cakes and Desserts Presentation | 2 | ||
BAK293A | Restaurant Desserts & Pastries Practicum | 3 | BAK293B | Breads and Cakes Practicum | 3 |
Cookery Track | Cookery Track | ||||
CUL293A | Culinary Practicum Part I | 2 | CUL180 | Garde Manger | 2 |
|
|
| CUL240 | Pacific Asian Cuisine | 2 |
|
|
| CUL293B | Culinary Practicum Part II | 3 |
Total | 13-14 | Total | 13 | ||
Year 3 | |||||
Semester |
| ||||
Course # | Course Name | Credits | Course # | Course Name | Credits |
FSM270 | Foodservice Human Resource Management | 3 |
|
| |
Baking & Pastry Track |
|
| |||
BAK299 | Baking & Pastry Capstone | 2 |
|
| |
Cookery Track |
|
| |||
CUL299 | Culinary Capstone | 2 |
|
| |
Total | 5 |
|
| ||
PROGRAM TOTAL | 61-63 | ||||
The Associate of Arts in Education program is designed to provide entry-level training for persons interested in working in educational settings and those planning to continue a path towards a higher degree in education. Emphasis is placed on gaining knowledge and an understanding of (1) diverse philosophies and perspectives which impact how we view education, (2) patterns of growth and development of young people, (3) the diversity of students’ needs and how to address those needs, and (4) the value of collaboration and community. Furthermore, students are expected to engage in critical thinking, problem solving, and continual reflection which are necessary skills for educators.
Program Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs):
Upon successful completion of the AA in Education program, students will be able to:
- Demonstrate professional and ethical conduct and communication within educational environments.
- Create and implement diverse teaching strategies and materials which address the diversity of our student population and optimize learning for all students.
- Exhibit skills in critical thinking, collaboration, creativity, and reflective practice.
General Education Requirements | ||
Course | Course Name | Credits |
English (Choose 1) | ||
EN110A | Freshman Composition with Instructional Lab | 4 |
EN110 | Freshman Composition | 3 |
Course | Course Name | Credits |
MA110A | Finite Mathematics | 3 |
CO110 OR | Critical Thinking for Civic Engagement OR Windows Applications | 3 |
HU120 | Pacific Cultures | 3 |
PY120 | General Psychology | 3 |
SI110/110L OR SI103/SI103L | Environmental Biology: Theory/Environmental Biology: Laboratory OR Introduction to Marine Biology: Theory/Introduction to Marine Biology: Laboratory | 4 |
Total | 19-20 | |
Major Requirements | ||
Course | Course Name | Credits |
ASL100 OR CH110 | American Sign Language I OR CHamoru I | 4 |
ASL110 OR CH111 | American Sign Language II OR CHamoru II | 4 |
ED150 | Introduction to Teaching * | 3 |
ED180A | Educational Methods I | 3 |
ED180B | Educational Methods II | 3 |
ED180C | Educational Methods III | 3 |
ED220 | Human Growth and Development * | 3 |
ED231 | Introduction to Exceptionalities * | 3 |
ED265 | Culture and Education in Guam * | 3 |
EN111 | Writing for Research * | 3 |
ED292 | Education Practicum | 3 |
| Choose two electives (6 credits) from the list below | 6 |
TOTAL | 41 | |
PROGRAM TOTAL | 60-61 | |
NOTE: Courses marked with an * are courses required by UOG/SOE.
**IMPORTANT NOTE: STUDENTS INTERESTED IN ATTENDING THE SCHOOL OF EDUCATION AT UOG | ||
Course | Course Name | Credits |
ASL100 OR CH110 | American Sign Language I OR CHamoru I | 4 |
ASL110 OR CH111 | American Sign Language II OR CHamoru II | 4 |
ED150 | Introduction to Teaching * | 3 |
ED180A | Educational Methods I | 3 |
ED180B | Educational Methods II | 3 |
ED180C | Educational Methods III | 3 |
ED220 | Human Growth and Development * | 3 |
ED231 | Introduction to Exceptionalities * | 3 |
ED265 | Culture and Education in Guam * | 3 |
CO125 | Introduction to Human Communication and Speech | 3 |
EN111 | Writing for Research * | 3 |
ED292 | Education Practicum | 3 |
CTE299A | Praxis I Review Part A | 2 |
CTE299B | Praxis I Review Part B | 1 |
| Choose one elective (3 credits) from the list below | 3 |
PROGRAM TOTAL | 60-64 | |
List of Elective Courses
COURSE | TITLE | CREDITS |
ASL100 | American Sign Language I (If not already taken to complete technical requirement) | 4 |
ASL110 | American Sign Language II (prerequisite: ASL100, If not already taken to complete technical requirement) | 4 |
ASL120 | American Sign Language III (prerequisite: ASL110) | 4 |
ASL130 | American Sign Language IV (prerequisite: ASL120) | 4 |
CD240 | Cognitive & Creative Development in Early Childhood | 3 |
CD260 | Social and Emotional Development | 3 |
CH110 | CHamoru I (If not already taken to complete technical requirement) | 4 |
CH111 | CHamoru II (If not already taken to complete technical requirement) | 4 |
CH200 | Immersion Method for CHamoru Language Teaching I | 3 |
CH220 | CHamoru Composition | 3 |
CO110 | Critical Thinking for Civic Engagement (If not already taken to complete technical requirement) | 3 |
CO125 | Introduction to Human Communication and Speech (If not already taken to complete technical requirement) | 3 |
EN210 | Introduction to Literature | 3 |
EN220 | Best Practices for Literacy Instruction | 3 |
HI176 | Guam History | 3 |
HM110 | Introductions to Community Services | 3 |
HM150 | Diversity in Human Services | 3 |
HU220 | Guam Cultures and Legends | 3 |
IN145 | Vocabulary Development for Intercultural Development | 3 |
IN170 | Introduction to Interpreting | 3 |
IN180 | Ecology of Deafness | 3 |
IN220 | Voice to Sign/Sign to Voice Interpreting | 3 |
PY125 | Interpersonal Relations | 3 |
TH101 | Introduction to Theatre | 3 |
VC125 | Digital Graphics: Raster | 3 |
WG101 | Introduction to Women and Gender Studies | 3 |
Course Sequence by Semester
Year 1 | |||||
Semester 1 | Semester 2 | ||||
Course # | Course Name | Credits | Course # | Course Name | Credits |
EN___ | English Composition Requirement | 3-4 | ED150 | Introduction to Teaching | 3 |
MA110A | Finite Mathematics | 3 | ED220 | Human Growth and Development | 3 |
PY120 | General Psychology | 3 | SI110/110L OR SI103/103L | Environmental Biology: Theory Environmental Biology: Laboratory OR Introduction to Marine Biology (3)/Marine Biology Laboratory | 4 |
| Elective | 3 | EN111 | Writing for Research | 3 |
Total | 12-13 | Total | 13 | ||
Year 2 | |||||
Semester 3 | Semester 4 | ||||
Course # | Course Name | Credits | Course # | Course Name | Credits |
ED180A | Educational Methods I | 3 | ED265 | Culture and Education in Guam | 3 |
HU120 | Pacific Cultures | 3 | ED180B | Educational Methods II | 3 |
ASL100/ASL110 OR CH110 | American Sign Language I & II (taught in one semester – 8 credits) OR CHamoru I | 4 | ED231 | Introduction to Exceptionalities | 3 |
CS151 OR CO110 | Windows Applications OR Critical Thinking for Civic Engagement | 3 | CH111 | CHamoru II – For those on the CHamoru track | 4 |
|
| For those in the Bachelor Foundation | |||
|
| CTE299A | Praxis I Review Part A | 2 | |
|
| CTE299B | Praxis I Review Part B | 1 | |
Total | 13 | Total | 13-16 | ||
Year 3 | |||||
Semester 5 |
| ||||
Course # | Course Name | Credits |
|
|
|
CO125 | Introduction to Human Communication and Speech | 3 |
|
| |
ED180C | Educational Methods III | 3 |
|
| |
ED292 | Education Practicum | 3 |
|
| |
| Total | 9 |
|
| |
PROGRAM TOTAL | 60-64 | ||||
Liberal Studies students will explore courses in a variety of disciplines and receive the critical thinking, communication, and problem-solving skills that will prepare them for an array of future careers and life-long learning. Guided by advisors and educators, students will carve out a path that is right for them, and must choose one (1) of four (4) tracks of specialization. Students in the program will also complete various general education requirements for transfer to a four-year program.
Program Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs):
Upon successful completion of the AA in Liberal Studies program, students will be able to:
- Plan for an advanced program of study in a particular field or to achieve a career goal, based on interests, skills, and an awareness of different disciplines.
- Examine local, regional, and global issues from multiple perspectives.
- Internalize their role as a global citizen in a local and/or regional context.
Students may choose one of the following tracks. Credits for the tracks come from elective credits. Courses chosen from related fields must be approved by an advisor, English Department Chair, or Registrar.
Liberal Studies Track | ||
General Education Requirements | ||
Course | Course Name | Credits |
English (Choose 1) | ||
EN110A | Freshman Composition with Instructional Lab | 4 |
EN110 | Freshman Composition | 3 |
Course | Course Name | Credits |
MA___ | Mathematics Requirement | 3-4 |
CO110 | Critical Thinking for Civic Engagement | 3 |
Natural and Physical Sciences (Choose 1) | ||
SI103/103L | Introduction to Marine Biology: Theory/ Introduction to Marine Biology: Laboratory | 4 |
SI105/105L | Introduction to Physical Geology/Introduction to Physical Geology Laboratory | |
SI110/110L | Environmental Biology: Theory/Environmental Biology Laboratory | |
Social and Behavioral Sciences (Choose 1) | ||
SO130 | Introduction to Sociology | 3 |
PY100 | Personal Adjustment | |
PY120 | General Psychology | |
WG101 | Introduction to Women and Gender Studies | |
Humanities and Fine Arts (Choose 1) | ||
ASL100 | American Sign Language I | 4 |
JA110 | Japanese I | |
CH110 | CHamoru I | |
KE110 | Korean I | |
Major Requirements | ||
Category A (Choose 1) | ||
HI121 | History of World Civilization I | 3 |
HI122 | History of World Civilization II | |
PI101 | Introduction to Philosophy | |
HM110 | Introduction to Community Services | |
WG101 | Introduction to Women and Gender Studies | |
Category B | ||
EN111 | Writing for Research | 3 |
Category C | ||
CO125 | Introduction to Human Communication and Speech | 3 |
Category D (Choose 1) | ||
HU120 | Pacific Cultures |
3 |
HI176 | Guam History | |
ED265 | Culture and Education in Guam | |
HM201 | Social Welfare & Development: Global Challenges | |
Category E (Choose 1) | ||
ED265 | Culture and Education in Guam | 3 |
PY100 | Personal Adjustment | 3 |
HM110 | Introduction to Community Services | 3 |
HI176 | Guam History | 3 |
HU120 | Pacific Cultures | 3 |
ASL110 | American Sign Language II | 4 |
CH111 | CHamoru II | 4 |
JA111 | Japanese II | 4 |
KE111 | Korean II | 4 |
SI103/SI1103L | Introduction to Marine Biology: Theory/Introduction to Marine Biology: Laboratory | 4 |
SI105/SI105L | Introduction to Physical Geology/Introduction to Physical Geology Laboratory | 4 |
SI110/SI110L | Environmental Biology: Theory/Environmental Biology: Laboratory | 4 |
Category F (Choose 1) | ||
TH101 | Introduction to Theatre | 3 |
EN210 | Introduction to Literature | |
Electives | ||
| Any college level course not previously taken | 3 |
| Any college level course not previously taken | 3 |
| Any college level course not previously taken | 3 |
| Any college level course not previously taken | 3 |
| Any college level course not previously taken | 3 |
| Any college level course not previously taken | 3 |
| Any college level course not previously taken | 3 |
| Any college level course not previously taken | 3 |
Program Total | 62-65 | |
Business Track | ||
General Education Requirements | ||
Course | Course Name | Credits |
English (Choose 1) | ||
EN110A | Freshman Composition with Instructional Lab | 4 |
EN110 | Freshman Composition | 3 |
Course | Course Name | Credits |
MA___ | Mathematics Requirement | 3-4 |
CO110 | Critical Thinking for Civic Engagement | 3 |
Natural and Physical Sciences (Choose 1) | ||
SI103/SI103L | Introduction to Marine Biology/Introduction to Marine Biology Laboratory | 4 |
SI105/SI105L | Introduction to Physical Geology/Introduction to Physical Geology Laboratory | |
SI110/SI110L | Environmental Biology: Theory/Environmental Biology: Laboratory | |
Social and Behavioral Sciences (Choose 1) | ||
SO130 | Introduction to Sociology | 3 |
PY100 | Personal Adjustment | |
PY120 | General Psychology | |
WG101 | Introduction to Women and Gender Studies | |
Humanities and Fine Arts (Choose 1) | ||
ASL100 | American Sign Language I | 4 |
JA110 | Japanese I | |
CH110 | CHamoru I | |
KE110 | Korean I | |
Major Requirements | ||
Category A (Choose 1) | ||
HI121 | History of World Civilization I | 3 |
HI122 | History of World Civilization II | |
PI101 | Introduction to Philosophy | |
HM110 | Introduction to Community Services | |
WG101 | Introduction to Women and Gender Studies | |
Category B | ||
EN111 | Writing for Research | 3 |
Category C | ||
CO125 | Introduction to Human Communication and Speech | 3 |
Category D (Choose 1) | ||
HU120 | Pacific Cultures | 3 |
HI176 | Guam History | |
ED265 | Culture and Education in Guam | |
HM201 | Social Welfare & Development: Global Challenges | |
Category E (Choose 1) | ||
ED265 | Culture and Education in Guam | 3 |
PY100 | Personal Adjustment | 3 |
HM110 | Introduction to Community Services | 3 |
HI176 | Guam History | 3 |
HU120 | Pacific Cultures | 3 |
ASL110 | American Sign Language II | 4 |
CH111 | CHamoru II | 4 |
JA111 | Japanese II | 4 |
KE111 | Korean II | 4 |
SI103/1103L | Introduction to Marine Biology (3)/ Introduction to Marine Biology Laboratory (1) | 4 |
SI105/105L | Introduction to Physical Geology (3)/ Introduction to Physical Geology Laboratory (1) | 4 |
SI110/110L | Environmental Biology: Theory (3)/ Environmental Biology: Laboratory (1) | 4 |
Category F (Choose 1) | ||
Course | Course Name | Credits |
TH101 | Introduction to the Theater | 3 |
EN210 | Introduction to Literature | |
MU110 | Chorale I | |
Business Electives | ||
| Elective (Any AC, SM, or MK, HS, VC, CUL, FSM course or related field) | 3 |
| Elective (Any AC, SM, or MK, HS, VC, CUL, FSM course or related field) | 3 |
| Elective (Any AC, SM, or MK, HS, VC, CUL, FSM course or related field) | 3 |
| Elective (Any AC, SM, or MK, HS, VC, CUL, FSM course or related field) | 3 |
| Elective (Any AC, SM, or MK, HS, VC, CUL, FSM course or related field) | 3 |
| Elective (Any AC, SM, or MK, HS, VC, CUL, FSM course or related field) | 3 |
| Elective (Any AC, SM, or MK, HS, VC, CUL, FSM course or related field) | 3 |
| Elective (Any AC, SM, or MK, HS, VC, CUL, FSM course or related field) | 3 |
Program Total | 62-65 | |
Health and Science Track | ||
General Education Requirements | ||
Course | Course Name | Credits |
English (Choose 1) | ||
EN110A | Freshman Composition with Instructional Lab | 4 |
EN110 | Freshman Composition | 3 |
Course | Course Name | Credits |
MA___ | Mathematics Requirement | 3-4 |
CO110 | Critical Thinking for Civic Engagement | 3 |
Natural and Physical Sciences (Choose 1) | ||
SI103/103L | Introduction to Marine Biology: Theory/Introduction to Marine Biology: Laboratory | 4 |
SI105/105L | Introduction to Physical Geology/Introduction to Physical Geology Laboratory | |
SI110/110L | Environmental Biology: Theory/Environmental Biology Laboratory | |
Social and Behavioral Sciences (Choose 1) | ||
SO130 | Introduction to Sociology | 3 |
PY100 | Personal Adjustment | |
PY120 | General Psychology | |
WG101 | Introduction to Women and Gender Studies | |
Humanities and Fine Arts (Choose 1) | ||
ASL100 | American Sign Language I | 4 |
JA110 | Japanese I | |
CH110 | CHamoru I | |
KE110 | Korean I | |
Major Requirements | ||
Category A (Choose 1) | ||
HI121 | History of World Civilization I | 3 |
HI122 | History of World Civilization II | |
PI101 | Introduction to Philosophy | |
HM110 | Introduction to Community Services | |
WG101 | Introduction to Women and Gender Studies | |
Category B | ||
EN111 | Writing for Research | 3 |
Category C | ||
CO125 | Introduction to Human Communication and Speech | 3 |
Category D (Choose 1) | ||
HU120 | Pacific Cultures | 3 |
HI176 | Guam History | |
ED265 | Culture and Education in Guam | |
HM201 | Social Welfare & Development: Global Challenges | |
Category E (Choose 1) | ||
ED265 | Culture and Education in Guam | 3 |
PY100 | Personal Adjustment | 3 |
HM110 | Introduction to Community Services | 3 |
HI176 | Guam History | 3 |
HU120 | Pacific Cultures | 3 |
ASL110 | American Sign Language II | 4 |
CH111 | CHamoru II | 4 |
JA111 | Japanese II | 4 |
KE111 | Korean II | 4 |
SI103/1103L | Introduction to Marine Biology/Introduction to Marine Biology Laboratory | 4 |
SI105/105L | Introduction to Physical Geology/Introduction to Physical Geology Laboratory | 4 |
SI110/110L | Environmental Biology: Theory/Environmental Biology: Laboratory | 4 |
Category F (Choose 1) | ||
Course | Course Name | Credits |
TH101 | Introduction to the Theater | 3 |
EN210 | Introduction to Literature | |
MU110 | Chorale I | |
Health and Science Electives | ||
| Elective (Any MA, SI, HL, NU, MS, CJ, HM courses or related field) | 3 |
| Elective (Any MA, SI, HL, NU, MS, CJ, HM courses or related field) | 3 |
| Elective (Any MA, SI, HL, NU, MS, CJ, HM courses or related field) | 3 |
| Elective (Any MA, SI, HL, NU, MS, CJ, HM courses or related field) | 3 |
| Elective (Any MA, SI, HL, NU, MS, CJ, HM courses or related field) | 3 |
| Elective (Any MA, SI, HL, NU, MS, CJ, HM courses or related field) | 3 |
| Elective (Any MA, SI, HL, NU, MS, CJ, HM courses or related field) | 3 |
| Elective (Any MA, SI, HL, NU, MS, CJ, HM courses or related field) | 3 |
Program Total | 62-65 | |
The categories A, B, C, D, E, and F above correspond to the following UOG gen ed categories:
Category A: Human Systems and Organizations (Tier II)
Category B: Core Foundation (Tier I)
Category C: Core Foundation (Tier I)
Category D: Cultural Perspectives (Tier II)
Category E: Uniquely UOG (Tier II)
Category F: Creative and Expressive Arts (Tier II)
Note on Major Requirements: Where more than one option is presented, choose one course from each category. Choose courses not previously taken for General Education or another category. If you are planning to transfer, you should choose courses that align with the general education requirements of your desired major at a four-year institution. Consult with your advisor to create your educational plan.
CHamoru Education and Culture Track | ||
General Education Requirements | ||
Course | Course Name | Credits |
English (Choose 1) | ||
EN110A | Freshman Composition with Instructional Lab | 4 |
EN110 | Freshman Composition | 3 |
Course | Course Name | Credits |
MA___ | Mathematics Requirement | 3-4 |
CO110 | Critical Thinking for Civic Engagement | 3 |
Natural and Physical Sciences (Choose 1) | ||
SI103/SI103L | Introduction to Marine Biology (3)/ Introduction to Marine Biology Laboratory (1) | 4 |
SI105/SI105L | Introduction to Physical Geology (3)/ Introduction to Physical Geology Laboratory (1) | |
SI110/SI110L | Environmental Biology: Theory (3)/ Environmental Biology: Laboratory (1) | |
Social and Behavioral Sciences (Choose 1) | ||
SO130 | Introduction to Sociology | 3 |
PY100 | Personal Adjustment | |
PY120 | General Psychology | |
WG101 | Introduction to Women and Gender Studies | |
Humanities and Fine Arts (Choose 1) | ||
CH110 | CHamoru I | 4 |
Major Requirements | ||
EN111 | Writing for Research | 3 |
CO125 | Introduction to Human Communication and Speech | 3 |
ED265 | Culture and Education in Guam | 3 |
ED150 | Introduction to Teaching | 3 |
ED220 | Human Growth & Development | 3 |
HI176 | Guam History | 3 |
CH111 | CHamoru II | 4 |
CH125 | CHamoru Expressions of Art | 3 |
CH200 | Immersion Method for CHamoru Language Teaching I | 3 |
CH220 | CHamoru Composition | 3 |
CH250 | Utugrafihan Chamoru, Guahan | 3 |
Electives (Choose 2) | ||
CH230 | Teaching CHamoru History and Culture | 3 |
EN220 | Best Practices for Literacy Instruction | 3 |
CH240 | CHamoru Language Content Standards | 3 |
Program Total | 60-61 | |
Students qualify for graduation once the following requirements are met:
- Achieve a 2.0 cumulative GPA as an undergraduate student.
- Meet individual program requirements, including major GPA (if applicable).
- Fulfill residency requirements – at least 12-degree applicable credit hours of coursework completed at the College.
- Successfully complete the program pertaining to their degree.
- Submit Application for Graduation to the Admissions & Registration Office by the applicable deadline and pay the graduation fee.
- Meet financial obligations to the school.
NOTE: A single course cannot be used to satisfy more than one course requirement in a program.
Effective fall Semester 2003, several academic policy changes were implemented to ensure that students are adequately prepared to meet business and industry standards. All Undeclared or newly Declared Students enrolled in regularly scheduled postsecondary courses must be enrolled in or have completed EN110 Freshman Composition general education requirement by the time they have enrolled in 12 credits of classes. They must also enroll in or have completed MA110A Finite Mathematics (or higher) general education requirement by the time they have enrolled in 15 credits. This means that students may take only nine to eleven (9-11) credits before they must begin meeting the general education requirements. All declared students in the Bachelor’s Degree program are required to successfully complete minimum standardized general education course requirements. For more information, refer to the Admissions Information and General Education Policy section of this catalog.
All candidates for a Bachelor’s Degree at the College must meet the general requirements listed above. Course requirements may identify Prerequisites that must be completed with a passing grade. Prerequisite course credit is not counted as credit earned towards the program unless it is a Bachelor’s Degree core course requirement.
A second certificate and/or degree may be granted provided that a student completes all additional major and general education requirements. Some programs of study offer more than one track; a student may earn a degree, which includes more than one track so long as the student completes the requirements before the degree is conferred.
Recognizing the necessity for students to succeed in the complex and rapidly changing workplace, Guam Community College offers a general education curriculum that introduces students to major areas of knowledge and methods of inquiry. All degree programs require an interdisciplinary general education component that promotes the development of intellectual skills that enable students to become effective learners and informed citizens. Critical thinking, the use of language and computation, appropriate social skills, global awareness and respect for diverse opinions are among the learning outcomes provided in the general education requirements of each program.
Guam Community College believes that general education provides the academic foundation necessary for students to achieve their life goals. General education is intended to offer students a breadth of quality student learning experiences, encourage their respect for cultural heritage, promote their ethical and responsible social behavior and facilitate their life-long learning.
The General Education program strives to foster student learning and skill development in civic engagement, critical thinking, understanding of the relationship between the individual and society, information literacy, oral communication, quantitative reasoning, and written communication.
Guam Community College believes that high quality general education opportunities for all citizens are necessary for democratic principles and practices to exist and for a sound economy to flourish. The College continually scrutinizes the general education curriculum in order to assure that all degrees and certificates granted by the College support this vision of general education and that it serves as a means to inspire hope, opportunity and responsibility in all its constituencies.
Requirements for General Education follow the options described below. Students declared prior to fall 2010 will follow the requirements indicated in the applicable catalog in which they first declared their major program at the College.
Notes on General Education requirements
Students are advised to check the requirements for their specific programs before taking General Education courses.
Courses chosen to meet the general education requirements may not be used to meet the Major Requirements of a student’s specific degree program.
The list contains courses with prerequisites, so students should make their choices carefully and thoughtfully. Students may consult a counselor or an academic advisor for guidance in choosing any of the course options listed.
IMPORTANT NOTE: Some programs require different levels of coursework to meet General Education requirements, please review the individual programs for more information.
Minimum program length of 120 semester credit hours awarded for achievement of student learning for a Bachelor’s of Science degree.
Program Student Learning Outcomes follow each program description in the following pages. SLOs intentionally describe the 3-5 central goals that students will have attained by the end of the program. In essence, SLOs encapsulate the knowledge, skills, and attitudes that students are expected to learn from their respective programs. The focus is on what students can do with what they have learned and this outcome should be evaluated in some way. Primarily, three questions essentially frame the articulation of SLOs:
- What do students know? (cognitive domain)
- What do they think and value? (affective domain)
- What can they do? (behavioral domain)
In this catalog, program SLOs describe the broadest goals for the program, particularly those that require higher-level thinking. They, therefore, require students to synthesize many discrete skills or areas of content. SLOs also ask students to produce artifacts such as term papers, projects, portfolios, demonstrations, exams or other student work. Most importantly, SLOs also need to be evaluated or assessed in some way so that accountability and improvement remain the hallmarks of a good program. A separate SLO Booklet is published and updated regularly to guide faculty in helping students achieve articulated course outcomes.
The College, in close collaboration with faculty and members of Advisory committees, continues to embark on an ongoing institutional effort to revise and update all its curriculum documents so that they remain responsive to industry and community needs.
SLO Mapping - ILO, PROGRAM, AND COURSE LEVELS
SLOs also align with collective program and institution level expectations for student learning translated into the curriculum and co-curriculum. Most importantly, these SLOs map to the curriculum, co-curriculum and other educational practices that provide students multiple opportunities for meaningful learning. SLO maps developed for three (3) different levels – ILOs, program, and course -- reflect the desired goals of learning experiences that the College continues to intentionally develop, structure, deliver, and evaluate on an ongoing basis.
The Bachelor of Science in Career and Technical Education (BS CTE) program aims to produce high-quality CTE educators who will possess technical expertise, pedagogical competencies and values to effectively teach 21st century skills, using culturally-responsive teaching, to diverse learners. The program conforms to the standards of the Association for Advancing Quality in Educator Preparation (AAQEP) and the National Board of Professional Teaching Standards (NBPTS-CTE). As designed, the program provides students with the necessary tools to seek employment in K-12, trade and technical schools, community colleges, and in industry or business environments. This program offers students the opportunity to articulate an Associate Degree in any career and technical education field of study to GCC’s Bachelor of Science in CTE. It also prepares students for CTE teaching certification with the Guam Educator Commission for Certification.
Refer to the Advance CTE website for additional information on Career and Technical Education (www.careertech.org).
Program Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs):
Upon successful completion of the BS in Career and Technical Education, students will be able to:
- Create an engaging classroom environment aligned to the needs of diverse learners.
- Plan, develop, and deliver curriculum that is based on rigorous and relevant expectations and culturally-relevant teaching methodology.
- Integrate into instruction effective and research-based teaching and learning principles embedded with best assessment practices and use of technology.
- Apply leadership and ethical principles in the implementation and management of CTE programs.
General Education Requirements | ||
Course # | Course Name | Credits |
English (Choose 1) | ||
EN110 | Freshman Composition | 3 |
EN110A | Freshman Composition with Instructional Lab | 4 |
Course # | Course Name | Credits |
EN111 | Writing for Research | 3 |
EN300 | Writing for Educators | 3 |
Mathematics | ||
Course # | Course Name | Credits |
MA115 (or higher) | Fundamentals of College Algebra | 3 |
MA151 | Introductory Statistics | 3 |
MA385 | Applied Statistics | 3 |
Literacy for Life Skills | ||
Course # | Course Name | Credits |
CO110 | Critical Thinking for Civic Engagement | 3 |
Humanities & Fine Arts | ||
Course # | Course Name | Credits |
CO125 | Introduction to Human Communication and Speech | 3 |
Natural & Physical Sciences (Choose one course and the corresponding lab from the following to meet the required 4 credits)** | ||
Course # | Course Name | Credits |
SI101/101L | Introduction to Chemistry (3) & Introduction to Chemistry Laboratory (1) | 4 |
SI103/103L | Introduction to Marine Biology (3) & Introduction to Marine Biology Laboratory (1) | |
SI105/105L | Introduction to Physical Geology (3) & Introduction to Physical Geology Laboratory (1) | |
SI110/110L | Environmental Biology: Theory (3) & Environmental Biology: Laboratory (1) | |
SI141 | Applied Physics I | |
SI 150/150L | Introduction to Microbiology: Theory (3) & Introduction to Microbiology: Laboratory (1) | |
SI131/131L | Human Anatomy & Physiology I: Theory (3) & Human Anatomy & Physiology I Laboratory (1) | |
SI132/132L | Human Anatomy & Physiology II: Theory(3) & Human Anatomy & Physiology II Laboratory (1) | |
**The exception to this would be SI141 which does not include a laboratory requirement | ||
Social & Behavioral Sciences | ||
Course # | Course Name | Credits |
ED265 | Culture and Education in Guam | 3 |
PY120 | General Psychology | 3 |
PY325 | Work Ethic in Career and Technical Fields | 3 |
Minimum General Education Requirements | 37-38 | |
Major Requirements | ||
Course | Course Name | Credits |
| CTE Area of Study | 40 |
ED150 | Introduction to Teaching | 3 |
ED220 | Human Growth & Development | 3 |
CTE300 | Introduction to Teaching CTE | 3 |
CTE305 | Foundations of Online Teaching | 3 |
CTE310 | CTE Methods of Teaching I: Planning and Preparation | 3 |
CTE320 | Classroom and CTE Laboratory Management | 3 |
CTE330 | Educational Technology | 3 |
CTE340 | CTE Methods of Teaching II: Instructional Delivery | 3 |
CTE350 | Assessment and Standards-Based Grading | 3 |
CTE400 | CTE Program Management and Leadership | 3 |
CTE410 | Methods of Teaching III: Project-Based Learning | 3 |
CTE492 OR CTE498 | Student Teaching-CTE OR CTE Student Learning (Classroom Teachers) | 12 |
CTE499 | Introduction to Action Research | 3 |
Total | 93 | |
Program Total | 125-126 | |
*For students holding an Associate’s or a Bachelor’s degree in a CTE field of study and have transferred in at least 52 college credits in their respective CTE field and some General Education requirements. Each student situation will differ.
Courses offered by the College are numbered as follows:
000-049 these courses are noncredit courses. These courses may satisfy prerequisite requirements and/or provide appropriate remediation for courses numbered 050-099 in the same subject areas.
050-099 these courses except for MA096, MA097, MA098, EN096, and EN097 are accepted toward meeting the requirements of the Adult High School and some Certificate/Degree programs.
100-299 These courses are accepted toward meeting requirements of the Associate of Arts and Associate of Science degrees conferred by the College. These courses are also accepted toward meeting the requirements of certificates conferred by the College.
Course numbers indicate the level of the course. Courses numbered 100-199 are intended for freshman or sophomore students; courses numbered 200-299 are intended for sophomore students.
Courses numbered 100-299 may be used to meet Adult High School Diploma requirements. Diploma Students taking courses numbered 100-299 to meet the Adult High School Diploma should select such courses with the advice and approval of their counselor or advisor.
Note: The course descriptions that follow are alphabetized by course alpha and number (i.e., from AC100 to WE220). They are also grouped by fields of study.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs) at the course level, follow these course descriptions. SLOs at the course level describe what students should be able to perform, apply, or produce in relation to how and what they have learned. In the course SLOs that follow, clear and intentional expectations are laid out, particularly as they define the goals of student learning experiences. In a nutshell, they specify what students should be able to know, do, or value after participating in planned learning activities.
With this AY 2025-2026 catalog, continuous efforts to revisit all curriculum documents so that SLOs become integral components of each and every course at the College have been completed. This effort will continue for all new courses.
Before the course descriptions, there is a notation about the frequency of offerings, i.e., spring only, fall only, or as needed. Summer courses are also scheduled as needed. The College, however, always reserves the right to cancel courses, due to low student enrollment or other justifiable reasons.
AC100 FUNDAMENTALS OF BOOKKEEPING AND ACCOUNTING
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: MA098 or higher
This course covers accounting principles to include interpreting source documents, analyzing business transactions; recording entries in a general journal; posting to the ledger, preparing the worksheet with adjustments; journalizing, adjusting and closing entries; preparing financial statements, and the post-closing trial balance.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Apply accounting procedures to properly record financial information about a business.
- Apply generally accepted accounting theory and principles to perform all the steps of the accounting cycle for a service and retail type business.
- Perform internal control procedures to protect and properly manage cash and other business assets.
AC110 PAYROLL ACCOUNTING
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: Placement into MA110A or higher
This course covers the most current methods and procedures of calculating payroll and payroll taxes. It includes the latest developments in payroll tax law, covering information on wages, payroll operations, employment practices, and voluntary employee deductions; differences between the USA and the Territory of Guam payroll accounting systems are examined.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Explain why laws and regulatory compliance pertaining to personnel and payroll records are integral to a company.
- Calculate wages, explore earnings records, and prepare a payroll register.
- Perform all aspects of payroll operations.
- Develop basic data analysis skills for accounting using Excel.
AC150 FEDERAL INCOME TAX I
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: MA098 or higher
A study of the basic forms and structures of federal taxation, particularly aspects which affect individual taxpayers, to include: components of tax formula, the use of the standard deduction. Personal exemption qualifications, filing systems, tax tables, exclusions from income, various categories of deductions, investment losses and passive activity losses, net operating losses, and tax credits.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Explain what the federal income tax is and distinguish it from other types of federal taxes.
- Demonstrate knowledge of the components of the basic income tax formula, understand when income and deductions are recognized and describe when they are excluded (or disallowed) or deferred for individuals.
- Apply necessary steps to compute a taxpayer's federal income tax liability and apply tax language and terms appropriately throughout the process of computing a taxpayer's federal income tax return.
AC210 INTRODUCTION TO FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: AC211
This course covers the basic fundamentals of financial management for a business. Students will learn about financial management with focus on statement analysis, procurement and utilization of funds, costs and problems associated with acquiring funds, forecasting profits gained through their use, markets, risk and rate of return, time value of money, valuation of stocks and bonds, dividend policy and financial planning and working capital management.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Describe the major financial markets and their role.
- Analyze financial statements to determine future prospects of a business.
- Forecast a financial statement using a set of financial assumptions.
AC211 ACCOUNTING PRINCIPLES I
Credits: 4
Prerequisite: Placement into MA098 or higher
This course prepares the student for entry-level accounting jobs, such as accounting clerk and bank teller. Students will interpret and apply accounting principles and concepts to record and report accounting data for sole proprietorship and merchandise business; apply internal control procedures, such as special journals and subsidiary ledgers; apply inventory costing methods; processing account issues for receivables, bank reconciliation and petty cash; calculate depreciation schedules for assets; and record data for intangible assets.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Apply accounting principles and concepts to record and report business financial data.
- Perform all the steps in the procedure of the accounting cycle for a service and merchandise business.
- Calculate inventory data using various types of costing methods.
AC212 ACCOUNTING PRINCIPLES II
Credits: 4
Prerequisite: AC211
Accounting theory and principles are discussed relating to corporations, manufacturing, budgeting and cost analysis. Specific topics include current and contingent liabilities, accounting for corporations, accounting for corporate income taxes, investments in bonds, accounting for bonds payable, the Statement of Cash Flows, Financial Statement analysis, job order and process costing systems.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Demonstrate proficiency in preparing corporate financial statements including the statements of cash flows and statement of stockholder's equity.
- Conduct a product cost analysis utilizing managerial accounting process.
- Illustrate the use of standards in budgeting.
AC225 HOSPITALITY INDUSTRY ACCOUNTING
Credits: 3
Course Offering: Fall
Prerequisite: AC211
This course presents the fundamentals of financial accounting through hospitality industry simulation-problems and experiences. Accounting topics include procedures for merchandise and supplies inventories, fixed assets and depreciation methods, current liabilities and payroll, internal controls of cash, receivables and payables. Major elements of financial statements for the hospitality industry are emphasized.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Implement procedures for merchandise and supplies inventories, fixed assets and depreciation methods, current liabilities and payroll, internal controls of cash, receivables and payables.
- Perform analysis and interpretation of financial statements of the hospitality industry.
- Discuss computerized accounting systems prevalent in hospitality businesses that use special journals and subsidiary ledgers.
AC233 ACCOUNTING ON THE COMPUTER USING QUICKBOOKS
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: AC212
Students will apply accumulated accounting knowledge and skills such as payroll, federal tax, inventory management, accounts payable, accounts receivable, and cash management. They will develop extensive skills using the features of QuickBooks accounting software.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Apply key features in QuickBooks Online and customize using best practice in bookkeeping principles.
- Utilize QuickBooks Online to manage daily bookkeeping tasks and develop an understanding of how the data is entered, processed and reviewed.
- Review accounting knowledge and adapt to computer accounting skills.
AC240 CERTIFIED BOOKKEEPER REVIEW
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: AC211
A detailed study and review structured to prepare students to pass the national test for Certified Bookkeeper (CB) given by the American Institute of Professional Bookkeepers (AIPB). This course covers specific topics such as adjusting entries, reconciliation and errors, payroll, depreciation, and inventory.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Utilize mastery-level skills required in bookkeeping.
- Apply proper procedures in bookkeeping.
- Discuss the universal Code of Ethics for bookkeepers.
AC250 FEDERAL INCOME TAX II
Credits: 3
Course Offering: Spring only
Prerequisite: AC150
This course is the second of two courses on Federal Taxation structure. Emphasis is given to the unique factors involved in taxation of individuals and other U.S. Federal tax returns such as a partnership and corporation. It includes the latest developments in federal tax laws, covering information on property transactions, retirement plans, partnerships/S corporation basis and loss limitations.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Explain basic tax policy considerations underlying the income tax law to arrive at reasoned solutions to problems for individuals, partnerships and corporations.
- Discuss how taxes affect economic decisions for individuals and business entities including depreciation, payroll, and retirement.
- Conduct tax research.
AC280 PERSONAL FINANCE
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: EN110 or higher
Students will develop a financial plan for their personal and professional use. Elements of financial planning are presented and include: financial goals and objectives; personal financial statements and budget; cash and credit management; personal tax planning; housing, insurance and investment decisions; and retirement. This course provides the basic foundation to understand and discuss the “language” of routine financial activities.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Analyze and compare elements of personal and professional financial plans.
- Apply critical thinking skills and concepts when developing a financial plan for personal and professional use.
- Present their financial plan project that reflects the acquisition of course content.
AC292 ACCOUNTING PRACTICUM
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: AC233 or Accounting Advisor Approval
This course provides students a supervised work experience where they apply the skills necessary to be successful in an accounting career. This course allows students to showcase their knowledge and skills in a well-established workforce prior to their graduation.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Apply theory learned in the classroom to the work environment.
- Practice effective interpersonal skills in the workplace.
- Document the synthesis of knowledge and skills gained through work experience in a reflection paper or electronic presentation.
AE103 BASIC BLUEPRINT READING
Credits: 3
This course will introduce the basic skills in reading and interpreting blueprint drawings and prepare basic to advanced technical sketches. Additionally, students will learn the basic principles, concepts, American National Standards Institute (ANSI) and International System of Units (SI) Metric drafting symbols and standards, terminology, and other related technical information contained on a mechanical or Computer-Aided Design (CAD) drawing.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Identify the basis for blueprinting reading and sketching.
- Create basic and/or advanced technical sketches.
- Apply symbols and notes to visually communicate drawings and sketches.
AE121 TECHNICAL ENGINEERING DRAWING I
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: AE103
This course involves the use of drawing instruments and techniques of drafting management skills for mechanical, civil, and architectural drawings involving freehand sketches, lettering, orthographic views and pictorial drawings. Students will learn how to use drawing instruments for accurate measurements with detailed instructions.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Explain basic components of a blueprint.
- Demonstrate proper use of drafting instruments to draw existing plans.
- Measure existing drawings for accuracy.
AE122 TECHNICAL ENGINEERING DRAWING II
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: AE121
This course involves the creation of working drawings of simple building structures, floor plans, front and rear elevations, left and right elevations, transverse and longitudinal sections, cabinets, closet and bar details, plumbing, electrical, and site and plot plans. Students will also render topographic maps.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Create a set of working drawings.
- Depict different elevation views accurately.
- Incorporate plumbing symbols into a typical house plan.
- Incorporate electrical symbols into a typical house plan.
AE138 BUILDING CODES, SPECIFICATIONS & CONSTRUCTION MANAGEMENT
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: Placement into EN110 or equivalent
In this course, students will study and apply local and national building codes and standards, construction documents, and office organization. This course will be of value to anyone who plans to enter or is presently working in the field of construction and/or engineering.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Explain local and national building codes and standards.
- Identify the process for acquiring a building permit.
- Explain the various agencies’ functions in the permitting process.
AE150 COMPUTER AIDED DRAFTING I (CAD I)
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: AE122
This course introduces students to computer aided drafting software as a drafting tool and to the use of computers in producing line drawings. Students will learn topics including equipment components, terminology, storing and retrieving drawings, and printing and plotting. Students will use the computer-aided drafting software application.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Produce line drawings using computer aided drafting technology.
- Demonstrate basic proficiency in the use of the computer aided drafting software.
- Explain basic equipment components and terminology used in computer aided drafting-related careers.
AE160 COMPUTER AIDED DRAFTING II (CAD II)
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: AE150
This course presents students with intermediate editing techniques in computer aided drafting. Students will learn the roles of an architectural/engineering CAD operator and will learn to use a 3D printer. Students will also gain knowledge and practical experience necessary for entry-level jobs requiring computer aided drafting. Formerly Computer Aided Drafting II (CADD II).
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Create a construction drawing set consisting of at least six sheets from a given design.
- Produce an electronic document that complies with building codes.
- Produce 3-dimensional editing figures with a 3D printer.
AE170 REVIT ARCHITECTURE ESSENTIALS
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: AE160
This course will teach students Revit’s functionality as it pertains to the design process. Students will create 3D architectural project models and set up working drawings. Technical training focuses on theory, concepts, and basic tools of BIM (Building Information Modeling) to work with Autodesk Revit Architecture.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Explain the purpose of Building Information Management (BIM) and how it is applied in Revit.
- Utilize the Revit Architecture workspace and interface.
- Create increasingly complex drawings in Revit.
ASL100 AMERICAN SIGN LANGUAGE I
Credits: 4
This course provides students with beginning skills in American Sign Language, including fingerspelling the alphabet, signing basic numbers and using basic vocabulary to facilitate communication with the Deaf in ASL. In addition, students will be introduced to deaf culture and the importance of using body and facial expressions to convey information and to develop visual acuity.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Demonstrate initial communication skills for basic conversation in American Sign Language (ASL) that includes basic vocabulary and fingerspelling of the alphabet and numbers.
- Practice the use of visual and gesture communication skills for basic conversation.
- Interact with deaf people in an accepting and sensitive manner.
ASL110 AMERICAN SIGN LANGUAGE II
Credits: 4
Prerequisite: ASL100
This course is a continuation of American Sign Language I. The course objectives are to continue to develop basic syntactic knowledge of American Sign Language, vocabulary, fingerspelling, and conversational skills. Aspects of the Deaf community and culture are also incorporated.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Demonstrate the use of American Sign Language that includes manually-coded English and fingerspelling.
- Demonstrate expanded vocabulary and communicative functions in American Sign Language.
- Engage in appropriate and meaningful interactions with members of the Deaf community.
ASL120 AMERICAN SIGN LANGUAGE III
Credits: 4
Prerequisite: ASL110
Corequisite: IN145
The course provides intermediate conversational skills in American Sign Language with an emphasis on expressive and receptive skills development. Students will further their understanding of American Sign Language syntax, vocabulary, and signing skills. Deaf culture will be further explored.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Utilize American Sign Language at an intermediate level.
- Expand ASL vocabulary as demonstrated through the development of grammatical structure within stories, narratives, and dialogues.
- Demonstrate appropriate interactions and communication skills using Deaf Culture facial grammar and body movement.
ASL130 AMERICAN SIGN LANGUAGE IV
Credits: 4
Prerequisite: ASL120
Corequisite: IN220
This is the fourth course in the American Sign Language (ASL) sequence. Students will learn advanced competency and fluency in American Sign Language, grammar, and syntax. Cultural features and variations in ASL are also addressed.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Competently communicate in American Sign Language.
- Apply appropriate signing skills to illustrate one’s understanding of the culture within the Deaf community.
- Demonstrate critical thinking and appropriate ethical responses required by the Registry of Deaf Interpreter’s Code of Professional Conduct.
AST100 INTRODUCTION TO AUTOMOTIVE SERVICE
Credits: 3
This course introduces the student to core principles in Automotive Service Technology, providing them with the foundational knowledge necessary for success in all additional Automotive Service Technology upper 100-level courses. Students will become familiar with basic concepts and practices related to automotive service, safety and customer service.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Apply proper shop safety concepts and practices.
- Describe good customer relations.
- Identify and properly use basic hand tools and shop equipment
- Explain how a gasoline engine functions.
- Diagnose basic automotive problems using measurements.
AST110 ENGINE REPAIR
Credits: 3
Course Offering: Spring Only
Prerequisite: DC approval
This course covers core principles in Engine Repair, to include the foundational knowledge necessary for more advanced study and experiential development of engine repair skills.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Verify engine mechanical timing.
- Measure camshaft for run-out, journal wear, and lobe wear.
- Remove engine cylinder head clean and visually inspect for cracks, warpage, and any damage to mating surfaces.
- Inspect and replace the camshaft and drive belt/chain.
AST113 HYBRID ENGINES AND MOTOR/GENERATORS
Credits: 4
Corequisite: AST260
This course introduces students to core principles of hybrid electric vehicle engine and motor/generator propulsion technology. Students will learn skillsets necessary for diagnosing and making repairs to hybrid electric vehicles.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Demonstrate proper safety practices when servicing high-voltage hybrid electric vehicles.
- Diagnose hybrid engine failures.
- Explain the operation of permanent magnet and induction electric motors.
- Differentiate the functionality of electrical inverter and converter components.
- Troubleshoot faults in the electric propulsion sensing system.
AST120 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION AND TRANS-AXLE
Credits: 6
Prerequisite: None
Corequisite: AST100
This strategy-based diagnostic offers students a theoretical and practical understanding of automatic transmissions and transaxles and provides students with the technical background, diagnostic strategies, and repair procedures they need to successfully repair automatic transmissions.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Differentiate between engine performance and transmission/transaxle concerns.
- Demonstrate how to properly drain and replace fluid and filter.
- Describe the operational characteristics of a Continuously Variable Transmission (CVT).
- Inspect oil delivery circuits.
- Assess planetary gear assembly components.
AST123 HEV ENERGY MANAGEMENT, TRANSAXLES, AND BATTERIES
Credits: 4
Prerequisite: AST113
This course introduces the student to core principles of hybrid electric vehicle energy management, transaxles, and batteries. Students will learn skillsets necessary for diagnosing and making repairs to hybrid electric vehicles.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Describe the functionality of a hybrid electric vehicle energy management system.
- Illustrate hybrid transaxle construction.
- Perform drive system fault analysis.
- Troubleshoot battery system faults.
AST130 MANUAL DRIVE TRAIN AND AXLES I
Credits: 6
Prerequisite: AST100
This strategy-based diagnostic course offers students a theoretical and practical understanding of manual transmissions and drive train and provides students with the technical background, diagnostic strategies, and repair procedures they need to successfully repair automatic transmissions when they enter the industry.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Diagnose drive train concerns.
- Bleed clutch hydraulic system.
- Describe the operational characteristics of an electronically controlled manual transmission/transaxle.
- Disassemble, inspect, clean, and reassemble internal transmission/transaxle components.
- Adjust drive pinion bearing preload.
AST133 BELTED ALTERNATOR STARTER (BAS), POWER ELECTRONICS, AND SUPPORT SYSTEMS
Credits: 4
Prerequisite: AST113
This course introduces the student to core principles of hybrid electric vehicle Belted Alternator Starter (BAS), power electronics, and support systems. Students will learn the skillsets necessary for diagnosing and making repairs to hybrid electric vehicles.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Describe the Belted Alternator Starter (BAS) system.
- Explain the functionality of the hybrid support systems power electronics.
- Diagnose hybrid power electronic system faults.
- Perform hybrid support system fault analysis.
AST140 SUSPENSION AND STEERING
Credits: 6
Course Offering: Spring Only
Prerequisite: AST100
This strategy-based diagnostic course offers students theoretical and practical knowledge of suspension and steering systems. Students will gain the entry-level technical background, diagnostic strategies and repair procedures they need to successfully repair suspension and steering systems when they enter the industry.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Identify and interpret suspension and steering system concerns.
- Demonstrate proper steps to disable and enable Supplemental Restraint System (SRS).
- Diagnose suspension system noise.
- Remove, inspect, service and/or replace front and rear wheel bearings.
- Perform pre-alignment inspections.
AST150 BRAKE SYSTEMS I
Credits: 6
Prerequisite: AST100
This strategy-based diagnostic course offers students a theoretical and practical knowledge of automotive brake systems. Students will gain the entry-level technical background, diagnostic strategies, and repair procedures they need to successfully repair brake systems.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Identify and interpret brake system concerns.
- Demonstrate proper steps to bleed and/or flush brake system.
- Diagnose poor stopping concerns.
- Inspect caliper mounting and slides/pins for proper operation, wear, and damage.
- Describe the operation of a regenerative braking system.
AST160 ELECTRICAL/ELECTRONIC SYSTEMS
Credits: 5
Course Offering: Fall Only
Prerequisite: AST100
This theory course offers students an in-depth conceptual understanding of automotive Electrical and Electronic Systems and provides students with the foundation needed for the advanced studies in the second of this two-part electrical course. Emphasis is given to interpretation and utilization of electrical diagrams.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Demonstrate knowledge of electrical/electronic series, parallel, and series-parallel circuits using principles of electricity (Ohm’s Law).
- Diagnose the cause of shorts, grounds, opens, and resistance problems in electrical/electronic circuits.
- Use wiring diagrams during the diagnosis (troubleshooting) of electrical/electronic circuit problems.
- Perform battery state-of-charge test.
- Determine the cause(s) of excessive key-off battery drain (parasitic draw).
AST170 HEATING, VENTILATION, AND AIR CONDITIONING (HVAC)
Credits: 6
Course Offering: Spring Only
Prerequisite: None
Corequisite: AST100
This strategy-based diagnosis course offers students theoretical and practical knowledge in Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning systems. It provides students with the technical background, diagnostic strategies, and procedures needed to successfully repair HVAC systems.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Conduct airconditioning performance test.
- Remove, inspect, reinstall and/or replace A/C compressor.
- Describe the procedure to remove and reinstall an evaporator.
- Diagnose temperature control problems in the HVAC system.
- Demonstrate correct use of refrigerant handling equipment.
AST180 ENGINE PERFORMANCE
Credits: 8
Prerequisite: AST260
This course introduces students to core principles in systems related to the performance of an engine providing them with the foundational knowledge necessary for more advanced study and experiential development of skills in diagnosing and making repairs to engine performance control systems.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Perform engine electronic control system diagnostics.
- Determine mechanical integrity of an internal combustion engine.
- Test ignition system input sensors to determine needed action.
- Demonstrate a cylinder cranking and running compression tests.
AST210 THEORY/PRACTICUM: ENGINE REPAIR
Credits: 3
Course Offering: Fall Only
Prerequisite: AST100, AST110
This theory/practicum course builds on AST110, offering students a more in-depth conceptual understanding of engine repair and providing them with the opportunity to apply this knowledge in continually developing their automotive skills.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Remove and reinstall engine assembly with minimal supervision.
- Repair problems related to the cylinder head and valve train.
- Diagnose and repair cylinder block related faults.
- Service cooling and lubrication system.
AST220 AUTOMOTIVE TRANSMISSION AND TRANSAXLE II
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: AST120
This course will present students with comprehensive theoretical and conceptual information in the area of automatic transmission / transaxle systems. Students are also given the opportunity to demonstrate their transmission / transaxle diagnosis and repair knowledge and skill through practical, experiential application.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Diagnose hydraulic pressure concerns.
- Perform in-vehicle transmission repairs.
- Overhaul transmission.
AST230 THEORY/PRACTICUM: MANUAL DRIVE TRAIN AND AXLES
Credits: 2
Course Offering: Spring Only
Prerequisite: AST100, AST130
This theory/practicum course builds on AST130, offering students a more in-depth conceptual understanding of manual drive trains and axles, and providing them with the opportunity to apply this knowledge in continually developing their automotive skills.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Perform general transmission and transaxle diagnostics with minimal supervision.
- Replace clutch pack components.
- Remove, disassemble, repair, and reinstall transmission, transaxle, and differential assemblies.
- Service and repair drive shafts, half shafts, and constant velocity joints.
AST240 THEORY/PRACTICUM: SUSPENSION AND STEERING
Credits: 2
Course Offering: Fall Only
Prerequisite: AST100, AST140
This theory/practicum course builds on AST140, offering students a more in-depth conceptual understanding of suspension and steering, and providing them with the opportunity to apply this knowledge in continually developing their automotive skills.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Remove and reinstall engine assembly with minimal supervision.
- Repair problems related to the cylinder head and valve train.
- Diagnose and repair cylinder block related faults.
- Service cooling and lubrication system.
AST250 THEORY/PRACTICUM: BRAKES
Credits: 2
Course Offering: Spring Only
Prerequisite: AST100, AST150
This theory/practicum course builds on AST150, offering students a more in-depth conceptual understanding of brakes, and providing them with the opportunity to apply this knowledge in continually developing their automotive skills.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Perform advance brake system diagnostics.
- Diagnose and repair faults in the hydraulic system.
- Determine drum brake failure causes and perform needed repairs.
- Replace power assist units.
- Diagnose antilock brake system malfunctions and perform needed repairs.
AST260 THEORY/PRACTICUM: ELECTRICAL/ELECTRONIC SYSTEMS
Credits: 5
Course Offering: Spring Only
Prerequisite: None
Corequisite: AST160
This is the second part of the Electrical and Electronic Systems specialty course. Students will learn advanced diagnostic and repair procedures offering them a more in-depth conceptual understanding of electrical and electronic systems providing them with the opportunity to apply this knowledge in continually developing their automotive skills. This course utilizes a strategy-based diagnostic approach to help students develop and master their technical trouble shooting skills.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Demonstrate proper use of a digital multimeter (DMM).
- Perform starting system circuit voltage drop tests.
- Diagnose (troubleshoot) charging system for causes of undercharge, no-charge, or overcharge conditions.
- Describe the process for software transfer, software updates, or reprogramming of electronic modules.
- Inspect and test gauges and gauge sending units for causes of abnormal readings.
AST270 THEORY/PRACTICUM: HEATING AND AIR CONDITIONING
Credits: 2
Course Offering: Fall Only
Prerequisite: AST100, AST170
This theory/practicum course builds on AST170, offering students a more in-depth conceptual understanding of heating and air conditioning systems, and providing them with the opportunity to apply this knowledge in continually developing their automotive skills.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Perform advanced diagnostics on air conditioning and heating systems.
- Replace air conditioning and heating system components with minimal supervision.
- Diagnose and repair operating and control system.
AST280 ADVANCED ENGINE PERFORMANCE
Credits: 8
Course Offering: Spring Only
Prerequisite: None
Corequisite: AST180
This theoretical and practical course builds on AST180, offering students a more in-depth conceptual understanding of engine performance. The course takes a strategy-based diagnostic approach that helps students master skills needed to diagnose and resolve engine performance concerns. Students will gain an understanding of current diagnostic tools and advanced performance systems as they prepare to service the engines of tomorrow.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Demonstrate required service on the fuel system.
- Diagnose the causes of emissions or driveability concerns with stored or active diagnostic trouble codes.
- Inspect and test computerized engine control systems using a graphing multimeter (GMM)/digital storage oscilloscope (DSO).
- Troubleshoot ignition system related concerns.
CD110 INTRODUCTION TO EARLY CHILDHOOD EDUCATION
Credits: 3
The course provides an overview of entry-level knowledge and skills in the early childhood education field as well as an overview of major domains (i.e. physical, cognitive, social, and emotional). The course also covers developmentally appropriate practices (DAP) in early childhood birth through age eight, careers, safety, employment skills, and job opportunities for those entering the early childhood education and related fields.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Differentiate among the physical, social, emotional, and cognitive developmental domains related to early childhood.
- Integrate activities and components of a developmentally appropriate learning environment for young children.
- Explore and discuss various careers in early childhood education that serve children from birth through age eight.
CD140 NUTRITION AND PHYSICAL HEALTH
Credits: 3
This course provides students with strategies to promote nutrition and physical health of young children in early childhood settings. Topics include developmentally and age appropriate meal planning, scheduling, and physical activities.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Demonstrate strategies that promote children’s nutrition.
- Design age appropriate physical activities for children from birth to eight years of age.
- Create healthy and balanced meal plans for young children.
CD180 LANGUAGE ARTS DEVELOPMENT IN EARLY CHILDHOOD
Credits: 3
Topics include knowledge of language development in young children, skills needed as educators to promote language development to include listening, speaking (oral), reading, and writing. Emphasis is placed on the planning and implementation of activities which enhance and develop language and literacy skills. In addition, students will develop resources and materials that are appropriate to teach language arts to young children using evidence-based practices which emphasize Universal Design for Learning to meet the needs of all abilities. Students will also learn best practices in promoting children’s language development within the context of cultural and linguistic diversity.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Compare and contrast language development theories (i.e. Skinner, Chomsky, Gesell, Piaget, and Vygotsky) as it relates to ages birth through eight years.
- Create activities that build literacy skills.
- Implement a lesson plan for young children which develops and enhances language skills.
CD221 CHILD GROWTH & DEVELOPMENT
Credits: 3
This course provides students with an overview of the interrelationship between physical, emotional, cognitive, language and social growth in young children from conception through the early primary school years. Topics include prenatal care, brain research, and the effects of heredity and environment. The roles of the family, culture, community and society and how they impact development is also explored.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Describe the social, physical, and cognitive development of children birth through age eight.
- Explain prenatal development and factors that promote a healthy pregnancy to include the first few years of life.
- Analyze the impact of family, culture, community and society on development.
CD240 COGNITIVE & CREATIVE DEVELOPMENT IN EARLY CHILDHOOD
Credits: 3
In this course, students will plan and implement developmentally appropriate practices that promote the cognitive and creative domains of development in young children birth to age eight. Students will be able to incorporate creativity in various subject areas to include music, visual and performing arts, language arts, science, and mathematics.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Incorporate creativity in all content areas of developmentally appropriate early childhood environments through original lesson plan design.
- Plan, write, and implement creative lessons and activities for young children that incorporate cognitive and creative goals aligned with Guam Early Learning Guidelines, Common Core, Next Generation Science Standards, and/or Guam Dept. of Education standards.
- Demonstrate current practices and methods for teaching lessons focused on the subject areas of music, art, science, and mathematics.
CD260 SOCIAL AND EMOTIONAL DEVELOPMENT
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: CD110
This course teaches skills needed to promote social and emotional development in young children and use positive guidance strategies to handle inappropriate behavior. Temperament, parenting styles, and child rearing issues such as feeding, potty training, and tantrums are a few of the topics covered. This course also provides students opportunities to plan and implement activities that promote children’s self-concept, emotional, social and pro-social development.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Demonstrate knowledge in the domains of social and emotional development in young children.
- Plan and implement a lesson plan which promotes cultural identity, self-concept, self-esteem, self-regulation, emotional, social and/or pro-social development.
- Apply skills in using positive guidance strategies in an early childhood education setting to include adult modeling and conflict resolution.
CD285 CHILDCARE MANAGEMENT
Credits: 3
This course provides students with an overview of local requirements for starting and managing a profitable childcare business on Guam. Students will learn financing, marketing, staff supervision, staff training, writing policies, licensing requirements, quality rating improvement systems, and operating procedures.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Identify current laws and regulations controlling the child care industry and different agencies responsible for licensing early childhood (EC) programs on Guam.
- Develop childcare facility policies to ensure safety and compliance with local regulations.
- Conduct an observation of a child care center facility on Guam using the Environmental Rating Scale.
CD292 EARLY CHILDHOOD EDUCATION PRACTICUM
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: Department Chair Approval
This course provides students with the opportunity to demonstrate professionalism and employ reflective practices while completing 135 practicum hours in an early childhood setting (birth to third grade) under the supervision of a certified professional. Practicum students will be required to assist in a school or center, as needed, which may include conducting observations and assessments, attending meetings, creating a conducive learning environment, and implementing age-appropriate activities. Students should be enrolled in their last semester of the Certificate and/or Associate of Science in Early Childhood Education program and completed their major courses.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Reflect on the practices, pedagogy, and resources in early childhood setting that serves children ages birth through age eight years.
- Implement developmentally and age-appropriate teaching, assessment and guidance strategies needed to effectively work with young children.
- Communicate with students, staff and families including those from diverse backgrounds and special populations.
CD293 EARLY CHILDHOOD CDA PRACTICUM
Credits: 12
This course integrates 480 hours of experience working with young children in an infant-toddler or preschool setting, and preparation of a Child Development Associate (CDA) Professional Portfolio. It covers the emotional, physical, intellectual, and social development of children birth to five years old and is designed to prepare students to successfully fulfill the requirements for the CDA credential.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Complete 480 practicum hours in an early childhood setting that serves children ages birth to five while adhering to The National Association for the Education of Young Children’s Code of Ethics.
- Create a professional portfolio as required by the CDA credentialing program’s guidelines (https://www.cdacouncil.org/credentials/apply -for-cda).
- Implement developmentally and age-appropriate teaching strategies in an early childhood program.
CE210 STATICS
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: MA161B and SI141
Statics is the study of bodies at rest - in a state of balance with their surroundings. Through the applications of the principles of statics, we answer such questions as: What load will the column have to support? What is the tension of the bridge cable?; What is the mechanical advantage of the block and tackle? Statics is an analytical subject and it makes extensive use of mathematics in all of its forms: Algebra, Geometry, and Trigonometry.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Successfully apply Algebra, Geometry, and Trigonometry as needed when solving problems.
- Identify and describe key concepts of Force Systems, Center of Gravity, Equilibrium, Force Analysis of Structures, Friction, and Movement.
- Identify and analyze given information and data and employ proper procedures and formulas to solve problems.
- Solve problems using appropriate technology.
CE211 PLANE SURVEYING I
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: MA161A
A beginning course in surveying techniques designed to give the student an understanding of the fundamentals of chaining, leveling, and proper use of the transit. Care and adjustment of instruments and office procedure are also considered. Provision is made by appropriate fieldwork for practical application of the techniques learned.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Describe the fundamentals of chaining, leveling, and use of transit as it relates to plane surveying.
- Demonstrate the proper use of plane surveying equipment.
- Utilize a task checklist to demonstrate the proper use of surveying equipment and tools.
CE215 CONSTRUCTION PROCEDURES
Credits: 3
A study of construction organization, building codes, foundations, construction materials, methods and techniques of cast-in-place reinforced concrete, precast and pre-stressed concrete, steel and masonry construction, wood and plastics, thermal and moisture protection and building equipment.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Explain the difference between precast and post stress concrete.
- Describe the process involving the construction of a building foundation.
- Chronologically sequence the steps related to the construction process.
CE222 PLANE SURVEYING II
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: CE211
This course is a continuation of Plane Surveying I dealing with modern surveying including construction surveying and surveying for engineering design. The students are introduced to modern surveying technology including Global Positioning Systems (GPS) and Geographic Information Systems (GIS). Reconnaissance and field procedures and methods are discussed and the students will be divided into survey teams and given area assignments to perform survey fieldwork including topographic surveys for contour maps. The students are exposed to the prospects of employment as survey and civil engineering technicians.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Successfully apply Mathematics including Algebra, Geometry, and Trigonometry as needed to solve surveying problems.
- Demonstrate a variety of surveying techniques.
- Apply appropriate skills using proper surveying instruments given various surveying tasks.
- Solve surveying problems using technology such as calculators or computers, total stations, global positioning systems, or leveling instruments as appropriate.
CE225 CONSTRUCTION PLANNING & ESTIMATING
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: AE12 and CE215
This course covers methods of estimating construction costs including excavation, highway, structures, piling and foundations; methods to determine qualities of materials, equipment, labor, and money required for construction projects; characteristics and capabilities of work equipment; methods of obtaining unit cost of in place construction; and field reporting practices and responsibilities of field inspection.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Determine costs needed for various construction projects.
- Estimate the amount of time required to complete a given construction project.
- Apply critical thinking to determine labor hours versus equipment costs versus material costs.
CH110 CHAMORU I
Credits: 4
This is a CHamoru language immersion course for beginners. Students will spend the semester learning to communicate in CHamoru through activity-based exercises on topics such as greetings, self-description, and home and work life. The focus of this class is on listening and comprehending. Students will also engage in activities that promote language revitalization.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Comprehend basic conversations in CHamoru on very familiar topics.
- Enunciate and ask common questions and respond to such questions in CHamoru.
- Report on language and cultural revitalization efforts on island.
CH111 CHAMORU II
Credits: 4
Prerequisite: CH110
This CHamoru language immersion course for novices is a continuation of CH110. Students will spend the semester communicating in CHamoru through storytelling, description, and conversation. The focus of this class is on listening, comprehending, and speaking. Students will also engage in activities that promote language revitalization.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Engage in simple conversations in CHamoru on familiar topics.
- Tell short stories in CHamoru with visual aids.
- Discuss language revitalization efforts on island and their connection to culture.
CH125 CHAMORU EXPRESSIONS OF ART I
Credits: 3
Corequisite: CH110 or CH111
With an emphasis on hands-on experience and performance, this course provides an immersive CHamoru language environment for students who are interested in studying one or more CHamoru art forms. Students will study Kåntan CHamorita, chant, dance, carving, body ornamentation, weaving, culinary arts, hut building, and/or other art forms. CHamoru stories, traditions, and ways of teaching and learning will promote the arts and CHamoru language acquisition.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Showcase skills in one or more CHamoru art forms.
- Discuss the role of art in perpetuating culture and language.
- Respect CHamoru traditions, art forms, and language.
CH200 IMMERSION METHOD FOR CHAMORU LANGUAGE TEACHING I
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: CH111
This course introduces students to foundational skills for teaching CHamoru language using the immersion method. Students will explore examples of immersion teaching, guiding principles, lesson plan development, and assessment from a practical approach. A major focus of the course is creating authentic contents for learning CHamoru in efforts to develop fluent CHamoru speakers over time.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Teach CHamoru language and culture using immersive techniques.
- Create an immersion-based lesson plan that reflects authentic literacy skills in the CHamoru language.
- Value immersive instruction as a method of perpetuating CHamoru language and culture.
CH220 CHAMORU COMPOSITION
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: CH111
Students in this course will develop literacy skills in CHamoru through reading, writing, revising, and editing short essays, legends, and stories in CHamoru. Students will explore language and engage in translation exercises.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Employ the writing process (prewriting, organizing, drafting, revising, editing) and writing strategies.
- Identify writing strategies used by authors.
- Compose short essays, legends and stories in CHamoru.
CH230 TEACHING CHAMORU HISTORY AND CULTURE
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: CH200
This course teaches students content and methods for teaching CHamoru history and culture. Students will be guided through periods of history from a CHamoru perspective. They will examine non-tangible aspects of culture within historical and contemporary resources, and develop projects that combine history and culture. Guest speakers and field trips will take learning and history out of the classroom.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Reapproach history from a CHamoru-centric perspective.
- Use cultural frameworks to analyze traditional and alternative sources of history.
- Feel equipped to share and apply knowledge of historical and cultural content in educational settings.
CH240 CHAMORU LANGUAGE TEACHING STANDARDS
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: CH111
This course develops students’ capacity to effectively implement Guam Department of Education’s CHamoru Language and Culture Content Standards and assess student language capabilities.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon Successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Unpack and implement GDOE CHamoru Language and Culture Content Standards.
- Demonstrate theory-supported second language teaching techniques and methodologies.
- Use performance indicators and proficiency scales for assessing language learning.
CH250 UTUGRAFIHAN CHAMORU, GUAHAN
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: CH111
This course examines the CHamoru orthography of Guam. It is a project-based course where students will study the Kumision I Fino’ CHamoru publication entitled Utugrafihan CHamoru Guahan (2024) and edit Chamoru-language texts appropriately following the orthography.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon Successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Demonstrate an appreciation of the history and value of the Guam orthography.
- Edit CHamoru language texts according to the conventions of the Guam orthography.
- Explain orthographical rules and provide examples.
CJ100 INTRODUCTION TO CRIMINAL JUSTICE
Credits: 3
This course offers an overview of the criminal justice system from its early historical development to its evolution within the United States. It also identifies the various agencies of justice-law enforcement, courts, corrections, and the juvenile justice system, their functions, expectations and interrelationships.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Describe the history and development of the Criminal Justice System.
- Identify the role of the Criminal Justice System in contemporary society.
- Describe the functions of law enforcement, courts and corrections.
- Describe the functions of probation, parole, and the Juvenile Justice System.
CJ101 JUVENILE JUSTICE PROCESS
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: CJ100
Corequisite: EN110 placement or equivalent
This course is designed to provide students with a fundamental understanding of the history, philosophy, and practical application of the American Juvenile Justice System. Students will examine the juvenile justice responsibilities of police, courts, and juvenile corrections with additional emphasis on current practices of Juvenile Justice agencies in Guam.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Describe the history, philosophy, and development of the Juvenile Justice System.
- Identify and distinguish the various components of the Juvenile Justice System.
- Apply Title 19 Guam Code Annotated, Chapter 5, The Family Court Act, to hypothetical situations.
CJ102 FIRST RESPONDER
Credits: 3
The First Responder course shall be at least 48 hours of classroom training. It aims to provide training in emergency medical care for those who are apt to be the first person responding to an accident. When the course is completed, the student will possess the same knowledge of patient care as the EMT, but not the same equipment skills. Can be repeated for credit.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Diagnose emergency situations and provide appropriate emergency treatment.
- Explain and discuss the role of a First Responder.
- Demonstrate the First Responder skillset at an acceptable level as required by local regulations.
- Demonstrate proficiency in BLS and CPR by passing the final skills practical exams and written exam required by the DOT to become a certified First Responder.
CJ104 DYNAMICS OF SUBSTANCE ABUSE
Credits: 3
This course is designed to introduce students to the problems of substance abuse in our society. Students will examine the history of dangerous drug use, basic pharmacology and classification, the social impact of drug abuse, physical and psychological consequences of drug use and dependence, various treatment modalities, legal implications of illicit drug use, and current law enforcement efforts.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Articulate the medical, social and/or psychological aspects of addiction.
- Demonstrate understanding of the different schedules under the Controlled Substances Act.
- Identify and apply the detection, suppression, apprehension and prosecution procedures of substance abuse violations.
CJ107 INTRODUCTION TO CORRECTIONS
Credits: 3
This course is intended as an introduction to the corrections system and will provide an overview of current institutional practices, policies, constitutional rights of offenders, and other legal issues. The course focuses on the relation of corrections to the criminal justice system, theories underlying correctional practices, and the role of institutions within the corrections system. It reviews the historical development of crime and corrections, sentencing, jails, prisons, correctional policies, agencies, prison life, challenges facing correctional populations, and the major programs within the corrections component of the criminal justice system. It includes analysis of probation, institutional treatment, parole, and community corrections programs.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Identify the role of corrections in the criminal justice system in the United States in relation to philosophies of punishment, sentencing practices, victim’s rights and institutional limitations.
- Trace the historical evolution of the correctional system in the United States.
- Explain the role of probation, parole, pretrial services, work release, and educational release programs.
- Explain and analyze the correctional process, the effectiveness of corrections and the role of corrections in a contemporary society.
- Describe the legal rights of inmates and the loss and restoration of civil rights.
CJ122 INTRODUCTION TO FORENSIC SCIENCE
Credits: 4
Prerequisite: CJ100
Cross Listed as SI122. This course introduces students to the field of forensic science. Students will be able to identify the various principles, methods and procedures used in the preservation, collection, processing, and investigation of the crime scene as well as identify the various scientific techniques used to evaluate and analyze the evidence to resolve criminal matters. Students will also be familiar with some of the legal and ethical issues in forensic science.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Describe the history and development of forensic science.
- Identify the role of forensic science within the criminal justice system.
- Identify the various analytical tools used to evaluate, process, investigate and adjudicate criminal cases.
- Describe the various scientific techniques used to preserve, collect and analyze evidence.
- Identify some of the legal and ethical issues in forensic science.
CJ126 OFFICER SURVIVAL
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: Instructor permission
This course provides law enforcement academy recruits with the knowledge and skills necessary to perform a variety of police tasks safely and effectively.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Identify the safety techniques to use when approaching a potentially dangerous or life threatening situation.
- List street survival skills an officer should acquire while on duty.
- Demonstrate the ability to apply officer safety and street survival skills at an acceptable level in mock situations.
CJ126L OFFICER SURVIVAL LABORATORY
Credits: 1
Prerequisite: CJ126
This course provides students with the opportunity to practice and demonstrate “hands on” application of survival skills learned in CJ126. The laboratory may be conducted by interested law enforcement agencies at the conclusion of the basic law enforcement academy.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Practice the various officer safety and street survival skills in mock situations.
- Demonstrate proficiency in the use of the various officer safety and street survival skills at acceptable levels.
CJ132 EMERGENCY VEHICLE OPERATOR COURSE
Credits: 3
This course is designed as a traditional course and prepares police and fire recruits to safely operate emergency vehicles used by their respective agencies. Enrollment is limited to students currently in the Criminal Justice Academies and Fire Science Academy.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Identify, apply, and practice the vehicle safety skills used during an emergency response.
- Explain and practice the proper operation of emergency vehicles.
- Identify and properly deal with hazards involved with operating emergency vehicles.
- Review the basics of defensive driving and understand the laws governing emergency vehicle operation.
- Demonstrate the safe use and maintenance of emergency vehicles required for successful completion of the various phases of the physical driving course.
CJ135 FIREARMS USE/SAFETY/CARE
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: Permission by CJ Advisor AND Valid Firearms Identification Card
This course is designed to teach law enforcement and corrections students the proper use and care of firearms and chemical weapons. Emphasis is placed on safety, use of deadly force, marksmanship, judgmental shooting, and the care and cleaning of weapons.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Understand the physical attributes and mechanics of a firearm.
- Apply knowledge of firearm safety.
- Demonstrate knowledge of firearm related laws.
- Practice safe use of firearms within a controlled environment.
- Demonstrate use of firearms at prevailing acceptable and passing levels.
CJ140 DEFENSIVE TACTICS
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: By permission
Stressing control through verbal persuasion is strongly preferred to physical force. This course is especially designed to control prisoners and maximize protection of the public, corrections officers, and inmates. Physical fitness is emphasized.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Perform control and self-defense tactics.
- Demonstrate understanding of prevention, intervention and resolution techniques.
- Demonstrate how to apply the use of force and the continuum of force.
- Explain the legal issues involved in handling persons in custody, detainees, prisoners and inmates.
CJ145 PHYSICAL DEVELOPMENT
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: Enrollment into a CJ Academy
This course is designed to develop a positive attitude toward physical fitness and to understand the relationship between physical fitness, productivity, health, and safety. This course is conducted through the Office of Continuing Education & Workforce Development for career public safety officers and recruits. Instructor permission is required.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Develop a positive attitude toward physical fitness.
- Demonstrate understanding of the relationship between physical fitness, productivity, health, and safety.
- Participate in physical development exercises.
- Demonstrate the use of the various physical development exercises.
CJ148 TRAFFIC LAW ENFORCEMENT
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: CJ100
Corequisite: CJ150
This course provides students with the knowledge and skills necessary in the identification and enforcement of Guam’s traffic laws. Students will be acquainted with the terminology, facts and concepts of pedestrian, bicycle and motor vehicle violations to include a comprehensive understanding of Title-16 Guam Code Annotated, the Vehicle Code of Guam. Additionally, students will be able to recognize what immediate steps are required at a traffic related scene necessary to protect life and property, how to give traffic citations, how to deal with DUI offender cases, how to operate radar and laser devices, and how to conduct traffic direction and accident investigation.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Interpret and apply Title 16, Guam Code Annotated (the Vehicle Code of Guam) and related statutes to hypothetical situations.
- Demonstrate the proper use, care, operations and limitations of Radar and Laser speed measuring instruments and other traffic enforcement devices.
- Demonstrate Guam Police Department (GPD) protocols concerning the enforcement of Guam’s Safe Streets Act of 2018 laws including DUI Checkpoint Procedures, DUI Traffic Stops, Field Sobriety and Breathalyzer Testing and Arrest and Post-Arrest Protocols.
- Demonstrate GPD Red-Light Running, Distracted Driving, and Click it or Ticket Seatbelt Enforcement Protocols.
CJ150 CRIMINAL PROCEDURE
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: CJ100
Corequisite: EN110 or EN110A
This course provides an overview of the criminal justice process, the court system, and the U.S. Constitution with emphasis on the method of case interpretation of the U.S. Supreme Court and the Criminal Procedure Code of Guam.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Identify the various legal sources that establish the basic rights of individuals accused or convicted of crimes in the United States.
- Describe the various stages and established procedures of the American Criminal Justice System.
- Identify landmark US Supreme Court and other appellate court decisions that impact the criminal justice process.
- Apply and demonstrate the use of the Guam Law and case law to hypothetical situations.
CJ200 CRIMINAL LAW
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: CJ100
Corequisite: EN110 or EN110A
This course is designed to introduce students to the history, philosophy, and application of U.S. Federal and Guam criminal laws. It provides students with an understanding of crime classifications, matters affecting criminal responsibility, criminal statutes including those of Guam, and the role of criminal law in contemporary society.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Describe the origin and evolution of U.S. Criminal Laws and the U.S. Federal and Guam/State Court systems and their relationship to each other.
- Identify the basic principles of Criminal Law.
- Distinguish the elements of various common law and statutory crimes.
- Apply Guam’s substantive criminal laws under the Guam Code Annotated (GCA) to hypothetical situations.
CJ204 INTRODUCTION TO CRIMINOLOGY
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: CJ100
This course provides a fundamental understanding of criminal behavior, crime topologies, and the various theories of crime causation. Students will also explore the efforts of society to remedy, correct, and prevent crime and delinquency.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Explain and analyze crime, criminology, and the criminal justice system.
- Evaluate the history and evolution of criminology and the criminal justice system.
- Identify the various theories of crime causation.
- Identify the various crime typologies.
CJ205 REPORT WRITING FOR LAW ENFORCEMENT
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: EN100R, EN100W or by permission from the CJ Advisor and/or Department Chair.
This course is designed to emphasize the key principles and techniques in the development of various types of report writing for law enforcement professionals. Report writing proficiency will focus upon evidence gathering, report organization, sentence and content development. Formerly CJ205 Police Report Writing.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Organize relevant information to write an effective report.
- Differentiate amongst the various types of evidence required for different law enforcement report forms.
- Demonstrate writing techniques for effective report writing.
CJ206 SOCIAL VALUES & THE CRIMINAL JUSTICE PROCESS
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: SO130
This course is designed to provide an in-depth exploration consistent with the philosophy that social value and ethics are basic principles of a sound criminal justice process, and the roles of the administration of justice practitioners in relation to the public they serve. Through interaction and study, the student will become aware of the interrelations and role expectations of the human dimension required by practitioners in developing empathy, sensitivity and acceptable behavior. Instruction on the importance of open communication and accountability to those within and without the justice process is explored.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Analyze community-policing strategies.
- Demonstrate the role of police and professionalism.
- Identify the various ethical issues of policing.
- Explain how political, social, and economic issues relate to law enforcement.
CJ209 CONCEPT OF POLICE OPERATIONS
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: CJ100
Corequisite: EN110 or EN110A
This course provides students with operational knowledge needed to function successfully in a modern police agency. Concepts are particularly useful for first-line supervisors and managers. Topics include effective supervision, communication skills, problem solving, time management, motivation and morale, effective discipline, interpersonal conflict, stress management, productivity issues, and performance appraisals.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Explain and evaluate the structure, organization, and management of police or other law enforcement agency.
- Explain and analyze the various types of police operations and the methods and strategies used to implement policies and other executive decisions.
- Demonstrate understanding of the interrelations, role, conflict and trends of police and law enforcement in modern society.
CJ225 CRIMINAL INVESTIGATION
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: CJ100 and CJ205 or advisor permission
This course provides students with the knowledge and technical skills necessary to successfully investigate crime scenes, identify suspects, and successfully present evidence in court. Skills learned and practiced include processing crime scenes, preserving and evaluating evidence collected, interviewing witnesses and suspects, case preparation, and presenting evidence in court.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Apply the various methods used in investigating criminal cases to hypothetical situations.
- Explain and evaluate the investigation, processing, and preservation of a crime scene.
- Identify and analyze the various methods used to obtain information.
CJ250 POLICE ORGANIZATIONAL THEORY
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: CJ100
Corequisite: EN110 or EN110A
This course examines and analyzes the traditional concepts, techniques, policies and operating systems in the police component of the criminal justice system. Basic knowledge of the police organizational function, structure, processes, and behavior is emphasized. Theories related to the practice applied to the administration of justice process and the comprehension of administrative phenomena is explored.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Apply the various management theories and styles.
- Explain and evaluate the structure and organization of police and other law enforcement agencies.
- Identify and analyze the concepts of leadership, decision making, accountability, responsibility, and liability.
CJ292 CRIMINAL JUSTICE PRACTICUM
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: DC or Advisor approval
This capstone course is for the Associate of Science Degree in Criminal Justice and a required course for the Certificate in Criminal Justice. In addition, this course allows students first hand, practical experience in observing a participating in the daily operations of an agency in a criminal justice related field. The principles, theories and methodologies acquired in the Criminal Justice courses will be applied to actual situations. The experience will create an awareness for specific problems encountered in a particular criminal justice related agency to further acquaint the student with terminology, facts and conceptions relating to that agency and develop within the student an understanding of the importance of that agency’s roles in the criminal justice process. Supervised work experience affords students the opportunity to develop skills necessary to succeed in the Criminal Justice field.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Integrate classroom knowledge and theories with outside work experience.
- Develop practical work-related skills.
- Explain the operations of a criminal justice related agency.
- Practice the daily operations policy of a criminal justice related agency.
CM101 COSMETOLOGY I
Credits: 10
The primary purpose of this course is for students to acquire basic manipulative skills in shampooing, haircutting, nail care, and skin care with compliance to infection control and all safety operations in order to obtain licensure and competency in entry-level positions required in the field of cosmetology. Students will have the opportunity to complete 450 hours of in-class and salon practices under the supervision of a licensed cosmetologist.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Perform analytical skills to determine the desired look for a client’s hair, skin, and nails.
- Apply entry level cosmetology techniques for hair, skin, and nails.
- Utilize proper sanitation and safety guidelines in accordance with the Guam Board of Cosmetology’s Rules and Regulations during all services rendered.
CM102 COSMETOLOGY II
Credits: 10
Prerequisite: CM101
This is a lecture/lab course offered in the second semester of the program. It includes instruction in haircutting, hair coloring, chemical texture, principles of hair design, hairstyling, and pedicure services. Successful completion of this course will help students reach the goal of obtaining licensure and competency in entry-level positions required in the field of cosmetology. Students will have the opportunity to complete 450 hours of in-class and salon practices under the supervision of a licensed cosmetologist.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Perform procedures in various haircutting, styling, chemical texture, and hair coloring services to a client’s satisfaction.
- Model basic nail services in a class and/or salon setting, to include foot and leg massage.
- Apply critical thinking and problem solving skills while conducting cosmetology services.
CM104A COSMETOLOGY III
Credits: 5
Prerequisite: CM102
This course emphasizes skills introduced and practiced in CM101 Cosmetology I and CM102 Cosmetology II, to develop in a salon/lab environment. Students will gain experience in a salon open to the public and is designed to give the students the opportunity to further enhance their cosmetology and/or barbering skills. The level of performance rendered is at a minimum competency needed for an entry-level skilled position in the field of cosmetology and/or barbering (450 clock hours). Students may recover clock hours via a Continuing Education CM192 Cosmetology Lab (5 credit) course. If a student is not present by the end of the second day of class they may be dropped.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Describe the skills and knowledge needed for hair coloring, chemical texture, basic styling, nail, and skin care and/or barbering services in a salon setting.
- Practice appropriate customer service skills when performing cosmetology and/or barbering services in a salon setting.
- Apply test taking strategies in preparation for the Guam Board of Barbering and Cosmetology exam to be a licensed cosmetologist and/or barber.
CM104B COSMETOLOGY IV
Credits: 5
Prerequisite: CM104A
This course builds on skills practiced in CM104A Cosmetology III to develop a mastery skill level in a salon/lab environment. The focus of this course is to prepare the student to successfully apply and pass the National Cosmetology Practical Examination. The College’s salon, which is open to the public, is designed to give the students the opportunity to perfect their cosmetology skills. The level of performance rendered, is above the minimum needed for an entry-level skilled position in the field of cosmetology (450 clock hours). Students will practice practical and written exam scenarios to prepare for the National Interstate Council of State Boards of Cosmetology Examination in order to obtain a Guam license to qualify for positions in the cosmetology field.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Apply skills needed for services in a salon setting based on the content domains of the National Cosmetology Practical Examination.
- Create a business plan utilizing marketing features such as a pamphlet or video that focuses on the student’s area of interest.
- Demonstrate preparedness to pass the written and practical cosmetology exam required by the National Interstate Council of State Boards of Cosmetology (NIC) and Guam Board of Barbering and Cosmetology (GBBC).
CO110 CRITICAL THINKING FOR CIVIC ENGAGEMENT
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: Placement into EN110 or equivalent
The world and our Micronesian region is facing environmental, political, and economic challenges that require civic engagement. This course provides students with the opportunity to practice fundamental thinking skills for approaching real-world challenges. Students will learn to approach civic and interpersonal challenges by evaluating evidence in order to develop solutions and draw informed conclusions.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Discuss the importance of civic engagement in our region and local community.
- Analyze arguments in various contexts.
- Explain an issue or problem using clear and direct language.
- Formulate a sound argument to advance a specific solution for a real-world challenge.
CO125 INTRODUCTION TO HUMAN COMMUNICATION AND SPEECH
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: Placement into EN110 or successful passing of EN097
In this course, students will apply communication theories, concepts and skills to their own real-world experiences. The goal is to develop students’ self-awareness, understanding of culture, and communication skills for more effective communication in a variety of contexts. Students will also prepare and present speeches. Formerly EN125.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Demonstrate listening and information gathering skills.
- Explain the role of culture in communication.
- Apply communication skills through actual applications.
- Develop and deliver speeches for a variety of purposes.
CS101 INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER SYSTEMS AND INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY
Credits: 3
This course provides students with an overview of computer technology, computer hardware and software, data communications, Internet resources, programming concepts and other technologies integral to everyday life.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Apply knowledge of computer systems and information technology such as history, terminology, algorithms, and other basic concepts.
- Choose the proper application to produce the desired result.
- Navigate the Internet using various resource tools.
CS104 VISUAL BASIC PROGRAMMING
Credits: 3
This course covers the introductory fundamentals of the Visual Basic programming language. Students will learn object-oriented and event-driven programming concepts and develop applications using Visual Basic programming language.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Design, create, build, and debug Visual Basic applications using the Visual Basic Integrated Development environment.
- Create Visual Basic applications using object-oriented programming techniques.
- Create Visual Basic applications using forms, controls, and events.
CS112 INTRODUCTION TO LINUX
Credits: 3
Introduction to Linux course presents students with an open-source alternative to Windows operating system. This course discusses installation, simple administrations, and usage of Linux systems as both workstation and server. Questions about where to find, how to install and configure, and how to use open-source software will be covered. This course will better prepare students for the Linux Professional Institute’s (LPI) Linux Essentials Professional Development Certificate exam.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Identify practical differences between Windows and Linux operating systems.
- Install a Linux workstation and perform a simple configuration.
- Use Linux system for everyday purposes.
CS151 WINDOWS APPLICATIONS
Credits: 3
The students will learn the fundamental nature of microcomputers: the hardware devices that make up the physical machine, the operating systems, and the major types of application software. Students are exposed to the concepts and applications of word processing, graphics, desktop publishing, spreadsheet, database, and communications software. They are shown the far reaching effects of computers and technology, and the applications that computers have to their own lives. Finally, the course provides students hands-on experience with real world applications using the Windows environment and the application software for Windows: Word Processing, Spreadsheet, Database and Presentation.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Understand the basic functionality of Microsoft Word, Excel, Access, and PowerPoint.
- Apply knowledge of Microsoft applications in completion of projects and activities.
- Integrate use of Microsoft applications in the Windows environment.
CS152 MACINTOSH APPLICATIONS
Credits: 3
The students will learn the fundamental nature of microcomputers: the hardware devices that make up the physical machine, the operating systems, and the major types of application software. Students are exposed to the concepts and applications of word processing, graphics, desktop publishing, spreadsheet, database, and communications software. They are shown the far reaching effects of computers and technology, and the applications that computers have to their own lives. Finally, the course provides students hands-on experience with real world applications using the Macintosh environment and the application software for Macintosh: Word Processing, Spreadsheet, Database and Presentation.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Understand the basic functionality of Microsoft Word, Excel, Access, and PowerPoint.
- Apply knowledge of Microsoft applications in completion of projects and activities.
- Integrate use of Microsoft applications in the Macintosh environment.
CS203 SYSTEMS ANALYSIS AND DESIGN
Credits: 3
This course offers a practical, streamlined, and updated approach to information technology systems analysis and design. Students will learn how to translate business requirements into information systems that support a company’s short-and-long-term objectives by applying project management concepts, tools, and techniques. Students will understand how IT supports business requirements in today’s intensely competitive environment through emerging technologies, such as agile methods, cloud computing, and mobile applications in systems analysis and design.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Describe the importance of system analysis and design in today’s dynamic business environment.
- Use an emerging technology in system analysis and design.
- Manage system implementation of an IT project.
CS204 C++ PROGRAMMING
Credits: 3
This course teaches object-oriented C++ programming language through the concepts of program specification and design, algorithm development, coding and testing using a modern software development environment. Topics covered include fundamentals of algorithms, flowcharts, input/output devices, programming concepts, problem solving, control structures, functions, arrays, strings, call-by-reference, and call-by-value. Throughout the semester, students will develop problem solving and critical thinking skills to solve computing problems.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Develop effective, logical algorithms to solve real-world problems.
- Write object-oriented C++ programs using core features of the language.
- Compile, run, and test object-oriented C++ programs using an integrated development environment.
CS205 NETWORK COMMUNICATIONS
Credits: 4
Networking has become the foundation of the modern world. The interconnection of computers, individuals, and society as a whole has become interdependent. The students will obtain the basic knowledge on local area networks (LANs), wide area networks (WANs), the Internet and the Cloud. They will be able to design a simple network such as a local area network. They will also learn how to keep up with the changing hardware and software and how to maintain networks and expand them as needed.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Demonstrate an understanding of how the Internet progresses from how we know it today, and how it will continue to evolve.
- Describe the Open Systems Interconnection model (OSI) and how it characterizes and standardizes the internal functions of a networking communication system by partitioning it into seven (7) abstraction layers.
- Design a basic network, make network connections using various access methods and troubleshoot network problems.
CS206 JAVA I
Credits: 3
This course introduces problem-solving methods and algorithm development using the object-oriented programming language Java. Students will learn to design, code, debug, and document programs using modern engineering techniques in a PC or Linux based environment, create Java applications that leverage the object-oriented features of the Java language such as encapsulation and polymorphism. Students will execute and run Java applications using Java data types and expressions, Java flow control constructs, arrays, etc.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Develop effective, logical algorithms to solve real-world problems.
- Write object-oriented Java programs using Java features, such as abstraction, encapsulation, and polymorphism.
- Compile, run, and test object-oriented Java programs using an integrated development environment.
CS211 JAVASCRIPT PROGRAMMING
Credits: 3
This hands-on course will provide students with the skills to design and develop dynamic and interactive web pages using JavaScript. The basics of web page creation using Hypertext Markup Language (HTML) and Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) will also be introduced.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Identify JavaScript basic syntax and command structure.
- Create programs using JavaScript programming language.
- Create dynamic and animated web pages through the integration of JavaScript with HTML and CSS.
CS212 PYTHON PROGRAMMING
Credits: 3
Python is a general-purpose programming language that is used in many areas. Students will learn the basic core concepts and techniques of programming. This hands-on course is an ideal programming language for beginners to start out with. This course will better prepare students for PCEP – Certified Entry-Level Python Programmer certification exam.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Identify basic syntax and command structure.
- Properly use commands to create programs to solve problems.
- Debug programs to find syntax and logical errors.
CS213 PHP PROGRAMMING WITH MySQL
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: CS211 JavaScript Programming
PHP: Hypertext Preprocessor is an open-source programming language that is used for developing interactive websites. MySQL is an open source relational database that is often used with PHP. Together, PHP and MySQL are becoming one of the most popular technology combinations for website development. This course teaches web development with PHP and MySQL. Students will learn how to install Apache, PHP, and MySQL open-source free software on the computers. This course covers both basic and advanced functions of PHP and MySQL to integrate object-oriented programming and how to build websites that incorporate authentication and security. Students will be able to use PHP and MySQL to build professional, dynamic, and database-driven websites.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Write a complete program using PHP programming language.
- Create a database using MySQL relational database language.
- Build a professional, dynamic and database-driven website using PHP and MySQL.
CS266 ADVANCED JAVA
Credits: 4
Prerequisite: CS206
This course builds on Java course CS206 or its equivalent and covers advanced programming topics. Designed for the more experienced Java developer, the students are expected to have a good working knowledge of the Java programming language before taking this course. Students will learn inheritance, interfaces, polymorphism, recursion, linked list, etc. and will apply the knowledge in writing Java programming applications. Students will also learn how to use object-oriented design and programming principles in their programs.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Create Java programs using arrays, lists, stacks, queues and linked lists.
- Create Java applications using the object-oriented features of the Java language, such as encapsulation, inheritance, and polymorphism.
- Create Java programs using recursion.
CS292 COMPUTER SCIENCE PRACTICUM
Credits: 1-6
Prerequisite: Complete at least 18 credits in Major Requirements
This course provides students a supervised work experience where they develop skills necessary to be successful in an information technology position. Formerly CS298.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs):
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Obtain supervised work experience to develop skills necessary to succeed in information technology positions.
- Demonstrate effective human relation skills with coworkers and subordinates according to the expectations of a supervisor.
- Apply principles of personal responsibility and ethical behavior to the community and in the workplace.
CS299 COMPUTER SCIENCE CAPSTONE
Credits: 4
Prerequisite: CS206
This course covers advanced programming topics. Students are expected to have a good working knowledge of Java, C++, PHP, and other programming languages before taking this course. This course provides students with the opportunity to complete at least three significant programming projects, which emphasize on-project definition, testing, presentation, and implementation. The projects demonstrate the knowledge and skills the students have acquired over the course of completing the Computer Science program.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Apply knowledge of fundamental algorithms, advanced features and concepts of the programming languages.
- Complete and test the fully designed projects.
- Deliver technical presentations.
CT100 INTRODUCTION TO CONSTRUCTION TRADES
Credits: 3
This course is designed to allow students to explore the construction industry and employment opportunities within a specific field. Students will learn basic construction safety, construction mathematics, hand tools, power tools, communication skills, teamwork, and critical thinking skills needed to succeed in the field of construction. Additionally, students will learn basic information for obtaining a career in each field which includes working conditions, general duties, and potential employment opportunities. Students will be eligible to acquire online certification through the National Occupational Competency Testing Institute (NOCTI).
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Demonstrate the care and maintenance of hand and power tools.
- Correctly use safety equipment common in a construction environment.
- Differentiate construction related occupations and the roles and responsibilities of each.
- Solve job-related problems by adding, subtracting, multiplying, and dividing numbers using fractions, decimals, whole numbers, ratios and proportions.
CT140 INDUSTRIAL SAFETY
Credits: 3
In this course, students will learn about concepts and habits regarding safety for the prevention of accidents resulting in personal injury and damage to building facilities and equipment. Students will also gain the knowledge of occupational safety practices, purpose and enforcement of local and federal safety requirements, risk analysis and assessment, and OSHA inspection procedures.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Identify occupational safety practices.
- Differentiate between local and federal safety requirements.
- Describe the process for an on-site OSHA inspection.
CT152 FUNDAMENTALS OF PLUMBING
Credits: 4
Prerequisite: CT100
This course introduces students to the use, safety, care, and maintenance of special tools and equipment for basic cold water supply (pipes, fittings, valves, safety devices, appliances), and drainage systems (sewers, drains, vents, traps, test, and maintenance). Students will be eligible to acquire online certification through the National Occupational Competency Testing Institute (NOCTI).
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Identify the various plumbing valves and devices.
- Explain water distribution and drainage systems.
- Demonstrate the safe and proper use of plumbing tools and equipment.
- Maintain and repair water and drainage systems.
CT152A PLUMBING LEVEL I
Credits: 4
Prerequisite: CT152
This course prepares students for an advanced study and experiential development of skills in plumbing. Emphasis will be on commercial plumbing. Students will focus on cast-iron pipefittings, carbon steel pipe and fittings, corrugated stainless steel tubing, fixtures and faucets, drain, waste and vent systems, and water distribution system. Upon completion of this course, students will be eligible to acquire online certification through the National Occupational Competency Testing Institute (NOCTI).
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Illustrate proper installation of various plumbing fixtures.
- Illustrate proper installation of pipefittings in residential and commercial settings.
- Explain the importance of pipefitting standards, codes, and specifications.
- Demonstrate the safe and proper use of plumbing tools and equipment.
- Perform water pressure tests on water supply systems.
CT153 INTRODUCTION TO CARPENTRY
Credits: 3
This course introduces students to the use, care, safe operations and maintenance of hand and power tools. Topics include handling of supplies and materials, construction safety, and construction mathematics. Upon successful completion, students will be eligible to acquire online certification through the National Occupational Competency Testing Institute (NOCTI).
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Utilize safety procedures in the carpentry profession.
- Identify tools, hardware, and equipment in the carpentry profession.
- Differentiate between rough and finishing carpentry.
CT154A MASONRY LEVEL I
Credits: 4
Prerequisite: CT100
This course will introduce students to basic masonry materials, tools, mathematical concepts, and techniques, such as the proper way to mix mortar by hand, lay masonry units, and practice safety precautions. Students will also learn the skills, attitudes, and abilities necessary to become a successful mason. Upon completion of this course, students will be eligible to acquire online certification through the National Occupational Competency Testing Institute (NOCTI).
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Describe modern masonry materials and techniques. Explain the importance of safety on a job site.
- Utilize proper techniques to mix mortar and lay masonry units.
- Adhere to safety guidelines on a job site.
CT154B MASONRY LEVEL II
Credits: 4
Prerequisite: CT154A
This course builds on content addressed in CT154A and will focus on advanced study in masonry. Students will learn about residential plans and masonry, drawing interpretation, openings and reinforced masonry, metal work, advanced laying techniques, effects of climate on masonry, construction inspection, and quality control. Upon completion of this course, students will be eligible to acquire online certification through the National Occupational Competency Testing Institute (NOCTI).
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Describe how to construct reinforced walls and masonry elements.
- Explain the need for moisture control and the techniques used to eliminate moisture problems.
- Interpret the various types of residential drawings.
- Analyze how standards and specifications are used to ensure quality control throughout the masonry industry.
CT165A ELECTRICITY LEVEL I
Credits: 5
This course introduces students to core principles in electricity: electrical safety, circuits, theory, National Electrical Code; the various electricity equipment including, but not limited to, device boxes and conduits. Students will review basic electrical construction drawings, residential electrical services, and test electrical equipment. Upon completion of the course, students will be eligible to acquire online certification through the National Occupational Competency Testing Institute (NOCTI).
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Demonstrate the safe and proper use of electrical tools and equipment.
- Apply skills needed to become a certified electrician.
- Explain the various electrical career paths.
CT165B ELECTRICITY LEVEL II
Credits: 5
Prerequisite: CT165A
This course introduces students to core principles in electricity. Students will review electrical blueprints essential for electrical wiring for commercial, industrial, and residential areas. Upon completion of this course, students will be eligible to acquire online certification through the National Occupational Competency Testing Institute (NOCTI).
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Illustrate knowledge of the National Electrical Code (NEC).
- Differentiate between residential, commercial, and industrial electrical blueprints.
- Apply the knowledge and skills related to alternating current, motors, conduit bending, conductor termination and splice, grounding and bonding, and circuit breakers and fuses.
CT165C ELECTRICITY LEVEL III
Credits: 5
Prerequisite: CT165B
This course covers the advanced principles in electricity. These principles include, but are not limited to, load calculations, conductor selection and calculations, and practical applications of lighting. Upon completion of this course students will be eligible to acquire online certification through the National Occupational Competency Testing Institute (NOCTI).
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Identify residential branch circuit requirements.
- Describe types of motor overload protection.
- Distinguish Class I-III hazardous locations.
- Interpret electrical diagrams related to the installation of distribution equipment.
CT165D ELECTRICITY LEVEL IV
Credits: 5
Prerequisite: CT165C
This is the final course in electricity. Students will learn advanced principles that include, but not limited to, specialty transformers, advanced controls, motor operations and maintenance, medium-voltage terminations/splices, and fundamentals of crew leadership. Upon completion of this course, students will be eligible to acquire online certification through the National Occupational Competency Testing Institute (NOCTI).
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Compute load calculations for residential and commercial applications.
- Explain the function and operation of basic electronic devices.
- Describe the various types of transformers.
- Identify the factors that affect motor reliability and lifespan.
CT172 PLUMBING, INSTALLATION AND DESIGN
Credits: 4
Prerequisite: AE103
This course provides the student with the application of methods and theory in installation and design of residential and commercial plumbing systems of cold water supply, hot water supply and drainage systems.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Determine correct elevations required in setting up wastewater lines.
- Properly install water pipes as detailed by given blueprints.
- Test all plumbing systems using a pressurized method.
CT173 ROUGH FRAMING AND EXTERIOR FINISHING
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: CT153
This course concentrates on basic structure construction, which includes footing and foundation, sill, floor, wall partition, roof framing, and door and window framing. This course prepares students for the National Occupational Competency Testing Institute (NOCTI) certification exam.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Summarize the types of drawings prepared for commercial and residential structures.
- Differentiate between the types and grades of steel framing materials.
- Describe the components of insulation associated hardware.
CT182 UNIFORM PLUMBING CODE
Credits: 3
This course provides students with the knowledge of the Uniform Plumbing Code and applicable local code. Students will use the Uniform Plumbing Code manual as an essential resource to determine specifications for the design, construction, and installation of various plumbing systems. Upon completion of this course, students will be eligible to acquire online certification through the National Occupational Competency Testing Institute (NOCTI).
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Describe the applicable local plumbing codes and their purpose.
- Explain the laws and ordinances governing plumbing systems.
- Determine the specifications for the design, construction and installation of various plumbing systems.
CT183 INTERIOR FINISHING
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: AE103
This course concentrates on interior finishing of basic structure construction, which includes windows, doors, floors, and ceiling trims. Upon successful completion of this course, students will be eligible to acquire online certification through the National Occupational Competency Testing Institute (NOCTI).
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Describe the safety hazards related to working with windows, doors, floors, and ceiling trim.
- Identify the different types of standard moldings and materials.
- Install various types of moldings.
- Estimate the cost of windows, doors, floors, and ceiling trims.
CT185A REFRIGERATION AND AIR CONDITIONING LEVEL I
Credits: 5
This course is an introduction to air conditioning and refrigeration. Students will focus on air conditioning and refrigeration safety, blueprint reading, copper, ferrous metal, and plastic piping, soldering and brazing, basic electricity, and introduction to cooling. Upon completion of this course, students will be eligible to acquire online certification through the National Occupational Competency Testing Institute (NOCTI).
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Explain the basic principles of heating, ventilation, air conditioning, and refrigeration (HVAC).
- Demonstrate safe and proper use of air conditioning and refrigeration tools and equipment.
- Illustrate how electrical power is generated and distributed.
- Summarize the fundamental concepts of the refrigeration cycle.
CT185B REFRIGERATION AND AIR CONDITIONING LEVEL II
Credits: 5
Prerequisite: CT185A
This course is the second of three courses for air conditioning and refrigeration. Students will learn about introductory Heating Ventilation Air Conditioning (HVAC), trade mathematics, tools, air distribution systems, vents, and maintenance skills for service technicians. Upon completion of this course, students will be eligible to acquire online certification through the National Occupational Competency Testing Institute (NOCTI).
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Identify the factors of air movement and its measurement in the air distribution systems.
- Explain the fundamental concepts of heating and combustion.
- Compute basic mathematical skills for HVAC.
- Demonstrate safe and proper use of air conditioning and refrigeration tools and equipment.
CT185C REFRIGERATION AND AIR CONDITIONING LEVEL III
Credits: 5
Prerequisite: CT185B
This course is the last of three courses for air conditioning and refrigeration. Students will learn about compressors, alternating current, introduction to control circuit troubleshooting, metering devices, leak detection, evacuation, recovery and charging. Upon completion of this course, students will be eligible to acquire online certification through the National Occupational Competency Testing Institute (NOCTI).
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Describe the equipment and method used to leak test refrigerant circuits.
- Explain how alternating current (AC) power is generated and used.
- Illustrate the function of refrigerant metering devices and their effect on refrigerants.
- Demonstrate safe and proper use of air conditioning and refrigeration tools and equipment.
CT196A FUNDAMENTALS OF OXYACETYLENE WELDING AND CUTTING I
Credits: 4
Corequisite: CT100
This course is the first of two courses on oxyacetylene welding and cutting. Students will focus on the identification, use, care, safe operations, maintenance, assembling and disassembling of welding equipment and tools. Upon completion of this course, students will be eligible to acquire online certification through the National Occupational Competency Testing Institute (NOCTI).
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Identify commonly used welding tools, supplies, and equipment.
- Illustrate the setup, light, and shut down processes of oxyfuel equipment.
- Demonstrate safe and proper use of various tools and equipment related to oxyacetylene welding and cutting.
CT196B FUNDAMENTALS OF OXYACETYLENE WELDING II
Credits: 4
Prerequisite: CT196A
This course is the last of two courses on oxyacetylene welding and cutting. Students will learn about working with torch flame and perform in-depth cutting procedures utilizing stand-alone and portable oxyfuel cutting machines. Upon completion of this course, students will be eligible to acquire online certification through the National Occupational Competency Testing Institute (NOCTI).
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Explain the good and inferior cuts and their causes.
- Illustrate the essential skills required for oxyacetylene welding.
- Model the proper techniques used for various oxyfuel cutting procedures.
CT197A SHIELDED METAL ARC WELDING I
Credits: 5
Prerequisite: CT100 (or permission of the instructor)
This course focuses on the skills and academic competencies necessary for safe, professional and effective practice in basic shielded metal arc welding. This course also introduces and emphasizes basic shielded metal arc welding skills, including selection of metals and electrodes, and making beads, fillet welds and groove welds. Emphasis will be placed on core principles in shielded metal arc welding, including use, care, safe operations and maintenance of welding tools; the use, care and safe handling of supplies and materials; the development of an appropriate attitude as related to professional work, and the acquisition of knowledge and information essential for success in initial pursuit of a career in the field of welding.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Demonstrate the knowledge and skills required for basic shielded metal arc welding including selection of metals and electrodes, the making of beads, fillet welds, and groove welds.
- Demonstrate the professionalism and an appropriate attitude necessary in the welding field.
- Acquire skills needed for an entry-level position in the welding field.
CT197B SHIELDED METAL ARC WELDING II
Credits: 5
Prerequisite: CT197A
This course builds on the content of CT197A. Students will learn gas metal arc welding (GMAW), gas tungsten arc welding (GTAW), flux cored-arc welding (FCAW), and submerged and plasma arc welding skills. Upon completion of this course, students will be eligible to acquire online certification through the National Occupational Competency Testing Institute (NOCTI).
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Describe equipment used for Flux Core-Arc Welding (FCAW), Gas Metal-Arc Welding (GMAW) and Gas Tungsten-Arc Welding (GTAW).
- Explain the welding preparation process for Flux Core-Arc Welding (FCAW), Gas Metal-Arc Welding (GMAW) and Gas Tungsten-Arc Welding (GTAW).
- Illustrate welding skills for gas metal, gas tungsten, flux cored arc welding, and metal to inert gas processes.
CTE300 INTRODUCTION TO TEACHING CTE
Credits: 3
Formerly: Foundations of Career & Technical Education
Prerequisite: Minimum requirement is an Associate’s Degree
This course provides students with the foundational skills, educational theories, and knowledge and develops dispositions required for teaching career and technical education.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Describe the characteristics of high-quality career and technical educators.
- Explain career and technical educator’s role in the public education reform.
- Devise a professional growth plan based on developmental teaching needs.
CTE305 FOUNDATIONS OF ONLINE TEACHING
Credits: 3
This course integrates theoretical knowledge with hands-on application, providing students with the tools to comprehend the principles of effective online teaching and course design and, more importantly, to apply them in real-world scenarios. Upon completion, participants will possess a strong foundation in online teaching methodologies, prepared to develop meaningful student-centered virtual learning experiences.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Identify key characteristics, external factors, and needs of online learners that have an impact on persistence and achievement of learning outcomes.
- Employ equitable instructional practices to foster persistence and enhance the achievement of learning outcomes.
- Design a course using the backward design approach to ensure alignment among learning outcomes, assessment, activities, and instructional materials., creating a cohesive learning experience.
- Develop a meaningful online teaching philosophy, synthesizing insights gained from the reflection of online teaching principles.
CTE310 CTE METHODS OF TEACHING I: PLANNING & PREPARATION
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: Minimum requirement is an Associate’s Degree
This course provides students with the framework, skills, and knowledge for writing a standards-based curriculum needed for successful teaching. Topics include inclusive teaching, learning domains, Understanding by Design (UbD), the rigor and relevance model, priority standards, goals, objectives, and assessments.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Develop clear and coherent CTE standards-based unit and lesson plans around rigor and relevance framework.
- Explain the concepts and principles of curriculum planning and design.
- Present the value and importance of instructional planning as an essential component of professional responsibility.
CTE320 CLASSROOM AND CTE LABORATORY MANAGEMENT
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: Minimum requirement is an Associate’s Degree
The course presents principles, strategies, and best practices in classroom and CTE laboratory management that promote a culture of learning and safety.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Compare and contrast various classroom management principles and models.
- Develop a CTE classroom, laboratory, and behavior management plan.
- Explain the CTE instructor's role in creating a culture of learning and safety.
CTE330 EDUCATIONAL TECHNOLOGY
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: Minimum requirement is an Associate’s Degree
This course provides students with strategies to integrate technology into instruction to develop their learners’ information literacy and digital citizenship skills.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Describe the benefits and challenges of and selection criteria for using the web, web-based content, and instructional software.
- Employ the steps in the Technology Integration Planning model in designing technology-supported classroom lessons.
- Formulate a professional rationale for using technology based on learning theories, educational standards, contextual conditions, and recent research.
CTE340 CTE METHODS OF TEACHING II: INSTRUCTIONAL DELIVERY
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: CTE310 or DC approval
This course presents effective teaching methods and practices that meet the needs of diverse learners. Topics include strategies for motivating students and differentiating instruction for diversity, inclusion, cultural relevance, and equity.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Discuss the importance of selecting appropriate instructional models and prioritizing standards in achieving learning outcomes.
- Apply instructional practices that promote inclusivity, motivation, and student achievement.
- Select engaging instructional strategies appropriate to students of varying abilities and skills.
- Evaluate strengths and weaknesses of instruction and the effectiveness of teaching strategies used.
CTE350 ASSESSMENT AND STANDARDS-BASED
GRADING
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: CTE310 or DC approval
Students in this course will learn how to plan and implement assessments, develop proficiency scales, and use standards-based grading.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Design formal and informal teacher-made assessment instruments to determine mastery of skills, ideas, or topics resulting from instruction.
- Write proficiency scales that articulate learning progression for each prioritized standard.
- Explain the characteristics, advantages, and limitations of different types of assessments and grading.
CTE400 PROGRAM MANAGEMENT AND LEADERSHIP
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: Minimum requirement is an Associate’s Degree
Using the High-Quality CTE Framework, students will evaluate a program of study to develop an understanding of well-designed and well-managed CTE programs. This course will also provide students with opportunities to practice leadership and collaboration to advance career and technical education ideals.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Discuss the history, benefits, issues, and trends in career and technical education.
- Evaluate a CTE program of study using the evidenced-based High-Quality CTE Program of Study Framework.
- Advocate CTE ideals and values through engagement in professional development, mentorship, and collaboration.
- Formulate a CTE philosophy statement.
CTE410 METHODS OF TEACHING III: PROJECT-BASED LEARNING
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: CTE310
Project Based Learning (PBL) is a learner-centered teaching method in which students learn concepts by engaging in meaningful and relevant projects to find answers to complex questions or address problems. Students in this course will learn to design, implement, and manage a high-quality project-based curriculum.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Discuss the concepts and principles of project-based learning design, implementation, and management.
- Plan and implement an interdisciplinary high-quality project-based unit plan.
- Develop assessment tools appropriate for project-based learning.
CTE492 STUDENT TEACHING-CTE
Credits: 12
Prerequisite: Completion of General Education courses, CTE concentration, and major courses
The Student Teaching is a 525-hour field experience plus 15 hours of seminar. The course aims to provide students the knowledge and skills to apply pedagogical competencies in the classroom. Under the observation of the instructor-coordinator, students plan and prepare instructional materials, and direct instructional roles. Students assess learning outcomes, assist in record-keeping, and perform other classroom teacher responsibilities. Students’ performance in this course will be evaluated using the Framework for Teaching standards. Students should be prepared to accept an assignment at any school and teach the CTE specialization. Eligibility requirements: This is the final course in the BSCTE program. To qualify for this course, students must have completed general education requirements, CTE area of concentration, and major courses.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Construct, implement, and assess lessons aligned to career and technical education national standards.
- Employ instructional strategies that are equitable, inclusive, and culturally responsive with the goal of meeting the needs of diverse learners.
- Provide a safe and positive learning environment conducive to learning.
- Practice reflective teaching for professional growth.
- Demonstrate achievement of learning outcomes and leadership through a portfolio.
CTE498 INTERNSHIP
Credits: 12
Prerequisite: Completion of general education, CTE concentration, and major courses
This semester-long course is designed for BSCTE students employed as full-time CTE teachers. Working closely with the participant’s supervisor, the BSCTE program instructor-coordinator provides consistent observation, coaching, and evaluation throughout the internship. Participants will apply current teaching theories in practical settings, while fostering critical reflection for ongoing professional growth. Evaluation of participants' performance will be based on the Framework for Teaching standards.
Student Learning Outcomes
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Construct, implement, and assess lessons aligned to career and technical education national standards.
- Employ instructional strategies that are equitable, inclusive, and culturally responsive with the goal of meeting the needs of diverse learners.
- Provide a safe and positive learning environment conducive to learning.
- Practice reflective teaching for professional growth.
- Demonstrate achievement of learning outcomes through a portfolio.
CTE499 INTRODUCTION TO ACTION RESEARCH
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: Complete ALL 300 Level CTE courses
Corequisite: EN300 & MA385
The course is structured around constructing an action research project to address a problem of practice.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Develop an action research proposal with strong connection to career and technical education.
- Evaluate action research utilizing the criteria.
- Reflect on the process of developing an action research proposal.
CUL140 CULINARY FOUNDATION I
Credits: 2
Prerequisite: FSM120
Corequisite: CUL160
This course introduces students to essential culinary terminology, concepts, and principles, covering fundamental skills such as preparing stocks, soups, and sauces. Students will learn a variety of cooking techniques, including dry heat methods such as roasting, grilling, and frying; moist heat methods such as boiling, steaming and poaching; and combination methods such as braising and stewing. The course emphasizes the application of food safety principles from the Food Safety and Sanitation course and reinforces the professionalism standards learned in Introduction to the Foodservice Profession. Key topics include mise-en-place, kitchen organization, sustainability, and the safe use and care of chef tools and commercial equipment. Additionally, students will explore taste, flavor, cooking, and plating principles. By the end of the course, students will know culinary terms and be able to select and prepare ingredients using the appropriate tools, equipment, and techniques to create high-quality dishes.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Identify equipment and tools used in a professional kitchen.
- List sustainable practices in the kitchen.
- Demonstrate knife skills and cooking techniques as applied to a given range of foods and recipes.
- Apply kitchen and food safety principles during food production.
- Conduct sensory analysis of finished products.
CUL160 CULINARY FOUNDATIONS II
Credits: 2
Prerequisite: CUL140 Culinary Foundations I
This course builds on the foundational skills presented in Culinary Foundation I. Applying the principles learned in CUL140, students will prepare stocks, grand and contemporary sauces, soups, vegetables, potatoes, grains, pasta, meat, poultry, fish and seafood using classic European and Mediterranean cooking techniques. Time management and organization are reinforced. Students will further study and practice dry heat, moist heat, and combination cooking techniques and prepare dishes with complimenting classical and contemporary sauces. Students will learn to fabricate meat, poultry, fish, and shellfish and prepare common mise-en-place incorporating classical knife cuts. Use and care of commercial equipment, tools, and facility, understanding of measurement and ratios and adherence to recipes and sustainable kitchen practices are embedded in this hands-on course. Following the attributes of a professional culinarian, students will demonstrate professionalism, respect of the culinary craft, and strict adherence to kitchen safety and sanitation procedures. Formerly titled Culinary Foundations II.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Demonstrate classic knife cuts.
- Prepare meat, poultry, fish, or shellfish using appropriate European or Mediterranean cooking techniques.
- Apply kitchen and food safety principles during food production.
- Prepare grains, vegetables, potatoes, or pasta using appropriate European or Mediterranean cooking techniques.
- Prepare the five French mother sauces and the three contemporary sauces (reduction, puree, and emulsion).
CUL180 GARDE MANGER
Credits: 2
Prerequisite: CUL160 Culinary Foundations II
This course provides students with an introduction to the art and technique of grad manger, encompassing the preparation of both hot and cold hors d’oeuvres, canapés, and appetizers. By implementing the principles of “total utilization,” students will acquire skills in forcemeat production, charcuterie, and food preservation. The curriculum will emphasize culinary principles, techniques, food safety, proper use and maintenance of equipment, and quality standards for cold and buffet presentations. In alignment with the characteristics of a professional chef, students are expected to exhibit professionalism, respect for the culinary arts, and a rigorous commitment to kitchen sanitation and procedures.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Demonstrate basic preparation of forcemeats such as, pates, galantines, terrines, and sausages using culinary principles and quality standards.
- Prepare various sandwiches, canapés, hors d'oeuvres, and appetizers using culinary principles and quality standards.
- Prepare composed salad, dressing, and marinades using culinary principles and quality standards.
- Reinforce the principles of food safety and sustainable food production.
- Demonstrate food presentation techniques using a variety of plates, platters, and trays.
CUL240 PACIFIC ASIAN CUISINE
Credits: 2
Prerequisite: CUL160 Culinary Foundations II
Corequisite: CUL180 Garde Manger
Students explore, prepare, serve, and evaluate traditional cuisines from Pacific and Asian countries, emphasizing ingredients, flavor profiles, cooking methods, and techniques. Through a series of Asian-themed buffet showcases, they acquire hands-on experience in menu and event planning, marketing, and time and labor management.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Explain the influence of geography, climate, history, and philosophy in each of the cuisines.
- Apply the principles of food safety and sustainable food production.
- Demonstrate the fundamentals of Asian or Pacific cooking principles and preparation techniques.
- Plan, organize, and implement buffet presentations.
- Evaluate visual appearance, flavor, taste, and texture of prepared food.
CUL293A CULINARY PRACTICUM PART I
Credits: 2
Prerequisite: CUL160
This is a faculty-supervised practicum designed to expand career knowledge, hone culinary skills with increasing speed, timing, and organization in an approved commercial foodservice establishment.
To ensure that students benefit from a well-rounded practicum experience, they will rotate in different areas of the kitchen and complete a task checklist.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Identify workplace culture, norm, and expectations.
- Apply effective time management, teamwork, and communication skills needed to work in a professional kitchen.
- Apply standards and procedures for safe food handling.
CUL293B CULINARY PRACTICUM PART II
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: CUL293A
This course is a continuation of Culinary Practicum Part I, where students will choose an area to specialize in, to include hot kitchen, cold kitchen and bakery/pastry/dessert section. The intent of each area of specialization is to further students’ culinary skills and abilities with regard to speed, timing, and organization.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Apply skills in food production related to area of specialization.
- Demonstrate effective time management and teamwork in a professional kitchen.
- Utilize feedback received from industry professionals.
CUL299 CULINARY CAPSTONE
Credits: 2
Prerequisite: CUL240
Based on contemporary North American cuisines, this course builds on the techniques and principles introduced and reinforced in the program. Skills in classical knife cuts, product identification, fabrication of meat, poultry, fish, and shellfish, preparation and cooking of a variety of meat, seafood, vegetables, potatoes, and pasta, plating techniques are refined and improved. Students will identify and define ingredients, flavor profile, and apply appropriate cooking techniques to produce quality a la minute plates. Use and care of commercial equipment, tools, and facilities, mise-en-place, understanding of measurement and ratio, and adherence to recipes and sustainable kitchen practices are emphasized. Following the attributes of a professional culinarian, students are expected to demonstrate professionalism, respect of the culinary craft, and strict adherence to kitchen sanitation procedures. At the end of the course, students will write standardized recipes for a 3-course plated menu, execute, and serve to industry professionals for judging.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Prepare grains, vegetables, potatoes, and pasta using appropriate cooking techniques.
- Prepare meat, poultry, fish, or shellfish using appropriate cooking techniques.
- Prepare a plated dessert with multiple components showcasing a variety of tastes, textures, and temperatures.
- Evaluate the quality of prepared dishes.
- Demonstrate the attributes of a professional culinarian.
BAK200 FOUNDATIONS OF BAKING & PASTRY
Credits: 2
Prerequisite: CUL160 Culinary Foundation II
This course introduces students to basic principles, skills, and techniques of baking and pastry. Special emphasis is placed on ingredient identification and function, weights and measures, safe use and care of baking tools and equipment and evaluation of quality characteristics. Students will apply basic baking principles and techniques in the production of yeast breads, cookies and pies, and pastry and laminated doughs, breakfast and individual pastries, custards, creams, mousses, soufflés, icing, glazes, sauces, and frozen dessert. Formerly CUL200
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Describe properties and functions of major baking ingredients.
- Utilize proper scaling and measuring techniques.
- Choose the appropriate technique and equipment for baking each product.
- Apply math skills to recipe conversion.
- Evaluate characteristics of quality of baked goods.
BAK220 INTERMEDIATE BAKING AND PASTRY
Credits: 2
Corequisite: BAK200 Foundations of Baking & Pastry (Formerly CUL200)
This course builds on the principles and techniques introduced in CUL200 Foundations of Baking and Pastry. Students are introduced to individually plated desserts using traditional and modern techniques including methods to develop desserts that are healthy or conform to dietary restrictions. Students will have the opportunity to gain practical experience in the production, assembly, and decoration of special occasion cakes.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Create plated desserts that are attractive and appropriate for a variety of food service venues.
- Prepare desserts that conform to specific dietary restrictions.
- Assemble and decorate cakes that meet quality standards.
BAK240 BOULANGERIE: ADVANCED BREAD TECHNIQUES
Credits: 2
Prerequisite: BAK200 Foundations of Baking & Pastry (Formerly CUL200)
This course aims to provide students with an advanced skill-based boulangerie education that explores both traditional and contemporary techniques in the production of artisan breads. Skills learned in the Foundations of Baking and Pastry course are reinforced. Emphasis is placed on hand shaping skills, innovative and decorative shaping is introduced along with the principles of artisan and viennoiserie through a variety of lean, enriched, and laminated yeast dough products applied in bakery operations.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Execute proper scaling, mixing, and baking techniques for different types of breads.
- Select equipment and tools needed to produce different types of breads.
- Control bread production costs by using the correct formula.
- Assess the quality of baked products.
BAK250 CAKES AND DESSERTS PRESENTATION
Credits: 2
Prerequisite: BAK220 Intermediate Baking (Formerly CUL220)
This course aims to teach cake production, assembly, and design inclusive of restaurant desserts and contemporary plating techniques.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Execute proper mise en place and mixing techniques for different types of cakes and desserts.
- Produce a variety of cakes and desserts.
- Evaluate the quality of prepared and decorated cakes and plated desserts.
BAK293A RESTAURANT DESSERTS & PASTRIES PRACTICUM
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: BAK220 Intermediate Baking (Formerly CUL220)
This course is a faculty-supervised practicum designed to expand students’ career knowledge and hone their skills in preparing quality desserts and pastries, maximizing within timing limits, and organizing within an approved commercial establishment.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Utilize pastry-making and baking equipment following safety standards.
- Produce classical and contemporary style pastries, desserts, and confections.
- Evaluate products for consistency using quality standards.
- Apply effective organizational and interpersonal skills in a professional kitchen environment.
BAK293B BREADS AND CAKES PRACTICUM
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: BAK220 Intermediate Baking (Formerly CUL220)
This course is a faculty-supervised practicum designed to expand students’ career knowledge and hone their skills in bread and cake production and cake decorating. To ensure that students benefit from a well-rounded practicum experience, they will rotate among different areas of the bakery and complete a task checklist.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Execute proper scaling, mixing, and baking techniques for different types of breads and decorated cakes.
- Select equipment and tools needed to produce different types of breads and decorated cakes.
- Evaluate breads and decorated cakes based on established quality standards, as applicable.
- Apply organizational and interpersonal skills in a work environment.
BAK299 BAKING & PASTRY CAPSTONE
Credits: 2
Prerequisite: FSM240 Menu Planning
This capstone course builds on the techniques and principles introduced and reinforced in the program, helping students to develop an understanding of the basic principles of baking. Emphasis of this course is placed on the fundamental planning principles of a proposed bakeshop concept.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Apply basic principles of bakery planning and layout.
- Plan for daily bakery production.
- Create a business proposal for a new bakeshop concept.
EC110 PRINCIPLES OF ECONOMICS
Credits: 3
This course is designed to help students understand the economic challenges and opportunities found in the United States mainland and Guam. This introductory course focuses on describing economic events, explaining why they occur, predicting similar future events, and recommending solutions. Financial responsibilities always impact people’s lives and their dependents. Understanding the relationship between financial decisions and outcomes is extremely important for all citizens.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Discuss with understanding the basic principles and theories of economics.
- Apply economic principles and theories to decisions societies make (Micro).
- Demonstrate understanding of the relationships between various global markets and the impact those relationships have on the entire world economy (Macro).
ED150 INTRODUCTION TO TEACHING
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: EN110
This course represents a realistic approach to the fundamentals of teaching as a career. Students will be introduced to large topics and contemporary trends in education to include discipline, history, philosophy, learning theories, teaching techniques, technology assessment, classroom management, and diversity. Rewards of teaching are explored as well as current challenges educators face.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Develop a philosophy of education that includes self-efficacy.
- Formulate a comprehensive academic plan related to a profession in education.
- Demonstrate critical thinking as related to the development of current educational practices and potential alternative pedagogy and practices which are aligned with the needs of our island’s student population.
ED180A EDUCATIONAL METHODS I
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: DC/Advisor Approval
This course provides the knowledge and skills necessary to plan, prepare, and implement educational activities and teaching strategies in a K-12th grade educational setting. The course is designed for individuals interested in pursuing a career in an educational setting. Course content focuses on identifying the diversity of learners’ needs, instructional approaches to best address this diversity, and planning and implementing activities.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Analyze and reflect on the essence of learning as related to the brain and to the diverse needs of students.
- Design at least two Guam-based learning centers based on Bloom’s Levels of Taxonomy which address multiple intelligences and learning styles.
- Develop and implement a lesson plan that is linked to one of the learning centers created.
ED180B EDUCATIONAL METHODS II
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: ED180A
This course provides experience in developing thematic units of learning and educational materials for classroom use in a K-12th grade educational setting. The course is designed for individuals interested in pursuing a career in an educational setting. Course content focuses on interdisciplinary thematic units linked to the Earth Charter, a literature-based thematic unit, and nonfiction-based thematic unit. Students are expected to demonstrate critical thinking and reflective practice.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Demonstrate the Earth Charter and its relevance in education.
- Include the Earth Charter principles into educational materials.
- Create two literature-based thematic units (one based on a novel, and one based on non-fictional text) which include relevant learning centers.
ED180C EDUCATIONAL METHODS III
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: ED180B
This course provides experience related Project-Based Learning, Writer’s Workshop, and Young Authors as a precursor for classroom use in a K-12th grade educational setting. The course is designed for individuals interested in pursuing a career in an educational setting. Course content focuses on experiencing and developing Project-Based Learning units, using the Writer’s Workshop process in developing reading materials for students and helping to develop the writing skills of K-12 age students in creating their own books as Young Authors all related to the Earth Charter. Students are expected to demonstrate critical thinking and reflective practice.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Incorporate the Earth Charter into classroom learning and materials.
- Develop Project-Based Learning units for diverse age levels of learners which relate to the Earth Charter Principles.
- Engage in and develop proficiency in the implementation of literature efforts such as Writer’s Workshop and Young Authors, developing written materials which are place-based and integrate the Earth Charter.
ED220 HUMAN GROWTH & DEVELOPMENT
Credits: 3
This course covers the study of human growth and development from birth to death with a special emphasis on the formative and school years. An overview of the interrelationship between physical, emotional, intellectual, and social growth will be presented. The role of the family, culture, community and society and the impact on development is also explored.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Describe the social, physical, and cognitive development of school-age learners.
- Explain the social, physical, and cognitive development of adolescent and young adult learners.
- Illustrate the impact of family, culture, community and society on development.
ED231 INTRODUCTION TO EXCEPTIONALITIES
Credits: 3
This course provides students with an introduction to exceptionalities. An overview of all aspects of exceptionality including etiology, legal aspects, assessment, and service delivery will be provided.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Describe ways to meet the needs of students with exceptionalities.
- Develop strategies to communicate with and empower families of students with exceptionalities.
- Explain the process of referral, screening, and assessment, including knowledge of the roles and responsibilities of primary members.
ED265 CULTURE AND EDUCATION IN GUAM
Credits: 3
This course focuses on aspects of Guam’s cultural development to include cultural reciprocity, cultural exchanges, and tensions. How these factors impacted Guam’s educational system will also be covered. The historical, current, and future impact of these topics on educators and educational methods will also be addressed.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Analyze the effect of current and past issues pertaining to Guam’s cultural development and education system.
- Project future problems that may affect Guam’s community and educational system to include diversity issues.
- Engage in social and/or political action directed at improving education on Guam.
ED292 EDUCATION PRACTICUM
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: Permission from course instructor and Education Department Chairperson
This course provides students with the opportunity to demonstrate professionalism, employing reflective practices while working and/or volunteering 135 hours in a K-12 school setting under the supervision of a mentor. Students will be required to assist their mentor as needed which may include conducting observations, attending meetings, creating a conducive learning environment, grading, and implementing age-appropriate lessons and activities.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Demonstrate appropriate professional behavior.
- Effectively and respectfully communicate with students, staff and families including those from diverse backgrounds and special populations.
- Implement various developmentally appropriate teaching, assessment and guidance strategies needed to effectively work with students in Kindergarten to twelfth grade.
EMS103 EMERGENCY MEDICAL TECHNICIAN (EMT) - BASIC
Credits: 8
Corequisite: HL131
The goals and objectives of this course are to improve the quality of emergency medical care. Students will attain the skills and competencies to the level of Emergency Medical Technician-Basic to serve as a vital link in the chain of the healthcare team. This includes all skills necessary for the individual to provide emergency medical care at a basic life support level with an ambulance service or other specialized service. Upon completion of this course, students will be eligible to test for the National Registry of EMT (NREMT), a national certifying examination.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Assess and communicate the nature and seriousness of the patient’s condition and extent of injuries required for emergency medical care.
- Apply appropriate emergency medical care based on assessment findings of the patient’s condition.
- Properly and effectively handle the patient to minimize discomfort and prevent further injury.
EN068 LANGUAGE ARTS LITERACY
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: Placement via CASAS assessment (236)
This course is designed to develop and improve the students’ current reading skill level as determined by the Comprehensive Adult Student Assessment System (CASAS) and writing skills. The course incorporates the College and Career Readiness Standards (CCRS) for adult education; the standards will enhance students’ reading and writing skills which will prepare them for postsecondary education and the workforce. Relevant individualized instruction provides reading and writing activities to enable students to become empowered, competent, critical, and reflective in their reading and writing. At the end of each semester, students enrolled in this course are required to complete the posttest component of CASAS; students scoring a 239 or above in the CASAS reading assessment will be considered to have achieved the Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs) for the course and can be awarded a grade for the course.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Determine central ideas or themes of a text and analyze their development; summarize the key supporting details and ideas.
- Interpret words and phrases as they are used in a text, including determining technical, connotative, and figurative meanings, and analyze how specific word choices shape meaning or tone.
- Write arguments to support claims in an analysis of substantive topics or texts, using valid reasoning and relevant and sufficient evidence.
- Develop and strengthen writing as needed by planning, revising, editing, rewriting, or trying a new approach.
EN081 LITERATURE SURVEY
Credits: 3
This course is an application of English Language
Arts standards called for in the College and Career Readiness Standards for Adult Education. This course provides adult students with an opportunity to read and comprehend literature, including stories, dramas, and poems. Areas of instruction include the structure of and literary elements contained in the noted genre, reading comprehension, vocabulary development, and literature-based composition.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Determine a theme or central idea of a text.
- Conduct literary analysis.
- Write informative/explanatory texts to examine and convey complex ideas, concepts, and information.
EN091 FUNDAMENTALS OF COMMUNICATION
Credits: 3
This course is a study of communication and speech; it introduces students to the evolving process of communication. Basic channels of communication, principles of interpersonal communication, group communication, and the preparation and delivery of speech presentation are aspects that will be covered. This course incorporates the College and Career Readiness Standards (CCRS) for Adult Education. Relevant individualized instruction provides reading, writing, listening, and speaking activities to enable students to become empowered, competent, critical, and reflective in their communication.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Prepare for and participate effectively in a range of conversations and collaborations with diverse partners, building on others' ideas and expressing their own clearly and persuasively.
- Present information, findings, and supporting evidence such that listeners can follow the line of reasoning, and the organization, development, and style are appropriate to task, purpose, and audience.
- Make strategic use of digital media and visual displays of data to express information and enhance understanding of presentations.
EN096 BASIC ENGLISH LEVEL I
Credits: 4
This course provides integrated reading and writing instruction for students who require extensive preparation to succeed in college-level English courses or in certification into the workforce where applicable. Upon successful completion of the course, students will progress to Basic English Level II (EN097).
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Practice critical thinking and reading comprehension techniques to analyze literal, interpretive, and applied college-level texts.
- Construct basic sentences and short paragraphs using proper grammar and mechanics.
- Write coherent essays utilizing the writing process.
- Utilize technology and e-learning platforms to manage course materials and review academic progress, communicate, problem-solve, and research for information in the academic setting.
EN097 BASIC ENGLISH LEVEL II
Credits: 4
Prerequisite: Pass EN096 or reading score of 52-74 in the ACCUPLACER placement test.
Basic English Level II (EN097) provides reading and writing instruction for students who require intermediate preparation to succeed in college-level English courses or in certification into the workforce where applicable.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Demonstrate the process of brainstorming, organizing, drafting, revising, editing, and proofreading academic writing.
- Apply critical thinking skills when exploring college-level reading materials and composing academic writing.
- Create well-developed, coherent, and unified college-level essays.
EN110 FRESHMAN COMPOSITION
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: Placement into EN110 or equivalent
Emphasizing critical reading, writing, and thinking, this course focuses on communicating clearly and effectively using standard written English in an academic setting, as well as in other communities. Students will practice exploring ideas, conveying information, and developing their writing process. They will demonstrate logical reasoning, clarity, organization, and appropriate language choices in their writing.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Employ the writing process (prewriting, organizing, drafting, revising, editing) and writing strategies.
- Identify writing strategies used by authors.
- Compose effective and strategic essays.
EN110A FRESHMAN COMPOSITION WITH INSTRUCTIONAL LAB
Credits: 4
Prerequisite: Placement
Emphasizing critical reading, writing, and thinking skills, this course focuses on communicating clearly and effectively using standard written English in an academic setting, as well as in other communities. Students will practice exploring ideas, conveying information, and developing their writing process. They will demonstrate logical reasoning, clarity, organization, and appropriate language choices in their writing. The instructional lab component will provide grammatical and mechanical lessons and reinforce skills necessary for students to achieve the SLOs for successful completion of EN 110A. Students eligible for 110A can opt to take EN097.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Employ the writing process (prewriting, organizing, drafting, revising, editing) and writing strategies.
- Examine the connection between reading and writing.
- Compose effective and strategic essays.
- Utilize proper grammar and writing conventions to construct various sentence types to create sense, clarity, and stress in college-level writing.
EN111 WRITING FOR RESEARCH
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: EN110 Freshman Composition
This course builds on the content covered in EN110. Emphasis is placed on academic research processes and writing. Students will develop information literacy skills to access both primary and secondary sources. Students will also engage in critical analyses of print, electronic, and observational data.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Demonstrate competency in locating and evaluating credible primary and secondary sources.
- Develop an argumentative essay that summarizes, paraphrases, quotes, and synthesizes information gathered from research.
- Apply appropriate documentation style.
EN194 TECHNICAL COMMUNICATION
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: Completion of EN110 with a grade of C or better.
This course prepares students to communicate effectively for business, industry, and professions. Students will engage in the writing process and develop examples of technical communication as well as deliver professional, oral presentations.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Define technical communication.
- Create audience profiles to produce correctly written and formatted technical communication.
- Deliver professional oral presentations.
EN210 INTRODUCTION TO LITERATURE
Credits: 3
Course Offering: Fall & Spring
Prerequisite: EN110 Freshman Composition with a grade C or better.
This course is designed to familiarize students with the major divisions of literature: fiction, poetry, and drama. Students will develop an understanding of and appreciation for literary elements.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Recognize the differences between literary genres, including but not limited to poetry, fiction, and drama.
- Demonstrate basic familiarity and comprehension of vocabulary for discussing literary texts.
- Write analytically about literature.
EN220 BEST PRACTICES FOR LITERACY INSTRUCTION
Credits: 3
This course gives students instruction and hands-on practice in developing students’ literacy skills across content and language. Using theories pertaining to culturally relevant pedagogy, peer interaction, and scaffolding, students will learn to create real-world activities that incorporate strategies for listening, speaking, reading, and writing.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Value literacy strategies as a foundation for teaching content in all subjects.
- Integrate literacy instruction into culturally relevant pedagogy.
- Design activities that incorporate strategies for authentic literacy development.
EN300 WRITING FOR EDUCATORS
Credits: 3
Corequisite: CTE499: Introduction to Action Research
This course provides techniques and strategies for using writing to support learning across the curriculum. By discussing current research and best practices, creating discipline-specific writing assignments, and through the development of their own writing, students will further develop their skills for teaching literacy in content areas.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
- Create and assess writing assignments that support content areas.
- Evaluate student writing and provide feedback.
- Composen an annotated bibliography that supports writing and research for corequisite: CTE499: Introduction to Action Research.
FA192 FAMILY SERVICES PRACTICUM
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: Permission from advisor or Education Department Chairperson
Students will have the opportunity to implement their knowledge and skills while working under the mentorship of a qualified social services professional and faculty member. A minimum of 135 hours of work is required, which may include observations, meetings with clients and professionals, and professional development activities.
Student learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Demonstrate effective communication skills with clients and co-workers.
- Demonstrate appropriate competency needed in the effective delivery of human services.
- Demonstrate professionalism and ethical conduct within the field.
FS100 INTRODUCTION TO FIRE PROTECTION
Credits: 3
Course Offering: Fire Academy
Prerequisite: Instructor approval
This course covers the philosophy and history of fire protection; history of loss of life and property by fire; review of municipal fire defenses; study of the Professional qualifications. This course is designed for the person who seeks the knowledge and skills to function as an integral member of a firefighting team under direct or general supervision in hazardous conditions. Enrollment is limited to students currently in the Fire Science Academy.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Demonstrate the knowledge and skills to perform basic firefighting emergency and rescue operations and duties.
- Demonstrate the knowledge and skills to operate basic firefighting rescue tools and equipment.
- Demonstrate the knowledge and skills to pass the National Professional Qualifications System (NPQS) certification test for Firefighting II level.
FS101 INTRODUCTION TO FIRE SUPPRESSION
Credits: 3
Course Offering: Fire Academy
Prerequisite: Instructor approval
This course is a study of techniques of effective fire prevention to include fire hazards and causes; judging fire load, building construction, inspection techniques; storage of flammable and combustible liquids and hazardous materials security. This course is designed for career public safety officers and recruits
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Identify inspection techniques used in fire Explain strategies for effective fire protection.
- protection careers.
- Identify various types of building structures and explain the importance of basic fire resistance requirements.
FS103 FIREFIGHTER I
Credits: 8
Course Offering: Fire Academy
Prerequisite: By permission of CJ Department Chair
This course is based on the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) 1001, Standard for Fire Fighter Professional Qualifications. This course is designed for the person who seeks the knowledge and skills to function as an integral member of a firefighting team under direct or general supervision in hazardous conditions. Enrollment is limited to students currently in the Fire Science Academy.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Demonstrate the knowledge and skills to perform basic firefighting emergency and rescue operations and duties.
- Demonstrate the knowledge and skills to operate basic firefighting rescue tools and equipment.
- Demonstrate the knowledge and skills to pass the National Professional Qualifications System (NPQS) certification test for Firefighter I level.
FS104 FIREFIGHTER II
Credits: 3
Course Offering: Fire Academy
Prerequisite: Enrollment by permission of the GCC CJSS Department Chair
This course is based on the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) 1001, Standard for Fire Fighter Professional Qualifications. The course is designed for the person who seeks the knowledge and skills to function as an integral member of a firefighting team under direct or general supervision in hazardous conditions. Enrollment is limited to students currently in the Fire Science Academy.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Demonstrate the knowledge and skills to perform basic firefighting emergency and rescue operations and duties.
- Demonstrate the knowledge and skills to operate basic firefighting rescue tools and equipment.
- Demonstrate the knowledge and skills to pass the National Professional Qualifications System (NPQS) certification test for Firefighting II level.
FS105 FIRE PREVENTION
Credits: 3
Course Offering: Fire Academy
Prerequisite: Instructor approval
A study of techniques of effective fire prevention to include fire hazards and causes; judging fire load, building construction; inspection techniques; storage of flammable and combustible liquids and hazardous materials security. This course is designed for career public safety officers and recruits.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Explain the authority to inspect, responsibilities of the fire inspector, the types of organizational structures that may affect inspection activities and public education.
- List the steps involved to prepare for inspection and inspection procedures and the purpose of follow up inspections.
- List and explain the different types of occupancy classifications and the different components of the means of egress.
- List and describe the different types of fire protection systems, and list the components of an effective water distribution system.
FS107 REPORT WRITING FOR THE FIRE SERVICE
Credits: 3
Course Offering: Fire Academy
Prerequisite: By permission of CJ Department Chair
Emphasis on principle and techniques of report writing; methods of writing the basic who, what, when, where, why and how; and procedures of gathering information and developing various types of reports. Study is designed to produce proficiency in report writing and to reinforce and expand skills previously acquired.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Understand the importance of accurate report writing and record keeping.
- Understand the standards and formats of basic fire service report forms.
- Properly complete required reports relative to fire and other emergency incidents.
- Develop administrative reports, memorandum, and correspondence related to the fire service organization.
FSM100 INTRODUCTION TO THE FOODSERVICE PROFESSION
Credits: 2
This course provides an overview of the hospitality and foodservice profession, including standards and behaviors that are essential for success in this field. Topics include the history, growth, and development of hospitality, tourism, and foodservice, orientation to career opportunities and pathways in the hospitality and foodservice industry, ethics, resume writing, interviewing skills, and networking. Sustainable practices in the foodservice industry are also covered.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Identify the characteristics of professional standards in attitude, behavior, and attire within the foodservice profession.
- Explore career opportunities available within the foodservice industry to determine specialization.
- Using ethical principles, lead by example in personal and professional situations.
FSM105 FOODSERVICE SUSTAINABILITY
Credits: 2
This course is about sustainable practices in foodservice operations. Topics include sustainability, agriculture, water, energy, waste management, and sustainable food practices.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Explain the importance of sustainable practices in a foodservice operation.
- Assess the importance of menu development when it comes to product availability and its impact on the environment.
- Describe a variety of sustainable practices available to foodservice operators.
- Discuss practices that will help to control foodservice costs, showing good environmental stewardship.
FSM110 PROFESSIONAL DINING ROOM SERVICE: THEORY
Credits: 2
Corequisite: FSM110L (unless already successfully completed)
This is the theoretical component of a two-part course. This component introduces students to the principles of professional dining room service focusing on the practices of high-quality customer service, attributes of a professional server, the service process, and marketing a positive guest experience. Students must take this concurrently with FSM110L Professional Dining Room Service: Laboratory, unless already successfully completed. Successful completers have the opportunity to earn the National Restaurant Association Customer Service certification.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Identify the characteristics of high-quality customer service.
- Explain the importance of server appearance in high-quality service.
- Create a formal customer service plan.
FSM110L PROFESSIONAL DINING ROOM SERVICE: LABORATORY
Credits: 1
Prerequisite: FSM110(unless already successfully completed)
This is the laboratory component of the FSM110 theory course. This is a hands-on training that provides students with fundamental technical skills in professional table service. Students will be introduced to systems, procedures, and techniques that enhance guest dining experience. Students will learn topics including techniques of suggestive selling, handling difficult and special situations, and the role of technology in the guest service process. Students must take this concurrently with FSM110 Professional Dining Room Service: Theory, unless already successfully completed.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Execute opening and closing duties following the restaurant standard operating procedures.
- Demonstrate the appropriate service sequence for the different types of service.
- Apply techniques in handling difficult and special situations in a restaurant setting.
- Perform cooperatively as a part of a service team.
FSM115 PURCHSING AND RECEIVING
Credits: 2
This course presents students with the concept of purchasing and practice of receiving in quality foodservice operations. Course objectives include: determining order quantities, writing effective purchase specifications, formal and informal price comparison, proper receiving, storage, product issue procedures, quality standards, regulations governing food products, purchasing ethics, and vendor relations.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs):
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Identify the concepts and principles related to effective purchasing and receiving procedures.
- Explain the importance of implementing proper purchasing and receiving procedures.
- Develop product specifications for a variety of food products.
FSM120 FOOD SAFETY & SANITATION
Credits: 2
This course aims to develop student understanding of the principles of food safety and sanitation and apply them in foodservice operations. Students will learn about the study of foodborne illnesses, biological, chemical, and physical hazards, cross contamination, the flow of food and Hazards Analysis Critical Control Point (HACCP), Safety Data Sheets (SDS), waste disposal and recycling, emergency policies for kitchen and dining room injuries, pest control, and appropriate types and uses of fire extinguishers. The course prepares students for the National Restaurant Association Food Protection Manager Certification exam.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs):
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Apply the basic principles of food safety.
- Practice good personal hygiene practices and personal appearance standards to life.
- Evaluate food safety and sanitation practices of a foodservice operation.
FSM130 PROFESSIONAL BAR AND ALCOHOL MANAGEMENT
Credits: 3
This course introduces students to the concepts of beverage management and alcohol service. Students will learn about bar management, controlling beverage costs, legal aspects of professional alcohol service, and marketing of alcohol beverage products. Furthermore, students will use the ServSafe Alcohol training modules to learn best practices for providing responsible alcohol service. Students will acquire an understanding of the criminal and civil liability relating to sale and service of alcohol. Through role play simulation, students will learn how to assess signs of intoxication, prevent guest intoxication, and deal with difficult situations while maintaining effective guest relations. Students’ knowledge will be assessed using the National Restaurant Association ServSafe® Alcohol Certification Exam.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- List beverage control procedures for receiving, storing, and issuing products.
- Explain the importance of providing responsible alcohol service.
- Implement proper procedures for dealing with non-compliant customers and intoxicated guests while maintaining effective guest relations.
FSM145 CULINARY AND BUSINESS MATH
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: MA098 or placement into college-level math
This course equips students with essential math skills tailored for the culinary and foodservice industry. Key topics include weight and measurement conversions, calculating food and portion costs, determining menu pricing, managing revenue and expenses, and analyzing profit and loss statements. Students will engage in hands-on activities, problem-solving exercises, and a comprehensive semester-long project to apply these skills in real-world scenarios.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Convert customary and metric units of measurements commonly used in the foodservice industry.
- Scale, cost, and price standardized recipes accurately.
- Analyze a profit and loss statement to assess financial performance.
FSM154 FOODSERVICE NUTRITION
Credits: 3
This is an introductory study of the science and principles of nutrition as it applies to foodservice operation. Students will describe the characteristics, functions, and food sources of major nutrients and evaluate recipes and menus using dietary guideline recommendations, food guides, and food labels. Topics also include principles of nutrient needs throughout the life cycle and its application to menu planning and food preparation, and maximization of nutrient retention in food preparation and storage. Successful completers will have the opportunity to earn the National Restaurant Association Nutrition course certificate.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Identify the characteristics and functions of each major nutrient.
- Evaluate recipes and menus using dietary guideline recommendations, food guides, and food labels.
- Analyze one’s own diet by applying nutritional principles and concepts.
- Create a one-week menu using the Food Exchange System.
FSM222 FOODSERVICE COST
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: FSM145 Culinary Business Math
This course develops students’ understanding of costs control procedures in purchasing, receiving, storing, issuing, and during food production and service. Topics include the importance of cost management in foodservice operations, menu engineering, and controlling labor and other related costs. Students will engage in problem-solving exercises, case studies, and complete a semester-long course project. Successful completers have an opportunity to earn the National Restaurant Association course certificate.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Identify key terms, principles, and concepts related to cost control in foodservice operations
- Explain the critical role of cost control in ensuring profitability of foodservice operations by managing food, labor, and operational expenses effectively.
- Analyze cost control strategies of foodservice operations from purchasing to service to optimize profitability.
FSM240 MENU PLANNING
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: FSM145 Culinary Business Math
In this course, students explore the fundamentals of menu planning and design. Key topics include costing, pricing, menu engineering, nutrition, and the various types of menus suited to different operations, along with marketing strategies for those operations. Throughout the semester, students will undertake a project that challenges them to develop a restaurant concept and create a suitable menu.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Develop a menu following the principles of menu layout and design.
- Apply the seven principles of menu planning.
- Utilize menu engineering to analyze menus.
FSM254 FOODSERVICE MARKETING
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: FSM240 Menu Planning
This course explores the fundamental principles and strategies of marketing within the foodservice industry. Key topics include the marketing process, market environment analysis, customer behavior, and the use of communication channels in sales promotions, publicity, and public relations. Students will participate in a comprehensive, semester-long marketing project. Upon successful completion, students may qualify for the National Restaurant Association course certificate.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Identify key terms, principles, and concepts related to foodservice marketing.
- Apply foodservice marketing concepts and principles in various food service scenarios.
- Prepare a marketing plan for a foodservice operation.
FSM255 FOODSERVICE ACCOUNTING
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: FSM145 Culinary Math
This course provides an introduction to foodservice accounting, focusing on the essential financial concepts and practices needed for effective management in the industry. Students will learn to interpret and analyze financial statements, including profit and loss statements and balance sheets, to assess the financial health of foodservice operations. Through practical applications, participants will develop skills in applying accounting principles to inform strategic decision-making. Upon successful completion, students may qualify for the National Restaurant Association course certificate.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Identify key terms, concepts, and principles associated with foodservice accounting.
- Apply accounting concepts and principles in foodservice operations to support decision-making processes.
- Interpret financial statements, including profit and loss statements and balance sheets to evaluate the financial health of foodservice operations.
FSM269 FOODSERVICE MANAGEMENT & LEADERSHIP
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: No prerequisite No prerequisite identified in curriculum doc.
This course aims to develop essential managerial and leadership skills, equipping students with the knowledge and competencies needed to excel in foodservice supervisory and management roles. Through an in-depth curriculum, students will prepare for the National Restaurant Association ManageFirst certification exam.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Identify key terms, principles, and concepts related with management and leadership within the foodservice industry.
- Explain the impact of management and leadership competencies on the success of foodservice operations.
- Apply management and leadership principles and concepts to solve challenges in diverse foodservice scenarios
FSM269B LEADERSHIP SEMINAR PART I
Credits: 1
Corequisite: FSM269C Leadership Seminar Part II
This course is a continuation of Leadership in Restaurant and Foodservice Operations designed to provide awareness of individual leadership styles. Through research, case studies, and guest speakers, students will learn the pros and cons of, examine behaviors associated with, and compare world leaders who exemplify each leadership style i.e. Transformational, Transactional, Servant, Commanding, Distributive, and Situational. Through this course, students will explore their own leadership style and identify leadership qualities they want to develop. Formerly RES269B.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Identify behaviors associated with different leadership styles.
- Identify leadership qualities students want to develop.
- Evaluate styles of leadership using an online leadership assessment tool.
FSM269C LEADERSHIP SEMINAR PART II
Credits: 1
Corequisite: FSM269B Leadership Seminar Part I
Through participation in an experiential learning at an on- or off-campus organization, students apply leadership knowledge and skills learned and acquired in FSM269A and FSM269B. In collaboration with an organization advisor or supervisor, students will develop a project goal to which leadership skills, i.e. goal setting, decision making, motivating others, and delegating tasks will be applied and evaluate project and performance in collaboration with an organization advisor.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Develop project goals in collaboration with an organization advisor.
- Apply leadership skills, i.e. goal setting, decision making, motivating others, and delegating tasks, in the execution of a project.
- Evaluate project and performance in collaboration with an organization advisor.
FSM270 FOODSERVICE HUMAN RESOURCES MANAGEMENT
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: Placement or completion of EN110
This course introduces students to key functions of human resource management, which includes recruitment and selection of best employees; orientation and training to optimize performance; building effective teams; facilitating performance appraisal; developing productivity standards, professional development programs, benefits, and compensation structure; managing a safe workplace; and effective labor relations. Human resource management concepts and practices are learned through case studies, application exercises, and field project exercises. Successful course completers will obtain the National Restaurant Association ManageFirst® course certificate, which signifies student achievement of competencies.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Create a human resource management handbook.
- Evaluate good human resource management strategies.
- List key functions of human resource management.
FSM292 FOODSERVICE PRACTICUM
Credits: 4
Prerequisite: FSM222 Cost Control
This course allows students to apply the restaurant management principles learned in the program. They will evaluate operations, policies, and procedures related to guest experience, cost management, human resources, and marketing, making recommendations for improvement. Throughout the semester, students will meet regularly with their faculty mentor and worksite advisor, and will maintain an electronic portfolio to document their learning and complete the required Practicum evaluation forms.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Apply customer service principles in the execution of work.
- Assess restaurant operations policy and procedures.
- Create a portfolio following the NRA course portfolio development standards.
FSM299 FOODSERVICE MANAGEMENT CAPSTONE
Credits: 3
Corequisite: FSM292 FoodService Practicum
This course offers an in-depth study of essential business management concepts, principles, and procedures which include customer service, menu management, human resource management, analysis and decision-making. Successful course completers have the opportunity to earn the National Restaurant Association course certificate.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Explain how enhancing quality should be the focus of an operation’s improvement philosophy.
- Develop a quality improvement plan for a foodservice operation.
- Create a business concept proposal for a foodservice operation.
HI121 HISTORY OF WORLD CIVILIZATION I
Credits: 3
This course explores the most important aspects of world civilizations from pre-historic time to 1700 A.D. It investigates the process of cross-cultural encounters between peoples of different cultural regions or civilizations. Attention is paid to migrations of peoples, the creation of long-distance trade networks, the transfer of technology, along with the various political, social, economic, and cultural features of the civilizations.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Discuss the impact of geographical features in the formation and evolution of early civilizations and societies.
- Conduct a historical analysis of an ancient civilization.
- Explain the origins and diffusions of the world’s major religious traditions.
HI122 HISTORY OF WORLD CIVILIZATION II
Credits: 3
This course discusses how the cultures, economies, and societies of the world developed since 1500 C.E. It explores issues of class and class conflict, personal and cultural identity, race, work, industrial development, colonialism, political and economic life pertaining to the history of world civilizations. The course examines a variety of historic experiences, discoveries, and inventions that have shaped modern society.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Identify major-social-cultural themes in World Civilization from 1500 to present.
- Apply principles and theories to major events related to world civilizations.
- Analyze how local, national, or international policies developed in the past continue to impact contemporary lives.
HI176 GUAM HISTORY
Credits: 3
This course covers the ancient settlement period prior to Ferdinand Magellan's arrival in 1521 up to the modern United States military buildup on Guam. The Spanish, Japanese and United States administration periods and development of self-rule will be discussed and analyzed. Students will also learn about the diverse influences that have contributed to the culture and history of Guam.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Demonstrate knowledge of Guam history.
- Examine CHamoru culture and values.
- Identify the qualities that make Guam unique.
HL120 MEDICAL TERMINOLOGY
Credits: 2
This course provides students with the elements of medical terminology. The study includes origins of medical terminology, the basic structure of medical words, word element combinations, medical terminology for medical specialties, and medical abbreviations.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs):
- Define 350 medical words and elements.
- Build and dissect medical terms from roots/suffixes to understand the word element.
- Define abbreviations and symbols.
HL131 BASIC LIFE SUPPORT FOR HEALTHCARE PROVIDERS
Credits: 1
The AHA’s BLS course trains participants to promptly recognize several life-threatening emergencies, give high-quality chest compressions, deliver appropriate ventilations and provide early use of an Automated External Defibrillator (AED). Reflects science and education from the American Heart Association Guidelines Update for CPR and Emergency Cardiovascular Care (ECC). The AHA’s BLS Course is designed for healthcare professionals and other personnel who need to know how to perform CPR and other basic cardiovascular life support skills in a wide variety of in-facility and prehospital settings (cpr.heart.org, 2022).
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Demonstrate how to perform bag mask ventilation.
- Demonstrate knowledge and skills of cardiopulmonary resuscitation for adults.
- Apply concepts to use an Automated External Defibrillator (AED).
HL135 HEARTSAVER FIRST AID CPR AED
Credits: 1
This course is for anyone with little or no medical training who needs a course completion card for their job, regulatory (e.g., OSHA), or other requirements or anyone who wants to be prepared for an emergency in any setting. Upon successful course completion, students receive a course completion card, valid for two years.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Perform Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation (CPR) on an adult manikin.
- Practice effective use of an Automated External Defibrillator (AED) on an adult victim.
- Administer basic first aid techniques.
HL150 STUDY OF DISEASE
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: HL120
This course provides the basic concepts and characteristics of disease processes, which include disease description, etiology, signs and symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, prognosis, and prevention and terminology pertaining to injuries and disease process.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Describe the etiology of commonly encountered diseases.
- Identify signs and symptoms of common diseases.
- Define basic medical terminology as related to diseases.
HL190 INTRODUCTION TO ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY FOR ALLIED HEALTH PROFESSIONAL
Credits: 4
Prerequisite: EN097 or EN110 placement or equivalent
This course is designed to serve students in the Career Technical Programs. This course will be part of the Medical Assistant Program core curriculum. Material covered includes the structure and function of the human body. Basic chemistry and cell structures are covered, as well as the organization of tissues, organs, and organ systems. Correlations can then be made between this material and disease states commonly encountered in the practice of these fields.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Describe the effects on cells placed in an isotonic solution, hypertonic solution, or a hypotonic solution.
- Differentiate between the effects of the sympathetic system and parasympathetic system on system organs.
- Describe common diseases, symptoms, and etiologies as they apply to each system.
HL201 MEDICAL LAW & ETHICS
Credits: 3
Through this course, students are provided the opportunity to apply working knowledge of laws to the practice of Medical Assisting and related healthcare fields.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Describe the difference between legal and ethical responsibilities in patient care and management.
- List the current patients’ rights according to the American Hospital Association (AHA).
- Evaluate the consequences of failing to adhere to medical law and ethics as related to the clinical medical office.
HL202 NUTRITION
Credits: 3
This course provides students with the basic knowledge of nutrition. The knowledge from this course will allow students to understand the relationship between health and nutrition and how to make wise choices that contribute to a healthy lifestyle. The course further discusses methods in optimizing the use of different food choices in reducing or avoiding health-related implications and/or illnesses.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Identify and describe the six main classifications of nutrients and their effects on the body.
- Analyze the recommended guidelines based on the food pyramid that help promote a healthy lifestyle.
- Recommend a dietary meal plan that addresses preventive and/or corrective treatment for common illnesses.
HL252 PATHOLOGY FOR HEALTH PROFESSIONS
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: HL190
The objective of this course is for the students to gain an understanding of underlying principles, manifestations and clinical implications of disease processes and alterations of function in body systems in all age groups through clinical case study.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Describe type II Hypersensitivity Reaction, and how it induces hemolytic anemia. (Immunopathology)
- Describe the distribution of fluid between the intracellular and extracellular compartments. (Fluid and hemodynamics)
- List common causes and discuss the pathogenesis of pneumonia. (Respiratory pathology)
HM110 INTRODUCTION TO COMMUNITY SERVICES
Credits: 3
Students will become familiar with services available in the community to meet human needs and to provide support needed to address social problems. Emphasis is on the development of knowledge from the perspective of a consumer and of skills necessary to locate, gain access to, and effectively utilize such services.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Apply different theories to understand the person in their environment.
- Identify the various types of community services available in Guam.
- Define social problems and analyze how community services can address social problems.
HM150 DIVERSITY IN HUMAN SERVICES
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: SO130 Introduction to Sociology
The course examines concepts and principles concerning human diversity. It sensitizes students to the complex social-economic political issues diverging from human equality, conflict resolution, as well as examining the effects of social injustice toward persons of race, gender, sexual orientation and disability. Additionally, students are provided awareness of social change affecting the professional commitment to ensure nondiscriminatory treatment and equal access for clients at all levels of practice interventions.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Analyze the needs and strengths of diverse groups.
- Assess how personal assumptions, biases, and prejudices influence how people interact with one another.
- Apply strategies to demonstrate culturally appropriate human services practices.
HM180 HUMAN SERVICES PRACTICUM ORIENTATION
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: HM110 Introduction to Community Services
The course is designed as a “bridge course” to foster a learning environment that enables students to explore their career pathway in human services. Students gain the knowledge of what to expect from a practicum experience and build awareness about the various human service practicum sites, services provided to its clients, as well as meeting with practicum instructors. By the end of the course, students select the practicum site to conduct field practicum hours.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Describe the structure, populations served, and services/programs of human services agencies in Guam.
- Identify potential practicum sites based on career and education goals and personal values.
- Demonstrate professionalism and effective communication skills when interacting with human services agencies.
HM201 SOCIAL WELFARE & DEVELOPMENT: GLOBAL CHALLENGES
Credits: 3
Students will differentiate social welfare from an international and cross-cultural perspective while focusing on the importance of cultural and value systems. Students will examine society’s allocation of resources, the development of informal and formal systems of care, and the roles and functions of social work.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Describe basic concepts of the structure and functions of social welfare.
- Explain social work pertaining to human behavior and the social environment within a bio-psycho-social-spiritual framework.
- Assess the ways that global trends shape the future of social work and social work education.
HM205 FOUNDATIONS OF CASE MANAGEMENT
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: HM201 Social Welfare and Development: Global Challenges
The course examines strengths-based case management practice models, interpersonal skills to foster a client-driven culturally sensitive partnering approach to care, communication/interviewing skills, service delivery, service coordination planning and proper documentation in case management. Students will further recognize the role of case managers within human service agencies and informal support systems.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Identify the primary roles and responsibilities of the case manager in the human services setting.
- Apply case management skills such as effective communication and interviewing skills in a culturally sensitive manner.
- Demonstrate writing techniques for effective documentation and Subjective Objective Assessment Plan (SOAP) notes.
HM225 SUBSTANCE MISUSE PREVENTION: PROGRAM PLANNING AND IMPLEMENTATION
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: PY120 General Psychology
The course critically examines the field and practice of prevention services to promote mental health and wellness in community settings. Students will gain knowledge of evidence-based prevention research and programming, as well as facts about drugs and other prevention work such as community readiness, strategic program implementation, and sustainability. Students will experience data-informed and community-driven program planning aimed at substance misuse prevention and mental health promotion.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Define behavioral health and the role of prevention activities in promoting community health and wellness.
- Describe three dominant theoretical orientations in substance misuse prevention: behavioral health continuum of care, socio-ecological model, public health approach.
- Articulate the six prevention strategies and apply them in systematic substance misuse prevention programming.
- Apply the role of cultural humility, health communication, and ethical principles in prevention programming.
HM250 ETHICS AND VALUES IN HUMAN SERVICES
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: HM150 Diversity in Human Services
The course is designed to help students integrate values and ethics into all aspects of human services and its related fields.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Differentiate between personal values, professional values, and ethical guidelines in human services.
- Apply professional ethical codes and relevant theories to ethical decision making.
- Analyze ethical dilemmas that may arise in a variety of settings and organizational contexts.
HM292 HUMAN SERVICES PRACTICUM
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: HM110 Introduction to Community Services
Corequisite: HM201 Social Welfare and Development: Global Challenges
Students will have the opportunity to apply their knowledge and skills while working under the mentorship of a qualified social services professional and faculty member. A minimum of 135 hours of work is required, which may include observations, meetings with clients and professionals, and professional development activities.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Demonstrate effective communication skills, professionalism, cultural competency, and ethical conduct working at a human services agency.
- Identify and adhere to the operational policies and procedures of a human services agency.
- Articulate classroom knowledge, professional codes of conduct, and theories with outside work experience.
HS150 WELCOME TO HOSPITALITY
Credits: 3
This course provides an overview of the hospitality, travel and tourism industry. Students will achieve an understanding of the concepts and facets of the hospitality, tourism and travel industry, interacting in the framework of product and service distribution systems. Students will learn, through career exploration, the importance of professionalism, guest relations, positive work habits, values, attitudes expected of hospitality employees, and career exploration.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Describe the main components of the hospitality, tourism, and travel industries.
- Explain the importance of guest relation skills and a hospitality attitude.
- Identify career opportunities in the hospitality, tourism, and travel industries.
HS152 CUSTOMER SERVICE
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: HS150
This course is designed to examine, challenge, and refine the principles of guest service management in various service organizations. Students will gain an understanding of "service products" and apply the tools to deliver these services and use these concepts in their own work experiences. Included is the American Hotel and Lodging Association Educational Institute's Guest Service Gold® program designed to train employees to be guest service-oriented to provide memorable service. A Certified Guest Service Professional (CGSP) examination is offered to those seeking a CGSP designation.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Utilize data to assess the guests’ wants and needs.
- Apply the accepted protocol for resolving guest complaints.
- Design a customer service campaign that appeals to the wants and needs of a guest.
HS155 BASIC HOTEL AND RESTAURANT ACCOUNTING
Credits: 3
This is an introductory course in basic hotel and restaurant accounting. Emphasis is placed on understanding and use of financial reports such as trial balance, income, and balance sheet statements. Topics such as the double entry system and types of inventory systems are included. Uniform systems of accounts for use in the lodging and restaurant industry is discussed.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Utilize the uniform systems of accounts to create a chart of accounts.
- Demonstrate accurate journaling with the double-entry system and analyze income and balance sheets.
- Summarize accounts and perform a trial balance in accordance with accounting standards.
HS157 TOURISM PLANNING AND DEVELOPMENT
Credits: 3
This course provides an overview of the tourism industry and how its components-destination, marketing, demand, and travel, interact with each other in order to create a successful tourism product. Students will learn principles of destination planning, development, and marketing and apply these principles in the study of Guam's tourism industry.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Explain the importance of tourism in the economy.
- Discuss the components of a tourism system.
- Create a tourism marketing program for Guam.
HS158 INTRODUCTION TO MICE
Credits: 3
This course provides students with knowledge and abilities that prepare them to assist with or manage the implementation and monitoring of meeting, exposition, event, or convention (MEEC). Students will learn tasks, activities, and issues involved in producing a meeting or event. Course competencies are aligned to Meeting and Business Event Competency Standards (MBECS) – which are global, industry-endorsed descriptions of the knowledge and abilities that meeting professionals need in order to be successful.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Describe the role and function of a meeting planner.
- Identify the legal and ethical responsibilities of a meeting planner.
- Create a project management plan for meeting, exhibition, event, and convention (MEEC).
HS160 HOSPITALITY SUPERVISION
Credits: 3
This course provides hospitality students with proven ways to get maximum results by directing and leading, within a hospitality supervision context. Students will learn to juggle the expectations of management, guests, employees, and governmental agencies. In addition, students will develop creative strategies for effectively managing change and resolving conflicts.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Identify fundamental supervisory responsibilities.
- Describe how supervisors work with the human resources department to recruit new employees.
- Describe issues supervisors should be aware of as they assume the role of team leader.
HS211 MANAGING FRONT OFFICE OPERATIONS
Credits: 3
Managing Front Office Operations provides an in-depth look at management of the front office and how this department interacts with other hotel departments to create a memorable guest experience. This course presents a systematic approach to front office procedures by detailing the flow of business through a hotel, from the reservations process to check-out and account settlement. It also examines the various elements of effective front office management, paying particular attention to the planning and evaluation of front office operations and to human resources management.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Describe the importance of operating an efficient front office in view of overall hotel performance.
- Apply various front office skills in the four stages of the guest cycle.
- Demonstrate knowledge of front office terminology and guest relations strategies when presented with various work situations.
HS215 MANAGING HOUSEKEEPING OPERATIONS
Credits: 3
Housekeeping is critical to the success of today's hospitality operations. This course exemplifies what it takes to direct day-to-day operations of this department, from big-picture management issues to technical details for cleaning each area. This course provides students with an understanding of managing housekeeping operations and provides strategies and tools to achieve housekeeping standards that meet guest expectations.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Describe and distinguish the role of housekeeping in a hotel operation.
- Apply concepts of environmentally sound procedures for sustainable housekeeping.
- Summarize the routine of guest room cleaning from room assignments, through inspections, and turndown service.
HS216 HUMAN RESOURCES MANAGEMENT
Credits: 3
This course is an introduction on managing the important human resources who provide services within a hospitality operation. Students will learn the latest strategies for attracting employees, minimizing turnover, and maximizing productivity. Topics include organizational culture and social responsibility issues, including what companies are doing (and not doing) right.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Describe employment laws, planning, and staffing.
- Explain human resources development activities such as staff orientation, socialization, training, and evaluation.
- Evaluate compensation and labor issues.
HS254 HOSPITALITY AND TRAVEL MARKETING
Credits: 3
This course examines the hospitality and travel marketing system. Students will learn the different types and roles of hospitality and travel industry organizations, how marketing applies to different travel components and various departments of a hospitality organization. Topics such as core principles of marketing, marketing approaches, strategic and tactical marketing, marketing research and analysis, marketing strategy, marketing plan development, and methods to effectively implement and control as well as evaluate the marketing plan will be covered.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Explain the core principles of marketing and their application to the Hospitality and Travel components of the tourism industry.
- Conduct marketing research by developing a survey relevant to the chosen topic.
- Create and present a Marketing Plan of their choice.
HS255 INTRODUCTION TO AIR TRANSPORTATION INDUSTRY
Credits: 3
This course will provide a broad overview of the aviation industry. Students will develop a basic knowledge and foundational skills to enhance their understanding of the complex network of the aviation industry with an emphasis on airline/airport management. This comprehensive introductory course aims to provide students with an overview of the air transportation system and the interdependence among its components: airlines, airports, civil aviation authorities and air navigation services. It prepares students for careers in airline and air transportation, and airport operations.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Identify the major components and interactions of the aviation system and the interdependence of the airlines, airports, civil aviation authorities and other regulatory entities.
- Understand the relationship between the airlines and airport services in providing passenger services for air travel.
- Construct a tour package for a market segment.
HS257 PRINCIPLES OF TOUR GUIDING
Credits: 3
This course prepares students to become professional tour guides. Students will learn the principles of tour guiding and knowledge about Guam's history and culture. Students will visit Guam's historic and scenic sites and perform the role of tour guides.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Describe how tour guides manage groups and keep them safe.
- Explain the importance of customer service.
- Apply public speaking techniques to describe historic and scenic sites.
HS265 SUSTAINABLE TOURISM
Credits: 3
This course will describe sustainable tourism as a form of tourism that fosters learning experiences and appreciation of the natural environment within a region or a culture. It will offer the student an insight to sustainable tourism and how it supports a social-cultural industry that is sustainable, enhances a destination and promotes businesses of an ecotourism nature.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Describe why sustainable tourism is an environmentally focused, responsible and sustainable type of tourism.
- Compare and contrast the differences between nature based, cultural, and adventure tourists.
- Explain career opportunities in the sustainable tourism field and how best to use this training to become a travel professional of the new century.
HS266 INTERNATIONAL HOTELS: DEVELOPMENT & MANAGEMENT
Credits: 3
This course prepares students for leadership roles in tomorrow’s worldwide lodging industry. Future international hotel managers will need a fuller understanding and deeper appreciation of management and marketing applications within a globalized context.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Describe the phases of hotel development and the criteria for selecting a location for an international hotel.
- Explain the qualities required for a manager in an international hotel and the importance of understanding cultural diversity.
- Cite the future growth of international hotels in the era of globalization.
HS268 MANAGING TECHNOLOGY IN THE HOSPITALITY INDUSTRY
Credits: 3
This course is an overview of the information needs of lodging properties. It will cover basics of purchasing, implementing, maintaining, and managing a variety of technology systems used in hospitality and security precautions needed.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Identify common technology systems used in hospitality operations.
- Describe the elements of a rooms management module.
- Define various threats to technology systems and the security precautions needed.
HS292 HOSPITALITY AND TOURISM PRACTICUM
Credits: 3
This course allows students to apply their knowledge and skills via on-the-job training in the hospitality and tourism industry.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Apply appropriate management styles in the workplace.
- Exercise the importance of customer service in the hospitality and tourism industry.
- Demonstrate desirable workplace behaviors such as punctuality, communications, and proper appearance.
HU120 PACIFIC CULTURES
Credits: 3
Pacific Cultures takes a look at the exploration of the Pacific peoples and their diverse cultural and biological heritages. The course provides a comprehensive survey about Pacific Island cultures. The course further examines the first migrations of indigenous navigators through the age of European exploration and colonialism, as well as exploring the unique cultural configurations of ritual practice, cosmology, and society.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Describe the culture, economy, and politics of the island nations and territories.
- Compare and contrast various Pacific Island cultures.
- Explain relevant sociological concepts as it applies to decolonization efforts to transform Pacific Island regional development and modernization.
HU220 GUAM CULTURES & LEGENDS
Credits: 3
This course covers Guam’s cultural development and conflicts. Cultural environments both past and present are explored. Emphasis is made on the study of CHamoru culture through folklore. Students will learn the effect of cultural interchange that will enable them to answer specific questions from visitors with a more accurate and deeper explanation.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Identify the basic principles and theories of the origin of the CHamoru people and their culture.
- Demonstrate an understanding/appreciation of the CHamoru people and their culture.
- Apply basic principles and theories of the CHamoru people and their culture.
IN145 VOCABULARY DEVELOPMENT FOR INTERCULTURAL DEVELOPMENT
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: ASL110
Corequisite: ASL120
This course provides students with information and instruction to develop skills aimed at increasing vocabulary and word choice repertoire for effective interpreting. This course will also include the study of how language is culturally based, the effects of culture on intercultural communication and possible cultural conflicts.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Demonstrate critical thinking and appropriate responses in any social context using local, national and global vocabulary skills.
- Improve and expand vocabulary in American Sign Language (ASL) conversation to include the use of idioms, common expressions, and other figures of speech.
- Develop strategies and word choice repertoire to facilitate effective interpreting.
IN170 INTRODUCTION TO INTERPRETING
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: ASL110
Corequisite: ASL120
This course addresses basic theory and practice of interpretation in a variety of settings. Students will be introduced to the communication process as a whole and the way messages are constructed within the Deaf and Hard of Hearing community. Information on linguistic register, cultural characteristics, ethics and professional conduct, and the modes of interpreting will be explained and discussed.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Explain the various modes of interpreting such as simultaneous, consecutive, and sight translation.
- Identify settings for interpreting (i.e. educational, legal, medical) and demonstrate appropriate skills needed to facilitate communication.
- Adhere to a set of values or code of ethics established for interpreters according to the Registry of Interpreters of the Deaf (RID).
IN180 ECOLOGY OF DEAFNESS
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: IN170
This course will expand the student's knowledge of the impact of deafness on language and cognitive development and the socialization of Deaf individuals in a hearing world. Students will also be acquainted with characteristics of Deaf culture.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Identify and describe the impact of deafness on language and cognitive development.
- Analyze and evaluate the concept of ecology of deafness.
- Reflect on the ways in which school learning communities help improve programs, strengthen families, invigorate community support, and increase student success as related to the Deaf community.
IN220 VOICE TO SIGN/SIGN TO VOICE INTERPRETING
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: ASL120
Corequisite: ASL130
This course focuses on building expressive and receptive skills, such as interpreting a message from spoken English into American Sign Language and vice versa. The course will further enhance understanding of what an interpreting career entails. It also assists students in developing voice to sign and sign to voice interpreting skills, to include cognitive processing skills.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Interpret American Sign Language into spoken English (sign to voice).
- Interpret spoken English into American Sign Language (voice to sign).
- Explain the dynamics of voice to sign and sign to voice.
IN292 SIGN LANGUAGE INTERPRETING PRACTICUM
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: IN220
This course is designed to expose ASL students to real-world interpreting experiences under the supervision of a professional in the field or related field who will serve as their mentor. This course focuses on the challenges and benefits of working in various settings (educational, medical, community & legal), following a code of ethics, and decision-making skills. Students will be expected to exhibit ethical conduct and characteristics of a professional interpreter while at all practicum placement sites and assignments related to practicum.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Conduct accurate interpreting services (voice to sign and sign to voice) within a cross-cultural context.
- Apply professional interpreting work ethics at entry-level proficiency in a real world setting.
- Reflect on the practicum experience to include identification of strengths, weaknesses, and ways to improve interpreting work.
IT103 DIRECT CURRENT CIRCUITS
Credits: 4
This beginning course in electricity provides a thorough, comprehensive, and practical coverage of direct current circuit's concept and application. It covers electrical safety, scientific notation, electricity, resistors, ohm's law, series circuits, parallel circuits, series-parallel circuits, conductors and insulators, analog and digital multimeter, batteries, magnetism, and electromagnetic induction.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Follow national, state, and local industry established electrical safety.
- Explain and illustrate the elements and properties of electrical circuits.
- Design, analyze, and calculate electrical quantities of series, parallel, and series-parallel circuits.
IT104 ALTERNATING CURRENT CIRCUITS
Credits: 4
Prerequisite: EE103
This second course in electricity provides a thorough, comprehensive, and practical coverage of alternating current circuit's concept and application. It includes basics of trigonometry, alternating current and voltage, capacitance, capacitive reactance, capacitive circuits, inductance, inductive reactance, inductive circuits, RC and RL time constant, alternating current circuits, resonance, and filters.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Follow national, state, and local industry established electrical safety procedures.
- Illustrate and describe AC voltage and the characteristics of AC voltage source.
- Design, experiment, and troubleshoot alternating current circuits.
IT130 PROJECT MANAGEMENT FOR IT
Credits: 3
This course is designed to provide basic project management skills with a strong emphasis on issues and problems associated with delivering successful IT projects. The module is designed to provide an understanding of the particular issues encountered in handling IT projects and to offer students methods, techniques and 'hands-on' experience.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Identify the fundamentals of project management.
- Demonstrate effective project execution and control.
- Implement general business concepts, practices, and tools to facilitate project success.
IT131 SERVER TECHNOLOGY
Credits: 3
This course builds on student’s existing mid- to upper-level knowledge and experience with personal computer operating systems and networks. Students will learn to utilize advanced skills and concepts necessary for management of server technology.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Describe different types of servers, identifying their hardware and software components.
- Explain disaster-recovery concepts and techniques.
- Configure servers for optimal performance.
IT211 IT ESSENTIALS
Credits: 4
This course covers the fundamentals of computer and mobile device hardware and software, and advanced concepts such as security, networking, and the responsibilities of an IT professional. Students who complete this course will be able to describe the internal components of a computer, assemble a computer, install operating systems, and troubleshoot them using software tools and diagnostics. Students will be able to connect to the internet and share resources in a networked environment. Students will also be introduced to new topic versions such as DNS records, spam management, virtual LAN (VLAN), privacy, and gaming. Additional topics that will be covered include Operating System Upgrades, Windows Configuration, and IT Professional knowledge.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Install components to build, repair, or upgrade personal computers.
- Explain how computers communicate on a network.
- Implement basic host, data, and network security.
IT242 PRINCIPLES OF VOICE AND DATA CABLING
Credits: 3
The Principles of Voice and Data Cabling course is designed for students interested in the physical aspects of voice and data network cabling and installation. This course stresses documentation, design, installation, laboratory safety, as well as working effectively in group environments. Students will become familiar with cabling issues related to data and voice connectivity, media and transmission practices, and cabling customer support. This course provides an overview of cabling and networking industry standards as well as emerging cabling technologies.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Define standards and codes pertaining to the installation, testing and certification of network cables.
- Install and terminate enterprise network cabling systems.
- Test and certify enterprise network cabling systems.
IT243 FIBER OPTICS INSTALLATION
Credits: 3
Students enrolled in this course will work with fiber optics cables, gain knowledge of fiber optics, and will learn how to splice, terminate, and test fiber optics cables/systems.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Define standards and codes pertaining to the installation, termination, and testing of fiber optic cables.
- Install, terminate, and splice fiber optic cables.
- Test, troubleshoot, and certify fiber optic cables.
IT265 COMPUTER NETWORKING I
Credits: 5
The first course in the CCNA curriculum introduces the architectures, models, protocols, and networking elements that connect users, devices, applications and data through the Internet and across modern computer networks - including IP addressing and Ethernet fundamentals. By the end of the course, students will be able to build simple local area networks (LAN) that integrate IP addressing schemes, foundational network security, and perform basic configurations for routers and switches.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Build a simple Local Area Network (LAN).
- Perform basic configurations for routers and switches.
- Implement IPv4 and IPv6 addressing schemes.
IT266 COMPUTER NETWORKING II
Credits: 5
Prerequisite: EE265
The second course in the CCNA curriculum focuses on switching technologies and router operations that support small-to-medium business networks and includes wireless local area networks (WLAN) and security concepts. Students learn key switching and routing concepts. Perform basic network configuration and troubleshooting, identify and mitigate LAN security threats, and configure and secure a basic WLAN.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Configure switch security to mitigate LAN attacks.
- Configure IPv4 and IPv6 floating static routes.
- Implement VLANs and trunking in a switched network.
IT267 COMPUTER NETWORKING III
Credits: 5
Prerequisite: IT266
The third course in the CCNA curriculum describes the architectures and considerations related to designing, securing, operating, and troubleshooting enterprise networks. This course covers wide area network (WAN) technologies and quality of service (QoS) mechanisms used for secure remote access along with the introduction of software-defined networking, virtualization, and automation concepts that support the digitalization of networks. Students gain skills to configure and troubleshoot enterprise networks, and learn to identify and protect against cybersecurity threats. They are introduced to network management tools and learn key concepts of software-defined networking, including controller-based architectures and how application programming interfaces (APIs) enable network automation.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Utilize single-area OSPFv2 in both point-to-point and broadcast multi-access networks.
- Implement IPv4 ACLs to filter traffic and secure administrative access.
- Perform network management protocols to monitor the network.
IT268 COMPUTER NETWORKING IV
Credits: 5
Prerequisite: IT267
Computer Networking IV focuses on WAN technologies and network services required by converged applications in a complex network. The course enables students to apply the selection criteria for network devices and WAN technologies to meet network requirements.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Write access control lists (ACLs) to filter traffic.
- Implement remote access and site-to-site Virtual Private Networks (VPNs).
- Configure router to router for WAN.
IT271 ADVANCED COMPUTER NETWORKING I
Credits: 5
Prerequisite: EE268
This course is the first course in the Cisco Certified Networking Professional (CCNP) curriculum. This course will cover the configuration of Cisco routers for operation in large or growing multiprotocol Internet works. This course includes lectures and labs that focus primarily on scalable technologies and the Cisco IOS software features that are most useful in building large or growing Internet works. These features include scalable routing protocols such as Open Shortest Path First (OSPF), Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP), Intermediate System to Intermediate System (IS-IS), Border Gateway Protocol (BGP), Variable Length Subnet Mask (VLSM), Classless Inter Domain Routing (CIDR), route redistribution, and route summarization.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Identify scalable technologies for growing internet works.
- Configure CISCO routers for operations.
- Implement the EIGRP, IPv6, and OSPF in an enterprise network.
IT283 NETWORK SECURITY +
Credits: 3
This course is targeted toward an Information Technology (IT) professional with the recommendation that he/she has networking and administrative skills in Windows-based TCP/IP networks and familiarity with other operating systems, such as NetWare, Macintosh, UNIX/LINUX, and OS/2, who wants to: further a career in IT by acquiring a foundational knowledge of security topics; prepare for the CompTIA Security+ Certification examination; or use Security+ as the foundation for advanced security certifications or career roles.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Identify fundamental concepts of computer security.
- Identify security threats.
- Implement cybersecurity resilience using secure network administration principles.
IT284 CCNA SECURITY
Credits: 5
The CCNA Security equips students with the knowledge and skills needed to prepare for entry-level security specialist careers. This course is a hands-on, career-oriented e-learning solution that emphasizes practical experience. CCNA Security aims to develop an in-depth understanding of network security principles as well as the tools and configurations required to secure a network.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Describe the basics of securing a network.
- Apply firewall technologies to secure the network perimeter.
- Implement Adaptive Security Appliances (ASA) firewall configuration using the CLI.
IT285 Cybersecurity Operations
Credits: 5
The course aligns with the Cisco Certified CyberOps Associate (CBROPS) certification. Candidates need to pass the 200-201 CBROPS exam to achieve the Cisco Certified CyberOps Associate certification. The CBROPS exam tests a candidate’s knowledge and skills related to security concepts, security monitoring, host-based analysis, network intrusion analysis, and security policies and procedures.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOS)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Explain how to investigate endpoint vulnerabilities and attacks.
- Demonstrate the process to prevent malicious access to computer networks, hosts, and data.
- Classify the various types of network attacks.
IT292 INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY PRACTICUM
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: Advisor approval
This course provides students with hands-on experience to prepare for employment within the computer networking field. They will apply theory and skills to practical situations in a networking environment.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Practice professionalism in a networking environment.
- Integrate classroom knowledge and theories with external work experience.
- Develop practical work related skills.
JA110 JAPANESE I
Credits: 4
This course provides students’ basic Japanese language conversation, grammar, and useful expressions used in daily life situations. Speaking in Japanese and building vocabulary is emphasized in this course. Students will learn to read and write Hiragana and Katakana. Cultural aspects of Japan’s society are also discussed to better understand the language and its people.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Comprehend simple spoken conversations.
- Converse in simple Japanese language in a variety of everyday life situations.
- Read and write simple sentences written in Hiragana and Katakana.
JA111 JAPANESE II
Credits: 4
Prerequisite: JA110
This is an intermediate language course with emphasis on reading and writing Japanese. Students will learn how to read and write in Hiragana, Katakana, and basic Kanji.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Read and write sentences in the Japanese alphabet: Hiragana and Katakana.
- Learn to write Basic Kanji.
- Practice speaking in Japanese.
KE110 KOREAN I
Credits: 4
This course is an introductory course in the Korean language. Students will develop language skills in pronunciation, basic grammar, reading, and writing. Students will learn grammatical structures and vocabulary that are necessary for basic conversation, developing both a solid foundation in the Korean language and insights about the culture.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Exhibit basic understanding of Korean culture and social norms.
- Comprehend simple Korean language sentences and be able to answer appropriately in the correct contexts.
- Converse in Korean using culturally acceptable expressions.
KE111 KOREAN II
Credits: 4
This course will enable learners to achieve the intermediate level of speaking, listening, reading, writing and utilizing grammar skills in Korean. Students will also learn the context of various aspects of Korean culture and society. Formerly titled Intermediate Korean.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Exhibit advanced understanding of Korean culture and social norms.
- Comprehend advanced Korean language sentences and be able to answer appropriately in the correct contexts.
- Acquire test-taking skills necessary for taking the Test of Proficiency in Korean (TOPIK).
AEMA050 ALGEBRA I
Credits: 3
This course is the first of three general mathematics courses designed to prepare students for college level mathematics courses or to have basic mathematical skills to succeed in the workplace. The Adult High School mathematics courses follow the College and Career Readiness Standards (CCRS) for Adult Education. The three shifts by CCRS (focus, coherence, and rigor) ensures that students understand and apply mathematical ideas.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Interpret the structure of expressions.
- Write expressions in equivalent forms to solve problems.
- Perform arithmetic operations on polynomials.
- Analyze proportional relationships and use them to solve real-word mathematical problems.
- Solve equations as a process of reasoning.
AEMA060 GEOMETRY
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: AEMA050
As one of the three mathematics courses, AEMA60 Geometry is designed to prepare students for college-level mathematics courses or to have basic mathematical skills to succeed in the workplace. Topics include Expressing Geometric Properties with Equations, Congruence, Similarity, Right Triangles, Geometric Measurement, and Dimension and Circles. The Adult High School mathematics courses follow the College and Career Readiness Standards (CCRS) for Adult Education. The three shifts by CCRS (focus, coherence, and rigor) ensure that students understand and apply mathematical ideas.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Experiment with transformations in the plane and develop definitions of rotations, reflections, and translations in terms of angles, circles, perpendicular lines, parallel lines, and line segments.
- Make formal geometric constructions such as copying and bisecting a segment, copying and bisecting an angle, constructing perpendicular lines, including the perpendicular bisector of a line segment with a variety of tools and methods.
- Prove geometric theorems, theorems involving similarity, and applying these theorems to solve problems.
- Draw and identify lines and angles, and classify shapes by properties of their lines and angles.
AEMA070 ALGEBRA II
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: AEMA050
This is a continuation of the AEMA050 Algebra 1. Topics include: Linear Equations, Linear Functions and their Graphs, Quadratic Functions, Exponential and Logarithmic Functions, Polynomials and Polynomial Functions, Radicals and Radical Functions, Rational Functions, Systems of Linear Equations, and Arithmetic and Geometric Sequences.
This course is the third of three general mathematics courses designed to prepare students for college-level mathematics courses or to have basic mathematical skills to succeed in the workplace. The Adult High School mathematics courses follow the College and Career Readiness Standards (CCRS) for Adult Education. The three shifts by CCRS (focus, coherence, and rigor) ensures that students understand and apply mathematical ideas.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Create equations that describe numbers or relationships.
- Solve equations as a process of reasoning.
- Interpret functions.
- Build functions.
- Understand ordering and the absolute value of rational numbers.
MA096 PRE-COLLEGIATE MATHEMATICS
Credits: 6
MA096 is a comprehensive lecture course that is designed for students to complete all developmental math requirements in one semester. Successful students will acquire the skills needed for a college-level mathematics course. Upon successful completion of this course, students may register for the credited math courses.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Compute operations with whole numbers, decimals, fractions, proportions and percentages.
- Solve applications and conversions with unit measurements.
- Calculate basic descriptive statistics and applications involving basic geometry.
- Solve equations and inequalities with real numbers.
- Graph a linear equation and a linear inequality.
MA097 PRE-ALGEBRA
Credits: 4
MA097 Pre-Algebra is the first level in a fundamental mathematics course. This is a course designed for students to acquire the basic algebraic skills needed for an intermediate algebra level mathematics course. This course may be conducted either at an accelerated pace for half a semester or traditional pace for a full semester. Classroom instruction is comprised of one or more of the following: accelerated, modular and mastery instructional strategies, computer-assisted learning, active learning, non-traditional learning strategies and/or traditional lecture-based strategies. Upon successful completion of this course, students may register for MA098.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Compute operations with whole numbers, decimals, fractions, proportions and percentages.
- Solve applications and conversions with unit measurements.
- Calculate basic descriptive statistics and applications involving basic geometry.
- Simplify expressions and solve equations and inequalities with real numbers.
- Graph a linear equation and a linear inequality.
MA098 INTERMEDIATE ALGEBRA
Credits: 4
Prerequisite: MA097 or placement
MA 098 Intermediate Algebra is the second level in a fundamental mathematics course. This is a course designed for students to acquire the fundamental algebraic skills needed for a college level mathematics course. This course may be conducted either at an accelerated pace for half a semester or traditional pace for a full semester. Classroom instruction is comprised of one or more of the following: accelerated, modular and mastery instructional strategies, computer-assisted learning, active learning, non-traditional learning strategies and/or traditional lecture based strategies. Upon successful completion of this course, students may register for MA110A.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Solve equations, inequalities and applications with real numbers.
- Graph and solve systems of linear equations and system of linear inequalities.
- Simplify and solve polynomial expressions and equations.
- Simplify and solve rational expressions and equations.
- Solve quadratic equations using the following methods: factoring, completing the square and quadratic formula.
MA110A FINITE MATHEMATICS
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: Placement or equivalent
This course is designed for students to meet their general education math requirement. Topics include linear, quadratic, polynomial, exponential and logarithmic functions, and finance applications. Students will be provided an introduction to Matrices and Linear Programming.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs):
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Demonstrate various methods for solving systems of linear equations and inequalities to include matrices.
- Determine the graphical and algebraic characteristics of quadratic, exponential and logarithmic functions.
- Solve for simple and compound interest and present and future value.
MA115 FUNDAMENTALS OF COLLEGE ALGEBRA
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: Successful completion of MA098 or placement
This course will prepare students with the fundamental algebraic skills needed to be successful in MA161A. Students will learn about polynomial equations, radical expressions, systems of equations and inequalities, functions, inverse function, graphing, rational, exponential, and logarithmic functions, and application problems.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs):
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Describe different types of functions and their graphs.
- Solve a variety of equations to include the graphing of two variable equations and quadratic equations.
- Model real-world situations using polynomial, exponential, and logarithmic functions.
MA151 INTRODUCTORY STATISTICS
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: Placement/eligibility to enroll in any credited GCC mathematics course.
This course discusses the technical terminologies, concepts, principles, and statistical methods that are important in the descriptive aspects of Statistics. Students will learn about the nature of Statistics as a field of study, data organization and summary, probability concepts and rules, discrete random variables and their distributions, and normal distributions.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Describe Statistics as a field of study.
- Define the technical terms and procedures used in organizing data.
- Differentiate among descriptive measures to summarize data.
- Apply the normal distribution using its attributes and basic probability rules.
MA161A COLLEGE ALGEBRA & TRIGONOMETRY I
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: MA115 or placement
This course is the first of two courses designed to provide the mathematical tools needed by students enrolled in selected technical occupational programs. Topics included in this course are equations and inequalities, functions and graphs, polynomial and rational functions, exponential and logarithmic functions, and systems of linear equations and inequalities with matrices.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Demonstrate methods for solving basic linear and polynomial equations and inequalities.
- Determine the graphical and algebraic characteristics of polynomial, rational, exponential, logarithmic, and other functions and their graphs.
- Perform alternative methods in solving systems of linear equations and inequalities graphically and algebraically.
MA161B COLLEGE ALGEBRA & TRIGONOMETRY II
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: “C” or better in MA161A
This course is a continuation of MA161A and upon successful completion, a student will be calculus ready. Topics included in this course are trigonometric functions, trigonometric identities and equations, and applications of trigonometry and discrete algebra.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Demonstrate understanding of the trigonometric concepts to solve trigonometry exercises and equations.
- Determine which definition, concept, and identity should be implemented to find solutions to application problems.
- Apply basic mathematical concepts and methods involving the concept of sequences, counting processes, probability and mathematical induction.
MA165 PRECALCULUS
Credits: 5
Prerequisite: Completion of MA115 with C or better, Placement
This course is designed to provide the mathematical tools needed by students enrolled in selected technical occupational programs and to be Calculus-ready. Topics included in this course are polynomial and rational equations, exponentials and logarithmic functions, systems of linear equations and inequalities, analytic and applications of trigonometry, sequences and series, and analytic geometry.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Differentiate among linear, polynomial, rational, exponential, logarithmic, and trigonometric functions and their graphs.
- Apply appropriate mathematical techniques to solve linear, polynomial, rational, exponential, logarithmic, and trigonometric equations.
- Utilize appropriate mathematical modeling techniques to solve linear, polynomial, rational, exponential, logarithmic, and trigonometric applications.
- Explain the characteristics of the conic sections graphically and algebraically.
MA203 CALCULUS
Credits: 5
Prerequisite: C or better in MA161B or MA165, placement, or approval of Department Chair
This course is an introduction to differential calculus. Areas of focus include limits, continuity, and differentiation of algebraic and trigonometric, logarithmic, exponential and other transcendental functions using the definition of derivatives product, quotient, and chain rule. Applications and Riemann Sums are also included.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Determine limits of a function.
- Find derivatives of algebraic functions using the definition of a derivative.
- Find derivatives of transcendental functions using product, quotient, and chain rules.
- Use limits and differentiation in real-life applications.
MA385 APPLIED STATISTICS
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: A Grade of “C” or better in MA151
This course illustrates statistical methods that attempt to derive and interpret inferences about populations based on samples taken from them. Students will learn about sampling distributions, central limit theorem, point estimation, interval estimation, small-sample (n<30) testing of hypotheses, large-sample testing of hypotheses, simple correlation, linear regression, analysis of categorical data, and nonparametric statistics.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Apply point and interval estimation.
- Test hypotheses on parameters from samples taken from populations with known distributions.
- Compare two or more populations using nonparametric methods on samples taken from distribution-free groups.
MHT100A INTRODUCTION TO DIESEL TECHNOLOGY AND PREVENTIVE MAINTENANCE I
Credits: 3
This is the first of two introductory courses that prepare students for the study within specific areas of the Medium/Heavy Truck Diesel Technology Program. In this course, students learn about workshop safety practices, proper usage of hand tools, special tools, testing equipment, and preventive maintenance procedures on diesel engines, fuel systems, air induction, and exhaust systems.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs):
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Differentiate between safe and unsafe workshop practices.
- Demonstrate proper usage of hand tools, special tools, and testing equipment.
- Perform preventive maintenance procedures on diesel engines, fuel systems, air induction, and exhaust systems.
MHT100B INTRODUCTION TO DIESEL TECHNOLOGY AND PREVENTIVE MAINTENANCE II
Credits: 3
This is the second of two introductory courses that prepare students for study within specific areas of Medium/Heavy Truck & Diesel Technology. The course focuses on preventive maintenance procedures involving the cooling system, lubrication system, cab and hood, safety equipment, hardware, heating ventilation & air conditioning, electrical and electronics, charging system, starting system, lighting system, frame and chassis, hydraulic and air brake systems, drivetrains, suspension and steering systems, tires and wheels, and frame with fifth wheel.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Identify brake system components and configurations.
- Distinguish the various components and configurations of suspension and steering systems.
- Depict drive train components and configuration.
- Perform preventive maintenance procedures on safety equipment hardware, heating, ventilation and air conditioning system,
- electrical/electronic, charging and starting system, lighting system, frame and chassis.
MHT110 DIESEL ENGINES PART I
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: MHT100A & MHT100B
This course introduces students to the theory and operation of diesel engines that includes general engine diagnostics, minor diagnosis and repair of cylinder head and valve train, engine block, lubrication system, and cooling system.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Explain general diesel engine operation and perform basic engine troubleshooting and repair.
- Demonstrate cylinder head and valve train diagnostics and repair.
- Expound engine block diagnostics and repair.
- Identify lubrication system components and diagnose and repair minor problems.
- Name the major parts and explain the functions of the cooling system and execute minor diagnostic and repair procedures.
MHT120 MEDIUM HEAVY TRUCK DRIVE TRAINS PART I
Credits: 3
This is an introductory course covering the functionality of diesel transmissions, fundamentals of diesel clutches, troubleshooting, and repair of basic transmission drivability faults.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Describe clutch operation.
- Discuss diesel transmission functionality.
- Troubleshoot elemental transmission drivability problems and repair elemental faults.
MHT130 BRAKE SYSTEMS PART I
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: MHT100A & MHT100B
This course provides instruction in Medium/Heavy Truck Brakes that includes basic diagnosis & repair of air supply and service systems, mechanical/foundation systems, and parking brakes.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Depict air supply and service systems operation.
- Identify mechanical/foundation system components and perform minor repairs.
- Explain parking brake operation.
MHT140 MEDIUM HEAVY TRUCK SUSPENSION & STEERING I
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: MHT100B
In this course students will learn about elements of Medium Heavy Truck Suspension & Steering that include introductory level steering system functions, diagnostics and repair, suspension system functions, diagnostics and repair, and wheel alignment diagnosis, adjustment, and repair.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Identify suspension and steering system components and configurations.
- Perform inspections and needed services of axle and axle aligning devices.
- Diagnose steering system issues.
MHT150 MEDIUM HEAVY TRUCK HEATING, VENTILATION, & AIR CONDITIONING
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: MHT100A & MHT100B
This course gives students basic instruction in Medium/Heavy Truck Heating Ventilation & Air Conditioning (HVAC) that include HVAC systems diagnosis, service, and repair, general A/C system diagnosis, service, and repair, A/C compressor and clutch, diagnosis, service, and repair, and evaporator, condenser, and related components, diagnosis, service, and repair.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Depict basic HVAC system operation.
- Troubleshoot general A/C system malfunctions.
- Explain A/C compressor and clutch operation and perform basic repairs.
- Describe evaporator, condenser, and related components' functionality.
MHT160 HYDRAULICS
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: MHT100A & MHT100B
This course provides students with fundamental instruction in Medium/Heavy Truck Hydraulic Systems that include entry level general hydraulic system diagnosis, service, and repair, hydraulic system pump diagnosis, service, and repair; and filtration-reservoirs (tanks) diagnosis, service, and repair.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Recognize general hydraulic system components and carry out entry level diagnosis, service, and repair.
- Ascertain basic hydraulic system failures and perform preliminary pump diagnosis, service, and repair.
- Perform fundamental filtration/reservoirs (tanks) diagnosis, service, and repair.
MHT170 MEDIUM HEAVY TRUCK ELECTRICAL/ELECTRONIC SYSTEMS PART I
Credits: 3
This course is designed to give students an elemental understanding of Medium/Heavy Truck Electrical/Electronic Systems that include general electrical systems diagnosis, battery diagnosis and repair, and starting system diagnosis and repair.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Perform general electrical systems diagnosis.
- Discuss battery construction and determine cause/s of battery failure.
- Demonstrate fundamental starting system diagnosis and repair.
MHT210 DIESEL ENGINES PART II
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: MHT110
This course builds on MHT110. Skills that students will learn include, systemic diagnosis and repair of induction and exhaust, fuel supply, mechanical fuel injection, electronic fuel management, and engine brakes.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Inspect engine exhaust system components to determine needed action.
- Utilize electronic service tools and service information systems to set performance parameters.
- Demonstrate knowledge of charge air cooler operation and testing.
- Perform cylinder contribution test using electronic diagnostic equipment.
MHT230 MEDIUM HEAVY TRUCK BRAKE SYSTEMS II
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: MHT130
This course prepares students to perform complex diagnostics and repairs on hydraulic brakes, power assist units, and air and hydraulic Antilock Brake Systems (ABS), and Automatic Traction Control (ATC).
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Systematically diagnose hydraulic brake systems.
- Utilize electronic testing equipment to perform diagnostics on dynamic brake control systems.
- Test vehicle/wheel speed sensors and circuits: adjust, repair, and/or replace as needed.
- Perform maintenance on wheel bearings.
MHT270 MEDIUM HEAVY TRUCK ELECTRICAL/ELECTRONIC SYSTEMS II
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: MHT170
This course builds on MHT170. The course of study includes lighting systems diagnosis and repair, and the diagnosis and repair of warning devices, gauges, and related electrical systems.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Locate faults in the lighting system and correct problems.
- Pinpoint failure causes in gauges and take proper action to correct situation.
- Ascertain cause of failure in warning devices and other related electrical systems and repair fault.
MK123 PRINCIPLES OF MARKETING
Credits: 3
This course is an overview of fundamental marketing concepts and applications in a technology-driven world. Students will learn the skills required to be successful marketers today.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Describe fundamental marketing concepts.
- Demonstrate oral and written communication skills using technological tools in marketing.
- Evaluate various marketing career opportunities.
MK124 SELLING
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: MK123
This course includes a comprehensive range of techniques of professional selling and ethical behavior in business with both consumer and organizational sales and settings. Students will develop skills for successful selling and relationship marketing while incorporating technology into the sales process.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Prepare and execute a sales presentation with the use of technology.
- Apply marketing knowledge by creating a promotional mix and pricing strategy for a product.
- Identify and examine the components and functions of the sales management structures, process, and responsibilities.
MK125 SOCIAL MEDIA MARKETING
Credits: 3
Social media is not just for personal socializing anymore. It is one of the hottest trends in the marketing field right now, and is essential in today's marketing success for any business. Students will gain valuable skills in social media marketing. This course will focus on implementation of social media marketing strategies across multiple platforms, to develop a winning social media marketing plan.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Explain how the use of social media marketing can improve marketing efforts for businesses.
- Develop a social media marketing plan, utilizing various platforms.
- Select the most effective social media platform for various marketing activities.
MK205 ENTREPRENEURSHIP
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: MK123
This course is an overview of the role of entrepreneurial businesses and its impact on the global economy. Students will evaluate skills and commitment necessary to successfully start and maintain a business.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Determine the characteristics and skills of a successful entrepreneur.
- Design a business plan utilizing the latest technology.
- Recognize the advantages and disadvantages of entrepreneurship as a career.
MK206 RETAILING
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: MK123 or Advisor’s approval
In today’s fast-paced and constantly changing economy, this course covers the perspective of the latest trends, fundamental retailing principles, practices to remain competitive, employing technological tools to fulfill society and consumer needs. The course enhances students’ understanding of retail planning, retail environment, marketing selection and analysis, retail operation management, and retail administration among other vital elements.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Explain the fundamental retailing concepts.
- Integrate merchandise management and supply chain strategies leading to excellent customer service.
- Develop a retail mix to satisfy customer needs in a competitive retail environment.
MK208 INTERNATIONAL MARKETING
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: MK123 or permission from Marketing Advisor
The course covers how international trade interacts and benefits the trading systems, the role of import and export, the global economy, and the strategies required to engage successfully in multinational corporations. This course is ideal for students to comprehend the fundamentals of International Marketing. Students will be able to utilize market planning techniques, analyze the global marketing environment, and understand how the trading of goods and services occurs between countries. Students will also be exposed to multinational strategies in relation to promotions, production, and marketing.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Explain the market conditions and the cultural and political practices that influence the international marketplace for companies.
- Describe the role of international regulations and how it impacts the existing national operational systems of a company.
- Develop marketing strategies for international promotions, production, and distribution.
- Evaluate the laws, legalities, and ethical issues that govern an industry internationally.
MK224 ADVERTISING
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: MK123
This course takes a comprehensive view of the advertising industry. It provides an introduction to fundamentals of advertising with emphasis on the importance of Integrated Marketing Communications (IMC). Students will learn application of conceptual advertising principles and design.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Describe career opportunities available in advertising.
- Develop an effective Advertising Plan.
- Analyze advertisements to ensure achievement of marketing communications goals/objectives.
MK292 MARKETING PRACTICUM
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: Second year standing
This course provides students a supervised work experience where they apply the skills necessary to be successful in a marketing career. This course allows students to showcase their knowledge and skills in a well-established workforce prior to their graduation.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Apply theory learned in the classroom to the work environment.
- Practice effective interpersonal skills in the workplace.
- Document the synthesis of knowledge and skills gained through work experience in an electronic presentation.
MS101 INTRODUCTION TO MEDICAL ASSISTING
Credits: 3
This course provides an introduction to the Medical Assisting program. The roles of the Medical Assistant in the patient care facilities are defined as well as fundamental administrative and clinical concepts and skills. Introduction to ethical and legal considerations is also provided.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Demonstrate basic knowledge of administration and clinical skills in the medical assisting field.
- Discuss ethical legal considerations and theoretical concepts regarding patient care.
- Classify patient coping mechanisms and communication methods.
MS120 CLINICAL MEDICAL ASSISTING: THEORY
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: MS141 Administrative Medical Assisting: Laboratory
Corequisite: MS121 Clinical Medical Assistant: Laboratory
This course will provide basic ambulatory care concepts and principles necessary for the performance of administrative duties. Students are provided with the knowledge of routine patient care and diagnostic procedures used to assess the health status of patients including vision testing, hearing testing, electrocardiography, and the knowledge to prepare the Administrative Office, equipment and supplies necessary to facilitate patient flow through the clinic and/or physician’s office.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Assess a potentially infectious situation to select the appropriate barrier/personal protective equipment (PPE).
- Demonstrate the proper use of medical equipment.
- Document the appropriate response in relation to the patient’s chief complaint.
MS121 CLINICAL MEDICAL ASSISTING LABORATORY
Credits: 2
Prerequisite: MS141 Administrative Medical Assisting: Laboratory
Corequisite: MS120 Clinical Medical Assistant: Theory
This course will provide basic ambulatory care concepts and principles necessary for the performance of administrative duties. Students are provided with the knowledge of routine patient care and diagnostic procedures used to assess the health status of patients including vision testing, hearing testing, electrocardiography, and the knowledge to prepare the Administrative Office, equipment and supplies necessary to facilitate patient flow through the clinic and/or physician’s office.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Differentiate between subjective and objective information.
- Analyze an electrocardiogram (EKG) tracing for common artifacts.
- Compare patient vital signs with current normal values.
MS125 CLINICAL MEDICAL ASSISTING: CLINICAL
Credits: 1
Prerequisite: MS120
Corequisite: MS121
In this course, the student will perform clinical Medical Assisting tasks in a designated medical clinic in the community under the supervision of the instructor. The student will demonstrate the necessary traits acceptable to the health care profession, including communication skills necessary for interacting with medical and allied health personnel. Students will perform routine patient care procedures to assist the physician in the examining room, obtain and record medical data from the patients, assist the physician with exams and/or treatments with minor surgery, prepare exam and treatment rooms, prepare patients for exams and/or treatments, measure and record vital signs, height and weight; and perform hearing vision screening and ECG tracings.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Record the patient’s chief complaint.
- Measure and record the patient’s vital or cardinal signs.
- Apply the principles of aseptic technique and infection control in the clinical setting.
MS140 ADMINISTRATIVE MEDICAL ASSISTING: THEORY
Credits: 2
Prerequisite: MS101
Corequisite: MS141, MS145 AND Instructor approval
This course provides students with basic concepts and principles of administrative medical office practices and procedures. The student will learn the basics of patient scheduling, billing, coding, and human resource management. This course prepares the student for the medical administrative front office.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Describe the mandatory policies required when initiating or terminating medical treatment.
- Demonstrate compliance with HIPAA guidelines.
- Apply patient scheduling principles.
MS141 ADMINISTRATIVE MEDICAL ASSISTING: LABORATORY
Credits: 2
Prerequisite: HL190
Corequisite: MS140, MS145, AND Instructor Approval
This course provides students with the laboratory setting to practice performing administrative office procedures that includes administrative planning functions for an ambulatory care facility, demonstration of various routine office reception and oral communication techniques. Role-playing to help create awareness of common administrative medical assistance and patient interactions, exercises in written communication, dictation and transcription, and completion of various forms related to patient records and office management of medical clinic or physician’s office are also explored in this course.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Demonstrate proficiency of an electronic health records system.
- Identify different types of patient appointment scheduling methods.
- Utilize medical coding and billing processes for insurance claims.
MS145 ADMINISTRATIVE MEDICAL ASSISTING: CLINICAL
Credits: 1
Prerequisite: HL190
Corequisite: MS140, MS141, AND Instructor’s approval
This course will provide the Medical Assisting Program students with an instructor-supervised experience as part of a health care team in the delivery of quality patient care. In the medical clinic, the student will practice all aspects of administrative medical office procedures.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Demonstrate proficiency of an electronic health records system.
- Apply professional code of conduct in the healthcare setting.
- Utilize medical coding and billing processes for insurance claims.
MS160 PHARMACOLOGY: DOSAGE AND CALCULATIONS
Credits: 2
Prerequisite: HL190
Corequisite: MS141
This course provides the students with the principles of pharmacology that includes identification and classifications of medications including the indications for use, desired effects, side effects, and adverse reactions. This course also includes interpretation of abbreviations and symbols, familiarization of local and federal standards and legislation as they relate to medications and their administration. The usage of appropriate references for obtaining drug information, and the demonstration of pharmacology related mathematics to include measurement conversions, and proper dosage calculations will also be key course content.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Identify the classifications of medications.
- Identify side effects and contraindications utilizing the Physician’s Desk Reference (PDR), drug handbooks, and resources.
- Demonstrate accurate occupational math and metric conversions for proper medication administration.
MS161 ADMINISTRATION OF MEDICATIONS LABORATORY
Credits: 1
Prerequisite: HL190
Corequisite: MS120
This course is an application of basic concepts and techniques required for medication administration. This will include patient care, documentation, and general competencies including the rationale for the equipment used for medication administration and the techniques for oral and parenteral medication administration. The student will satisfactorily demonstrate proper techniques during the performance of intramuscular, subcutaneous, intradermal injections, oral medication, and immunizations.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- List the six rights or rules of medication administration.
- Prepare and administer oral and parenteral medications.
- Give examples of post injections reactions and injuries.
MS180 INTRODUCTION TO CLINICAL LABORATORY
Credits: 2
Course Offering: Spring
Prerequisite: MS210 Administrative Medical Assisting: Laboratory
Corequisite: MS292 Clinical Medical Assisting: Theory
This course introduces the field of clinical laboratory science to include basic laboratory skills and phlebotomy. The students will demonstrate knowledge of clinical and laboratory procedures and identify roles of various laboratory personnel within the health care community. Perform Chemiluminescent Immunoassay (CLIA), waived or moderate laboratory tests, using basic to moderate laboratory instrumentation and equipment. Demonstrate competence in obtaining blood and other body fluid specimens, demonstrate the ability to effectively interact with patients, hospital personnel, reference laboratory, and describe quality control in the clinical laboratory.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Interpret the results of a urine human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG) quantitative test.
- Infer a patient's possible condition after performing a Hematocrit.
- Demonstrate proper technique when performing phlebotomy.
MS210 MEDICAL ASSISTING CRITIQUE
Credits: 1
Prerequisite: MS141
Corequisite: MS180
This course prepares Medical Assistant students for the National Certification exam. This course reinforces the value and importance of a credentialed allied health team member in the delivery of quality patient care.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Identify the importance of becoming a credentialed health care professional.
- Differentiate between a credentialed and non-credentialed medical assistant.
- Outline the certification preparation content with current medical practices.
MS220 MEDICAL ASSISTING SPECIALTIES
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: MS140, MS292
Corequisite: MS225
This course provides students with the principles of advanced medical assisting techniques and procedures in an ambulatory care facility. This course also provides students with a laboratory setting to practice advanced skills in clinical care procedures to assist the physician in an ambulatory care facility.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Process a patient for specialty examinations to include a pre-authorization.
- Compare and contrast the room set up for specialty examination versus routine exams.
- Create a medical directory for specialty clinics.
MS225 MEDICAL ASSISTING SPECIALTIES CLINICAL
Credits: 1
Prerequisite: MS292
Corequisite: MS220
This course provides students with the principles of advanced medical assisting techniques and procedures in an ambulatory care facility. This course also provides students with a laboratory setting to practice advanced skills in clinical care procedures to assist the physician in an ambulatory care facility.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Process a patient for a specialty examination to include pre-authorization.
- Set up room for specialty examinations.
- Demonstrate use of interpersonal and communication skills in the clinical setting.
MS292 MEDICAL ASSISTING PRACTICUM
Credits: 5
Prerequisite: MS121
Corequisite: MS180
The Medical Assistant Practicum course is a period of directed practice that consists of practical medical assisting experience in a medical clinic or other ambulatory care centers. Students will apply basic ambulatory patient care concepts and principles to demonstrate entry-level proficiency in the performance of their duties in the administrative and clinical areas of the designated medical facility. This course requires the completion of the all-technical and related technical requirements in the Medical Assisting Program with a grade of “C” or better and permission from the program director to begin internship.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Assist physicians and prepare patients for physical examinations or procedures.
- Apply effective oral and written communication in healthcare settings.
- Obtain a Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) Certificate of Completion which demonstrates understanding of HIPAA guidelines.
MU110 CHORALE I
Credits: 3
The GCC Chorale is a mixed voice (SATB) non-audition choir. The goal is the live performance of a wide variety of choral music. Music theory, sight reading and vocal technique appropriate for choral music will be taught.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Demonstrate appropriate use of breath support, resonance, and diction.
- Perform the selected choral music in live concerts with a high degree of proficiency.
- Identify and describe the interpretive markings in music.
MU115 CHORALE II
Credits: 1
The GCC Chorale II is a mixed voice (SATB) non-audition choir. The goal is the live performance of a wide variety of choral music. The course requires considerable group effort where cooperation and teamwork are stressed. Attendance at rehearsals and scheduled performances is an important element. Confidence, stage presence and vocal ability are important facets of the overall ensemble. May be repeated for credit.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Demonstrate expressive qualities in a varied repertoire of music.
- Perform with technical accuracy in prepared ensemble music.
- Participate as an ensemble member with an understanding of the variety of cooperative musical components.
NU101 NURSING ASSISTANT
Credits: 4
Prerequisite: HL131 (can be taken concurrently)
This course provides students with hands-on training necessary to administer safe high-quality care to patients. This course prepares students to function professionally and competently as Nursing Assistants working under the supervision of the LPN, RN, or MD in such clinical areas as hospitals, home health, community health, and mental health facilities. Graduates will be able to generate the knowledge and demonstrate skills that provide safe, competent care as required to pass the National Nurse Aide Assessment Program Examination which leads to becoming a Certified Nursing Assistant.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Demonstrate competence with all skills required for certification by the Guam Board of Nurse Examiners.
- Apply the Nursing Assistant principals and skills learned in the classroom/lab to the clinical setting.
- Demonstrate proficiency and knowledge of common elements required for preparation of the NNAAP (National Nurse Aide Assessment Program) written and practical examination.
NU160 PATHOPHYSIOLOGY & PHARMACOLOGY FOR PRACTICAL NURSES
Credits: 5
Prerequisite (limit one): SI150/SI150L
Corequisite: NU110
This course is a comprehensive study of human pathophysiology and pharmacology appropriate to the professional practical nurse role. The course will apply processes to the care and promotion of wellness across the lifespan. Major drug classes and drugs are presented with specific application to nursing care within the nursing process. Special attention will be placed on identifying goals and general principles of treatment for the selected disease processes; therapeutic range and toxic range of drugs; and understanding the bodily implications of improper dosing to the client.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Explain the impact of illness and medications on the physiological, psychological, sociocultural, and developmental variables.
- Apply standards of professional practice responsibility and accountability in pharmacologic intervention.
- Analyze the basic principles of pharmacology and the nursing process to selected drugs and their therapeutic use across the lifespan.
NU205 ADULT MEDICAL SURGICAL NURSING & CLINICAL SKILLS
Credits: 6
Prerequisite: SI132 Human Anatomy and Physiology II
Corequisite: NU215 Pathophysiology
This course covers introductory concepts related to the nursing profession to include the use of essential medical terminology in practice. The course will apply concepts related to the nursing process, focused assessments, critical-thinking, therapeutic communication, ethical issues, and nursing standards. Students will have the opportunity to practice and demonstrate basic therapeutic nursing interventions that are required of a registered nurse in a laboratory simulation setting and clinical practicum environment. The nursing student will perform the role of the registered nurse as a health care provider and will gain essential skills related to patient safety and quality care.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Utilize the nursing process by conducting overall patient assessments, collecting data, and identifying deviations from normal health status in clients across the life span.
- Demonstrate basic nursing skills in the safe effective care of clients across the life span in a laboratory and clinical environment.
- Apply therapeutic communication, appropriate use of medical terminology, and decision-making skills in the care of clients.
NU210 PHARMACOLOGY
Credits: 2
Prerequisite: SI132
Corequisite: NU205
This course is a comprehensive study of pharmacology appropriate to the professional nurse role. Students will apply processes to the care and promotion of wellness across the lifespan. Major drug classes and drugs are presented with specific application to nursing care within the nursing process. Students will also focus on identifying goals and general principles of treatment for the selected disease processes, therapeutic range and toxic range of drugs, and understanding the bodily implications of improper dosing to the client.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Explain the impact of illness and medications on the physiological, psychological, sociocultural, and developmental variables.
- Apply standards of professional practice responsibilities in pharmacologic intervention.
- Analyze the basic principles of pharmacology and the nursing process to selected drugs and their therapeutic use across the lifespan.
NU212 HEALTH ASSESSMENT
Credits: 4
Prerequisite: SI132
Corequisite: NU205
Students will learn to conduct a full examination of the patient using appropriate communication skills with an emphasis on the physical, cognitive, cultural, and psychosocial needs. The course also focuses on conducting a health assessment of the whole person, which includes health promotion, cultural
assessment, interviewing, health history gathering, and social determinants of health data to safely care for patients. Health assessment concepts and skills learned in the theory portion of the course will be practiced and evaluated in the lab.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Describe the role and responsibility of the professional nurse in health assessment and health promotion.
- Integrate communication and physical assessment techniques to conduct and document comprehensive nursing assessments across the patient’s life-span.
- Demonstrate physical examination skills including physical, behavioral, psychological, socioeconomic, and environmental assessments of health and illness parameters in patients, using developmentally and culturally appropriate approaches.
- Apply skills in obtaining a health history, facilitating a physical examination, and using clinical reasoning in the assessment of patients.
NU215 PATHOPHYSIOLOGY
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: SI132 Anatomy and Physiology II
Corequisite: NU205 Fundamentals of Nursing Concepts and Clinical Skills
This course is a comprehensive study of human pathophysiology and introduces students to the study of body systems and the treatments, manifestations, and mechanisms of disease across the lifespan. Students will learn the major pathophysiology concepts, with emphasis on the nurse’s role regarding assessment and analysis of diseases.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Apply principles of normal anatomy and physiology of human body systems to the pathophysiologic process of common health problems.
- Identify clinical manifestations of selected disease processes and health problems.
- Discuss the nurse’s role and responsibility for assessment of individuals experiencing health problems that result in pathophysiologic alterations.
NU220 ADULT MEDICAL SURGICAL NURSING
Credits: 8
Prerequisite: NU110, NU160, SI106
Corequisite: NU230, NU240
Utilizing current evidence based practice, this course focuses on health management; maintenance and prevention of illness; and care of the individual as a whole and deviations from the normal state of health. The administration of patient care includes using the nursing process, body systems disorders, diagnostic methods, surgical, non-surgical treatments, performing focused assessments, using critical thinking, and assisting with patient education. There will be an emphasis on the physical, cognitive, and psychosocial needs of the patient. The systems included are integumentary, musculoskeletal, respiratory, cardiac, vascular and hematology. Content is presented from a patient-centered approach based on Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs. Consideration is also given to the impact of health issues; the potential physical and mental adjustments as well as diversional and rehabilitative activities. Other concepts covered include therapeutic communication, medication administration and intermediate nursing skills that will be evaluated by instructors in lab and clinical settings. All experiences of students in the clinical setting shall be under the direct supervision of a faculty member.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Illustrate intermediate therapeutic nursing skills in a simulated lab and clinical setting as it relates to medical-surgical procedures and patient care.
- Apply nursing concepts and theories to identify interventions appropriate for planning, providing and evaluating patient care.
- Utilize concepts of problem-solving, critical thinking, interpersonal and therapeutic communication skills in care of the medical-surgical patient.
- Analyze the physical, cognitive, and psychosocial development and changes which occurs during young adult, middle-aged, and older adult years.
NU225 ADULT MEDICAL SURGICAL NURSING II & CLINICAL SKILLS
Credits: 8
Prerequisite: NU205 Fundamentals of Nursing Concepts and Clinical Skills
Corequisite: NU235
Utilizing current evidence based practice, this course focuses on and explores intermediate medical-surgical nursing concepts to provide holistic care to diverse individuals, families, and groups experiencing complex alterations in health. Students will learn about health management, maintenance and prevention of illness, and care of the individual as a whole. Students will gain experience in the administration of patient care which includes using the nursing process, body systems disorders, diagnostic methods, surgical and non-surgical treatments, perform focused assessments in the scope of the registered nurse, integrating critical thinking, and assist with patient education. Content is presented from a patient centered approach based on Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Use the nursing process to provide professional nursing care to promote health and wellness of culturally diverse patients across the lifespan in a variety of settings.
- Utilize concepts of problem-solving, critical thinking, interpersonal and therapeutic communication skills in care of the medical surgical patient.
- Analyze the physical, cognitive, and psychosocial development and changes which occur during young adult, middle-aged, and older adult years.
- Apply nursing concepts and theories to identify interventions appropriate for planning, implementing, and evaluating patient care.
NU230 MATERNAL AND NEWBORN CONCEPTS & SKILLS
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: NU110
Corequisite: NU240
This course provides students with the scope of obstetrics including care and assessment of newborns. This course covers theories of maternal health, the birthing process, physiology of pregnancy, maternal-infant bonding, and family dynamics including cultural considerations, ethics, and stress adaptation of newborns and their families. The focus is on promotion, disease intervention and detection of high risk factors with childbearing families. There is a special emphasis placed on the human growth and development related to the physical, cognitive, and psychosocial development from birth to 12 months of age. All experiences of students in the clinical setting shall be under the direct supervision of a faculty member. There shall be no more than eight (8) students for every faculty member in the clinical area.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Exercise safe, competent, patient-centered care of the obstetric and newborn client.
- Complete the nursing process, inclusive of assessment, planning, implementation, and evaluation in the care of the obstetric and newborn client, within the Practical Nurse scope of practice.
- Apply problem-solving, critical-thinking, interpersonal, and therapeutic communication skills in the care of the obstetric and newborn client.
- Integrate the concepts of the physical, cognitive, and psychosocial development which occur from birth to 12 months.
NU235 ADVANCED MATERNAL NEWBORN CONCEPTS & CLINICAL SKILLS
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: NU205 Fundamentals of Nursing Concepts & Clinical Skills
Corequisite: NU245 Advanced Pediatric Nursing Concepts & Clinical Skills
This course provides students with the scope of obstetrics including care and assessment of newborns and mother’s relative to the scope of practice for a registered nurse. Students will learn the theories of maternal health and patient education, the birthing process, physiology of pregnancy, maternal-infant bonding, and family dynamics including cultural considerations, ethics, and stress adaptation of newborns and their families. The course also focuses on health promotion, disease intervention, and detection of high risk factors with childbearing families.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Exercise safe, competent, and patient-centered care of the obstetric and newborn client.
- Apply the nursing process inclusive of assessment, planning, implementation, and evaluation in the care of the obstetric and newborn client, within the Registered Nurse scope of practice.
- Apply problem-solving, critical-thinking, interpersonal, and therapeutic communication skills in the care of the obstetric and newborn client.
NU240 PEDIATRIC NURSING CONCEPTS & SKILLS
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: NU110
Corequisite: NU230
This course builds on child growth and development from infancy to adolescence. Health problems of each age group are explored in more detail. The role of the practical nurse in meeting the health needs of children in a variety of settings is included. This course focuses on promoting, maintaining, and restoring the health of children and their families. All experiences of students in the clinical setting shall be under the direct supervision of a faculty member. There shall be no more than eight (8) students for every faculty member in the clinical area.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Utilize safe, competent, patient-centered care of the pediatric client and family.
- Complete the nursing process inclusive of assessment, planning, implementation, and evaluation in the care of the pediatric client, within the Practical Nurse scope of practice.
- Apply problem-solving, critical-thinking, interpersonal, and therapeutic communication skills in the care of the pediatric clients and their families.
- Analyze the physical, cognitive, and psychosocial development which occurs during toddler, preschool, school-age, and adolescent years.
NU245 ADVANCED PEDIATRIC NURSING CONCEPTS & CLINICAL SKILLS
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: NU205
Corequisite: NU235
In this course, students will learn about child growth and the development from infancy to adolescence and will explore the health problems of each age group. This course focuses on the role of the registered nurse in promoting, maintaining, and restoring the health of children and their families in a variety of settings.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Utilize safe, competent, patient-centered care of the pediatric client and family.
- Apply the nursing process in the care of the pediatric client.
- Apply problem-solving, critical-thinking, interpersonal, and therapeutic communication skills in the care of the pediatric client and the family.
- Analyze the physical, cognitive, and psychosocial development which occurs during toddler, preschool, school-age, and adolescent years.
NU250 MENTAL HEALTH NURSING
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: NU220
Corequisite: NU292
This course explores basic concepts, key principles, and the psychosocial needs of clients in behavioral and mental health care settings. The assessment of the client’s physical and behavioral responses to stress and mental illness throughout the life cycle is explored. Students will demonstrate therapeutic techniques that promote client’s mental health wellness in acute and community health care settings. All experiences of students in the clinical setting shall be under the direct supervision of a faculty member. There shall be no more than eight (8) students for every faculty member in the clinical area. Formerly NU140.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Apply concepts of the nursing process as it relates to mental health illness and stress.
- Identify four anxiety-reducing strategies students can implement in behavioral and mental health settings.
- Utilize therapeutic communication skills and interact with clients appropriately in behavioral and mental health settings.
NU252 MENTAL HEALTH CONCEPTS & COMMUNICATIONS
Credits: 4
Prerequisite: NU235 Advanced Maternal Newborn Concepts and Clinical Skills
Corequisite: NU295 Professional Nursing Practicum
This course focuses on the concepts of mental health illnesses and biological and psychological development. Biopsychosocial foundations of behavior, communication, and psychopharmacology are emphasized. Patient relationships and the use of effective and non-effective communication are addressed. The critical role of the registered nurse in prevention, early detection, and treatment of mental health disorders in children, adolescents, and older adults are emphasized. This course includes a clinical component where clinical practice utilizing the learning objectives and skills taught in theory are demonstrated in an in-patient, out-patient, or community setting.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Explain the pathophysiology, psychopathology, signs and symptoms, and treatments related to various psychiatric and mental health stressors.
- Utilize therapeutic communication skills and interact with clients appropriately in behavioral and mental health settings.
- Apply concepts of the nursing process as it relates to mental health illness and stress.
- Identify teaching strategies and information that assist the client experiencing psychological stressors meet their needs for health maintenance, promotion, and restoration.
NU280 NURSING TRENDS
Credits: 1
Prerequisite: NU220, NU230, NU240
Corequisite: NU250, NU292, NU281
This course is designed for students to study the trends and issues which affect current practice. The major focus includes the evolution of nursing, professional opportunities for the practice of nursing, the legal and ethical relationships in nursing, the economics of health care, the interpersonal relationship with patients and in the workforce among healthcare professionals and current issues in nursing.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Relate nursing care to the sociological and economic trends of health care, examining current issues that impact nursing.
- Formulate a plan for the process of employment and analyze leadership styles.
- Analyze the evolution of nursing and differentiate the roles of the professional nurse.
NU281 NCLEX-PN REVIEW & TRANSITION
Credits: 2
This is a preparatory course for NCLEX-PN to obtain licensure to practice as a Licensed Practical Nurse (LPN). This course will focus on exam content and test taking strategies.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Create a study plan to remediate in areas of identified learning needs.
- Analyze areas of strengths and weaknesses in nursing knowledge.
- Apply test taking strategies on predictor exams.
NU292 NURSING PRACTICUM
Credits: 6
Prerequisite: NU220, NU230, NU240
Corequisite: NU250, NU280, NU281
This course provides students with a clinical setting to practice basic and advanced therapeutic nursing interventions within the scope of an LPN. Selected clinical skills will involve clients/patients/residents of all ages with simple, well-defined problems. Communication, critical thinking, interpersonal, management, and leadership skills and the nursing process will be practiced as students assess and meet the duties of a practical nurse. Students will also lead educational activities that involve adult clients/patients/residents of all ages.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Utilize safe and competent advanced therapeutic nursing skills in a simulated lab and clinical setting as it relates to medical-surgical procedures and patient care.
- Apply the steps of the nursing process when interacting with clients to determine their health needs in the delivery of nursing care.
- Design an educational activity that involves clients of all ages.
NU295 PROFESSIONAL NURSING PRACTICUM
Credits: 6
Prerequisite: NU205 Fundamentals of Nursing Concepts and Clinical Skills
Corequisite: NU235 Advanced Maternal Newborn Concepts and Clinical Skills
This practicum course provides students with the theoretical and clinical setting which builds on and combines all knowledge and skills from prior courses. The course will focus on the nursing process, evidence-based practice, and quality improvement initiatives and will be emphasized throughout the learning experience. Students will develop and display key roles of delegation, leadership, multidisciplinary teamwork, education and ethical considerations in practice.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Utilize the nursing process, principles of health teaching, health promotion, illness prevention, and therapeutic communication while providing care for a diverse patient population with critical and complex disease states.
- Apply the knowledge and skills of quality improvement, evidenced based practice and patient safety to provide safe, cost-effective, quality care for diverse patients.
- Demonstrate accountability for developing and implementing a plan of care within the legal and ethical boundaries of nursing utilizing standards of professional practice and behavior for a diverse patient population with critical and complex disease states.
OA101 KEYBOARDING AND DOCUMENT PROCESSING
Credits: 3
This is an introductory course that focuses on the mastery of the keyboard and using correct typing techniques. Basic word processing concepts and applications are taught including an introduction to proper formatting of memorandums, business letters, reports, and tables.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Demonstrate the ability to key memorandums, letters, reports, tables, and other related items.
- Demonstrate typing techniques and skill in using the computer and printer.
- Demonstrate keyboard knowledge by completing a 3-minute timed-writing, keying at least 40 words per minute with no more than 5 errors.
OA103 FILING SYSTEMS
Credits: 3
This course introduces the basic principles of a records and information management program. Four filing systems (alphabetic, numeric, subject, and geographic) will be emphasized using both manual and electronic methods for storage and retrieval of records.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Index, code, cross-reference, and arrange personal names, business names, and organization names in correct filing order.
- Store and retrieve records using alphabetic, subject, numeric, and/or geographic methods of filing.
- Create, maintain, and access a computerized records management database.
- Demonstrate the procedures for records control and retention, including charge-out systems, electronic files control, and transfer methods.
OA109 BUSINESS MATH USING EXCEL
Credits: 3
This course provides practice in basic business math concepts and spreadsheet skills needed in today’s workforce. Topics to be discussed are math functions, fractions, percent, bank services, payroll, purchasing merchandise, markup and markdown, interest, credit and mortgages, and depreciation.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Demonstrate the traditional method of calculating to solve business problems.
- Create formulas in spreadsheets to solve business problems.
- Evaluate the benefits of spreadsheets in business documents such as payroll and bank reconciliations.
OA130 INFORMATION PROCESSING
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: OA101
This course provides students with basic to advanced skills using word processing software for preparing business letters, memos, tables, reports, and forms (including meeting minutes, agendas, itineraries, articles). Speed and accuracy in typing are emphasized.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Produce properly formatted letters, memorandums, reports, tables, and forms.
- Demonstrate technical skills (download, upload, and send) for business documents.
- Complete a 5-minute timed-writing, keying at least 50 words a minute with no more than 5 errors.
OA210 DATABASE MANAGEMENT SYSTEMS
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: CS151
This course introduces the basic concepts of a database management system. Topics include designing, creating, and using a database; querying a database; maintaining a database; sharing data among applications; and creating forms and reports.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Design database applications using Microsoft Access.
- Generate tables, forms, queries, and reports to manage data.
- Integrate Microsoft Access with Microsoft Office applications.
OA211 BUSINESS COMMUNICATION
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: EN110
Students will learn the basics of business communication. Students will practice applying real-world writing forms of communication, to include composing letters, memorandums, emails, reports, proposals, employment communications, and oral presentations. Students will learn how and when to be concise in communicating effectively. This course also prepares students for the job-interview process, resume writing, and application letters.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Write effective business memos, letters, and reports.
- Prepare and deliver effective oral presentations.
- Demonstrate effective interpersonal communication skills.
- Develop a practical job-search strategy, including writing successful resumes.
OA220 SPREADSHEET SYSTEMS
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: CS151
This course covers spreadsheet roles, advantages, and limitations. Standard spreadsheet software will be utilized to provide hands-on applications experience with creating, designing, utilizing, and integrating spreadsheets.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Create an Excel worksheet using formulas, built-in functions, and charts.
- Develop Excel spreadsheet databases, templates, and macros.
- Integrate Excel spreadsheets with other office applications.
OA230 ADVANCED INFORMATION PROCESSING
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: OA130
This course reviews word processing concepts and skills. It introduces advanced word processing functions to prepare documents that integrate files from various application programs (word processing, spreadsheets, database, and presentation graphics), the Internet, and other emerging technologies.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Apply proper document formats for business correspondence such as memorandums, letters, reports, tables, and forms.
- Create compound documents by integrating word processing, spreadsheet, database, and/or presentation application.
- Manage documents as a team.
OA240 MACHINE TRANSCRIPTION
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: OA130
Corequisite: EN110
This course focuses on transcription, proofreading, and editing techniques to produce accurate business documents in a word processing software. Emphasis is placed on building listening and decision-making skills to progressively increase production, speed and accuracy.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Transcribe text from dictated recordings using transcription equipment and a word processor.
- Utilize business document formats to transcriptions.
- Apply proofreading rules to transcription documents.
OA250 OFFICE PROCEDURES
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: OA211
Corequisite: CS151
This course focuses on knowledge and skills related to office procedures, systems, and routines. Topics include: the work environment, workplace technologies, written communication, records, presentations, customer and employee satisfaction, mail, travel, meetings and conferences, and career.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Explain an administrative assistant’s professional job attitudes.
- Display professional interpersonal skills.
- Demonstrate office management skills.
OA292 OFFICE TECHNOLOGY PRACTICUM
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: Permission from Advisor or Department Chairperson
This course provides students hands-on office experience to prepare for employment within the office technology field. Students will apply theory and skills to practical situations in an office environment.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Demonstrate professionalism in an office environment.
- Perform office tasks in an office setting.
- Evaluate office procedures.
PI101 INTRODUCTION TO PHILOSOPHY
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: None
This course will review the great philosophical traditions surrounding the eternal questions concerning nature and the human condition. Students will learn to analyze the great philosophies from Asia and the West in efforts to understand knowledge, reason, and faith. Introduction to Philosophy will challenge students to become more active and engaged ethical citizens by working with the community.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Analyze philosophical arguments for the strength of its evidence, internal consistency, and logic.
- Explain why a philosophical problem is significant.
- Utilize primary philosophical text to address a philosophical problem.
- Assess the relevance of given information to appraise a philosophical argument or conclusion.
PS140 AMERICAN GOVERNMENT
Credits: 3
This course provides students with fundamental knowledge about the history and principles of American government. Students will learn citizenship, political parties, the creation of law and policy, and the functions of the three branches of government. This course also provides essential working knowledge for those seeking a career in government service. It is appropriate for anyone seeking broader understanding of the relationships among the local, state, and federal governments.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Explain the central principles, institutions, procedures, and decision-making processes of the American political system.
- Identify the basic strengths and weaknesses of the American political system.
- Differentiate the legislative, executive, and judicial branches of government.
PY100 PERSONAL ADJUSTMENT
Credits: 3
This course invites students to engage in self-discovery and self-improvement in a supportive environment. Students should be willing to examine various personal and interpersonal issues such as self-concept, anger and violence, depression, happiness, love and intimacy, sexuality, moral and ethical development, gender roles, diversity, stress and other problems encountered throughout life. This course encourages students to think about their lives in a deeper and more meaningful way and to choose to live a deliberate life.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Explain and evaluate the importance of personal adjustment and the benefits of self-awareness and self-development.
- Identify and demonstrate the skills necessary for healthy communication and relationships.
- Recognize and evaluate the impact of societal expectations on human behavior.
PY120 GENERAL PSYCHOLOGY
Credits: 3
This course provides critical information about who we are and why we behave as we do. It promotes personal growth by providing insight and theoretical understanding of human thoughts and behaviors.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Explain the basic principles of psychology.
- Apply knowledge of ethical principles and limitations of research in psychology.
- Examine one’s self concept.
- Evaluate sources of information in the field of psychology.
PY125 INTERPERSONAL RELATIONS
Credits: 3
In this course, students will learn the value of workplace diversity and inclusion and how the quality of relationships lead to personal and organizational success. They will learn how to effectively utilize social media and other communication technologies. Additionally, students will develop self-confidence, team building and conflict resolution strategies, and proper ways to respond to personal and work-related stress needed to achieve success in a competitive workplace.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Identify the seven major themes that serve as a foundation for effective human relations.
- Explain the importance of teamwork in an organizational setting.
- Describe some of the major causes of conflict in the workplace.
- Implement effective stress-management strategies.
PY325 WORK ETHIC IN CAREER AND TECHNICAL FIELDS
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: CO110 Critical Thinking
This course applies work ethic principles as essential “soft skills” to succeed in career and technical fields of practice. Students will learn to incorporate human relations topics with work ethic training. The course is designed to include an eight (8) hour work ethic training component; thus, preparing eligible students who choose to take and pass a proficiency exam to earn a "Certificate of Work Ethic Proficiency" from the Center for Work Ethic Development.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Explain the value of work ethic principles.
- Demonstrate the seven work ethic skills as they apply to scenarios common in workplace experiences.
- Evaluate human relations pertaining to personal and interpersonal skills in workplace settings.
SI051 EARTH SCIENCE
Credits: 3
This course will focus on knowledge and understanding of life and physical science. Earth Science provides students with an understanding of how the different parts of the system works through the study of the Earth's cycles and spheres; the earth's place in the universe as well as its internal structure, tectonic plates, atmospheric processes, and hydrosphere are explored to help understand how Earth science interacts with society. Students will be active learners; they will observe, inquire, question, formulate and test hypotheses, analyze data, report, and evaluate findings. Students will have hands-on and active experiences throughout this course.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Discuss specific textual evidence that supports analysis of the development of the universe and the solar system.
- Analyze the earth's internal structure and the dynamic nature of the tectonic plates that form its surface.
- Explain the atmospheric processes that support life and cause weather and climate change.
SI061 BIOLOGY
Credits: 3
This course will focus on knowledge and understanding of the science of life. Biology provides students with an understanding of the structure, function, growth, origin, evolution and distribution of living organisms. Students will be active learners; they will observe, inquire, question, formulate and test hypotheses, analyze data, report, and evaluate findings. Students will have hands-on and active experiences throughout this course.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Describe the general composition of living organisms, including their cellular structures and functions.
- Cite specific evidence on the energy transformations that enable cellular activity.
- Describe the role of DNA and how it provides information for inheritable characteristics and genetic variation.
- Demonstrate the ability to use technology to make biological observations, and to collect and analyze data.
SI101 INTRODUCTION TO CHEMISTRY: THEORY
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: Placement into MA115 or equivalent
Corequisite: SI101L
Designed as a broad introduction to chemistry, topics include atomic theory and structure, chemical bonding, natural laws, interpreting the Periodic Table of Elements, and problem-solving such as dimensional analysis and stoichiometry. This is the theory portion of Intro to Chemistry, which satisfies natural and physical science requirements for general education.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Interpret the Periodic Table of Elements.
- Identify types of chemical reactions.
- Solve quantitative and qualitative problems including unit conversions and balance chemical reactions.
SI101L INTRODUCTION TO CHEMISTRY: LABORATORY
Credits: 1
Corequisite: SI101
This course is the laboratory portion for SI101 Introduction to Chemistry: Theory. Laboratory sessions provide hands-on experiences with chemicals, equipment and instruments, that reinforce and extend concepts presented in lecture.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Demonstrate proper conduct in accordance with safety procedures in the lab and use of basic chemistry lab equipment.
- Apply concepts of chemical reactions and equations to experiments and perform qualitative and quantitative problem-solving.
- Demonstrate ability to accurately follow prescribed procedures needed to complete lab handouts.
SI102 GENERAL CHEMISTRY WITH LABORATORY
Credits: 4
Prerequisite: MA161A
This course is designed to be a general chemistry course for students. Topics covered include the theories, laws, and principles of chemistry including atomic structure, nature of the chemical bond, and stoichiometric considerations of all aspects of inorganic chemistry. This course has a 30-hour laboratory component.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Demonstrate basic use of the Periodic Table of the Elements.
- Apply the scientific method through lab experiments and write lab reports.
- Apply critical thinking skills to solve quantitative and qualitative chemistry problems.
- Calculate conversions and balance chemical equations.
- Identify various types of chemical properties and their reactions.
SI103 INTRODUCTION TO MARINE BIOLOGY: THEORY
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: EN110 Placement or equivalent
Corequisite: SI103L Introduction to Marine Biology: Laboratory
This course provides students with an understanding of the general principles of marine ecology. Basic skills in gathering, interpreting, and understanding ecological data and identification of marine organisms will be acquired. This is the lecture portion of the course and students are required to register for the lab portion, SI103L Introduction to Marine Biology Laboratory.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Describe key chemical, biological, geological, and ecological processes within the marine environment.
- Identify and classify common marine organisms.
- Explain anthropogenic factors affecting the marine environment and its organisms.
SI103L INTRODUCTION TO MARINE BIOLOGY: LABORATORY
Credits: 1
Corequisite: SI103 Introduction to Marine Biology: Theory
This course is the laboratory co-requisite for SI103 Introduction to Marine Biology: Theory. Laboratory sessions and field trips reinforce and extend basic marine biology concepts, identification of marine organisms, and anthropogenic effects on the marine environment.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Apply an understanding of key chemical, biological, geological, and ecological marine processes within the field and natural marine environment.
- Identify and classify common marine organisms within the laboratory and field settings.
- Explain anthropogenic factors affecting the marine environment and its organisms while being in the laboratory or field setting.
SI105 INTRODUCTION TO PHYSICAL GEOLOGY
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: Satisfactory completion of EN100R and EN100W or Placement into EN110
Corequisite: SI105L Intro to Physical Geology Laboratory
Introduction to Physical Geology is the science of the earth, the materials that make up the earth and the forces and processes that shape the earth. Topics for this course will include minerals, rocks, earth’s internal structure, plate tectonics, geologic structures, the rock cycle, and surface/subsurface processes. This course, in a lecture format, is intended to be taken concurrently with a laboratory/field course, SI105L, where students will conduct laboratory and field investigations to reinforce course topics and expose students to Guam’s complete geologic history.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Explain how geologic processes shape the earth.
- Identify basic rock and mineral samples.
- Explain how geologic processes affect human activities and social economic welfare.
SI105L INTRODUCTION TO PHYSICAL GEOLOGY LABORATORY
Credits: 1
Prerequisite: Satisfactory completion of EN100R and EN100W
Corequisite: SI105 Introduction to Physical Geology
This course is the laboratory portion to the course SI105, Introduction to Physical Geology. Topics for this course will include minerals, rocks, earth’s internal structure, plate tectonics, geologic structures, the rock cycle, and surface/subsurface processes. This course is to be taken concurrently with the lecture course SI105. In this course students will conduct laboratory and field investigation that will reinforce the lecture course topics and expose students to Guam’s complex geologic history.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Explain how geologic processes shape the earth.
- Identify basic rock and mineral samples.
- Explain how geologic processes affect human activities and social economic welfare.
SI106 DRUG CALCULATIONS FOR PRACTICAL NURSING
Credits: 1
This course covers dosage calculation emphasizing critical thinking techniques to effectively, accurately, and safely calculate dosages of medications. It includes reading, interpreting and solving calculation problems encountered in the preparation of medication. This course involves measurements with the apothecary, avoirdupois, and metric systems. Students will review basic math skills and learn systems of measurement. They will also learn Dimensional Analysis for calculating dosages of oral, powdered, and parenteral medications, pediatric, and adult weight-based medication and intravenous medications.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Use basic arithmetic function and dimensional analysis to calculate accurate dosages.
- Utilize the metric, apothecary, and avoirdupois systems for dosage calculations.
- Calculate dosages based on body weight of pediatric and adult clients.
- Resolve calculation problems in the preparation of medication.
SI110 ENVIRONMENTAL BIOLOGY: THEORY
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: Successful completion of DevEd English or placement into college level English
Corequisite: SI110L Environmental Biology: Laboratory
This is a comprehensive survey course which focuses on environmental issues and concepts. The main focus of this course deals with tropical ecosystems that are unique to Pacific island regions. This course is the theory portion of Environmental Biology. Students taking this course are required to register for the lab portion of the course as a co-requisite.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Describe key chemical, biological, ecological, and atmospheric processes that affect organisms, with an emphasis on tropical island environments.
- Reflect personally upon the ecological, social and/or economic implications of climate change, conservation and sustainable use of resources, overpopulation, waste management and recycling.
- Integrate knowledge and observations obtained from lectures, labs and field trips in written reports, quizzes and exams.
SI110L ENVIRONMENTAL BIOLOGY: LABORATORY
Credits: 1
Prerequisite: Successful completion of DevEd English or placement into college level English
Corequisite: SI110 or successful completion of SI110
This is the laboratory portion of the SI110 Environmental Biology lecture course. The course applies hands-on laboratory exercises and experiments to illustrate and complement concepts discussed in the SI110 lecture course. Students will also be conducting class field trips to several selected environmental habitats around the island. The field trips are designed to provide firsthand experience and connectivity between environmental issues learned in the classroom and real world events. Students taking this course are required to register for the lecture portion of the course as a co-requisite.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Identify key chemical, biological, ecological and atmospheric processes that affect organisms, with an emphasis on tropical island environments.
- Reflect personally on the ecological, social, and/or economic implications of climate change, conservation and sustainable use of resources, overpopulation, waste management and recycling.
- Conduct a comprehensive data analysis process.
SI122 INTRODUCTION TO FORENSIC SCIENCE
Credits: 4
Prerequisite: CJ100
Cross Listed as CJ122. This course introduces students to the field of forensic science. Students will be able to identify the various principles, methods and procedures used in the preservation, collection, processing, and investigation of the crime scene as well as identify the various scientific techniques used to evaluate and analyze the evidence to resolve criminal matters. Students will also be familiar with some of the legal and ethical issues in forensic science.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Describe the history and development of forensic science.
- Identify the role of forensic science within the criminal justice system.
- Identify the various analytical tools used to evaluate, process, investigate and adjudicate criminal cases.
- Describe the various scientific techniques used to preserve, collect and analyze evidence.
- Identify some of the legal and ethical issues in forensic science.
SI125 SCIENTIFIC METHODS AND DATA ANALYSIS
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: SI101
This course puts emphasis on the Environmental Technician program and is an introduction to the practice of science, with a particular emphasis on Environmental Science. Environmental Technician students will be provided with an overview of the scientific methods and process, particularly within the context of observation-driven investigations. The course will include an introduction to the technology and methods used in data collection and environmental testing. The course will also include an introduction to the tools and methods used in science writing and data collection, the presentation and statistical analysis of scientific data, and searching and reviewing of the scientific literature. Finally, students will consider the nature of the theories that arise from, and provide a framework for the practice of science.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Explain in detail the steps of observation-driven investigations, including crafting of scientific questions and hypotheses, research design, experimentation and data collection, data analysis, interpretation and presentation.
- Demonstrate a basic understanding of the goals, structure, creation process, and types of scientific literature documentation in the environmental sciences.
- Identify the use of technology and equipment for data collection and analysis, including but not limited to environmental science.
SI131 HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I: THEORY
Credits: 3
Corequisite: SI131L or successful completion
This course provides a comprehensive study of the anatomy and physiology of the human body. It is the first of a two-part course sequence that covers the structure and function of cells, tissues, and the integumentary, skeletal, muscular and nervous systems. Students will learn about concepts of anatomy and physiology related to homeostasis and human disease processes. Upon completion, students should be able to demonstrate an in-depth understanding of principles of anatomy and physiology and their interrelationships. A laboratory component is required to supplement the theoretical aspect of lecture and will include microscopy, dissection, physiological experiments, and computer simulations.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Identify locations of major organs and bones of each system studied using anatomical terminology.
- Explain the interrelationships among molecular, cellular, tissue and organ functions in each organ system.
- Interpret the relationships between chemistry and physiology as they relate to cellular and sub-cellular processes; such as enzyme activity, cell-membrane function, muscle contraction, and nervous system control.
- Apply basic knowledge of anatomy and physiology in regards to the complementarity of structure and function when the body exhibits homeostasis and during pathological deviations from homeostasis.
SI131L HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I: LABORATORY
Credits: 1
Corequisite: SI131 or successful completion of SI131
SI131L is the laboratory component of SI131. The lab course will use a lab-based systems approach, with an emphasis on integrated structure-function relationships at the tissue, organ and organ system level. Laboratory exercises are designed to reinforce didactic material by providing hands-on experience with the subject matter. Students actively participate in simple chemical analysis, microscopic observations, perform dissections of specimens, and studies of anatomical models. The course begins with an overview of the human body. This is quickly followed by a review of chemistry and then moves on to explore the cellular and tissue levels of organization. The course then explores the covering, support, and movement of the body through investigation of the integumentary, muscular, and skeletal systems. Finally, the course will examine the structure, regulation, and integration of the body systems by learning about the nervous system.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Demonstrate basic techniques required in a laboratory for student safety and equipment preservation.
- Identify major organ systems and subcomponents of the integumentary, skeletal, muscular and nervous system utilizing models.
- Analyze data from computer-simulated laboratory exercises on cell transport, skeletal muscle physiology, and neurophysiology.
- Differentiate among the human organ systems from cats, fetal pigs, and other mammalian specimens.
SI132 HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY II: THEORY II
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: SI131
Corequisite: SI132L or successful completion
This course provides a comprehensive study of the anatomy and physiology of the human body. It is the second of a two-part course sequence that covers various organ systems of the human body including: cardiovascular, lymphatic, immune, respiratory, digestive, urinary, and reproductive systems. Emphasis is on understanding the physiology of negative and positive feedback mechanisms associated with these organ systems. Students’ foundational knowledge from SI131 is essential to understand how the structure and functions of each organ system works and is interrelated to each other. A laboratory component is required to supplement the theoretical aspect of lecture and will include microscopy, dissection, physiological experiments, and computer simulations. Students taking this course are required to register for the laboratory portion of the course as a co-requisite or have passed an equivalent to the laboratory portion.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Identify the components and subcomponents of the sensory, endocrine, cardiovascular, lymphatic, immune, respiratory, digestive, urinary, and reproductive systems.
- Explain the interrelationships among the sensory, endocrine, cardiovascular, lymphatic, immune, respiratory, digestive, urinary, and reproductive systems in maintaining homeostasis.
- Interpret the relationships between chemistry and physiology as they relate to cellular and sub-cellular processes such as vision; olfaction; taste; hearing; hormone action; antigen-antibody reactions; heart function; lung function; nutrition; metabolism and temperature regulation; and fluid, electrolyte and acid-base balance.
- Apply basic knowledge of metabolic pathways and their links to energy production and storage to the function of the respiratory, digestive, and urinary systems in regards to the complementarity of structure and function when the body exhibits homeostasis and during pathological deviations from homeostasis.
SI132L HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY II: LABORATORY
Credits: 1
Prerequisite: SI131 and SI131L
Corequisite: SI132 or successful completion of SI132
SI132L is the laboratory component of SI132. The lab course will use a lab-based systems approach, with an emphasis on integrated structure-function relationships at the tissue, organ and organ system level. Laboratory exercises are designed to reinforce didactic material by providing hands-on experience with the subject matter. Students actively participate in microscopic observations, perform dissections of specimens, and studies of anatomical models. The course begins where SI131L ends: special senses, regulation and integration of the body systems by examining the endocrine system, maintenance of the body through the cardiovascular, lymphatic, immune, respiratory, digestive, and urinary systems. Finally, the course will investigate the continuity of life through an examination of the reproductive system, development, and heredity.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Identify major organ systems and subcomponents of the sensory, endocrine, cardiovascular lymphatic, immune, respiratory, digestive, urinary, and reproductive systems using slides, models, specimens and diagrams.
- Describe the pathway of blood through the heart, urine through the kidneys, food through the digestive system and egg/sperm through the reproductive system.
- Analyze data from computer-simulated laboratory exercises on endocrine system physiology, blood analysis, cardiovascular dynamics, cardiovascular, physiology, respiratory system mechanics, chemical and physical processes of digestion, renal system physiology, and acid-base balance.
- Differentiate among the human organ systems (endocrine, cardiovascular, lymphatic, respiratory, digestive, urinary and reproductive systems) from cats, fetal pigs, and other mammalian specimens.
SI141 APPLIED PHYSICS I
Credits: 4
Prerequisite: MA161A
An Algebra-based course covering measurement, motion, forces in one (1) dimension, vectors, trigonometry, concurrent forces, work and energy, simple machines, rotational motion, nonconcurring forces, matter and fluids. The course emphasizes physical concepts as applied to an industrial technical field.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Define key terminology used in the physics field.
- Identify and classify common physical phenomena such as forces, friction, and center of gravity.
- Summarize common laws and rules of physics from Newton and Kepler and their application to everyday circumstances.
- Employ basic methods and observations to identify given data graphically or numerically and implement proper procedures to solve problems applying physical rules and formulas correctly.
SI142 APPLIED PHYSICS II
Credits: 4
Prerequisite: MA161A, SI141
A continuation of SI141 covering temperature and heat, the gas laws, wave motion and sound, static electricity, direct current, DC sources, magnetism, alternating-current, light, and reflection and refraction.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Calculate the momentum, impulse, force, and time of contact within a system.
- Apply and analyze between rotational and translational quantities and equations.
- Relate and apply density, specific gravity, mass and volume, pressure, area, pressure density, and depth concepts.
- Identify, relate and apply amplitude, frequency, angular frequency, period, displacement, velocity and acceleration associated with an oscillating system.
SI150 INTRODUCTION TO MICROBIOLOGY: THEORY
Credits: 3
Corequisite: SI150L or successful completion of SI150L with a “C” or better
This course presents basic principles of microbiology, including the role of microbes in the transmission of disease, the environment and useful applications. Topics include an overview of microbiology and aspects of medical microbiology, identification and control of pathogens, disease transmission, host resistance and immunity, microbial systems, flow of genetics in microbes and impacts microorganisms have on the environment. Upon completion, students should be able to demonstrate knowledge of microorganisms and the disease process. A laboratory component (SI150L) is required to supplement the theoretical aspect of lecture and will include microscopy, microbiology techniques and laboratory skills practical. Students taking this course are required to register for the laboratory portion of the course as a co-requisite or have passed an equivalent to the laboratory portion. This course is recommended for those majoring in the allied health and nursing programs and forensic science certificate.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Differentiate between the structure and function of microbial cells.
- Explain how microbial cells metabolize.
- Identify beneficial and detrimental host/microbe interactions in allied health and industrial setting.
- Assess human health and environmental conditions using microbiology fundamentals.
- Analyze the relationship of diseases and the microbial sources found in the different organ systems.
SI150L INTRODUCTION TO MICROBIOLOGY: LABORATORY
Credits: 1
Corequisite: SI150 or successful completion of SI150 with a “C” or better
This course is the laboratory component of SI150 Introduction to Microbiology: Theory. This course will use a lab-based systems approach, with an emphasis on integrated relationships with microbes, the environment and current technologies. Laboratory exercises are designed to reinforce didactic material by providing hands-on experience with the subject matter. Students actively participate in foundational and current microbiology techniques that show the importance of microbes in our daily lives and their central role in nature. Microscopic observations, investigative experiments to evaluate and identify microbes involved in the allied health field will be performed. A strong emphasis on laboratory safety is expected as part of their professional behavior in this class. Students taking this course are required to register for the lecture portion of the course as a co-requisite or have passed an equivalent to the lecture portion. This course is recommended for those majoring in the allied health and nursing programs.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Use common microbiology instrumentation at a proficient level.
- Interpret experimental results to include the identification of each microorganism.
- Identify possible treatments for pathogens.
- Apply proper aseptic techniques while performing microbiology procedures.
- Apply standard operating procedures in the disposal of biological hazards.
SI155 WASTE SITE WORKER SAFETY: HAZARDOUS WASTE OPERATIONS AND EMERGENCY RESPONSE (HAZWOPER)
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: EN110 MA110 placement or equivalent, SI101 (or equivalent or higher), SI110 or SI103, SI125.
This course provides 45 hours of training in the protection, health and safety of workers involved in storage, disposal, or treatment of hazardous substances, cleanup of hazardous waste sites, and emergency response operations for threats or releases of hazardous substances. The curriculum meets requirements of the Occupational Safety and Health Administration Code of Federal Regulations 29 1910.120., also known as OSHA 29 CFR 1910.12.
Note: Entrance to this course requires that students be physically capable of wearing and working in the different levels of Personal Protective Equipment (PPE), as well as wearing and using respiratory protective devices. This involves obtaining a physician’s statement that the student is cleared to wear and work in PPE and respiratory equipment. For students currently employed in a workplace engaged in HAZWOPER work, and who have the necessary experience and skills of their trade, a waiver may be granted by the Department Chairperson.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Demonstrate understanding of employees’ rights and responsibilities, and an employer’s responsibility for a safety and health program with respect to OSHA 29 CFR 1910.120, and other related regulations.
- Demonstrate understanding of a Job Hazard Analysis, Health and Safety Plan (HASP), and emergency response plan.
- Demonstrate skills in completing hands-on activities including, but not limited to, the use of respirators, levels of Personal Protective Equipment (PPE), and identification and verification of unknown substances.
SM108 INTRODUCTION TO BUSINESS
Credits: 3
This course provides foundational knowledge for students in supervision and management as well as students studying related disciplines in business and computer science. Students will study resume preparations, ethics and social responsibility, the private enterprise system, economic challenges in a global market, entrepreneurship, goods and services distribution, e-commerce transactions, basic management concepts A-Z, technology management, financial statements, federal reserve system, and career opportunities.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Evaluate the private enterprise system and determine the roles of business, competitors, and entrepreneurs.
- Construct the stages in the development of management ethical standards.
- Discuss the forms of business ownership and organization.
SM205 PURCHASING
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: SM108 Introduction to Business
This course provides insight for students to a career in purchasing, such as a retail buyer or a procurement officer for an organization. It focuses on the broad spectrum of retailers, both large and small, selling either merchandise or services and making key management decisions to provide value to their customers and developing a long-term advantage over their competitors. Key strategic issues are examined in developing a retail strategy with an emphasis on financial considerations and store management issues. The procurement cycle is studied with emphasis on vendor partnerships, negotiations, pricing analysis, and policy considerations.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Describe the impact of purchasing and supply chain management on the competitive success and profitability of modern organizations.
- Identify the ethical, contractual, and legal issues faced by purchasing and supply chain professionals.
- Explain the purchasing cycle, various types of purchasing documents, and types of purchases.
SM208 PERSONNEL SUPERVISION
Credits: 3
This course prepares students to be supervisors in a challenging modern workplace. It is based on the premise that organizational variables including diversity in the workforce, computer and communication technology, and the design of organization structures are constantly changing. Overall, this course focuses on discussing important supervision concepts and providing fundamental skills necessary for applying these concepts. Students will learn the critical role of a supervisor in an organization and the abilities needed to be successful.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Explain the role, characteristics and skills of a supervisor and the principles of planning, leading, controlling, staffing, and organizing at the supervisory level.
- Identify and discuss the human skills necessary for supervision.
- Describe employee needs and apply motivational skills to address them.
- Articulate applied supervision concepts.
SM211 E-COMMERCE MANAGEMENT
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: SM108 or permission from the Department Chair
E-commerce has paved the way for companies to sell their products and services to consumers and businesses throughout the world. Most companies now utilize e-commerce to market and sell their products and services, as well as conduct financial transactions. This course will provide the basic knowledge necessary in managing an online business.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Explain the basic requirements of a business website.
- Differentiate the four Internet business models.
- Describe the importance of e-commerce in today's business management.
SM215 INTERNATIONAL MANAGEMENT
Credits: 3
This course teaches students the managerial process in a global context and illustrates how culture affects the managerial process. Students will study international strategic planning, organizing global structures, effective directing, leading, international human resources management, cross-cultural business practices, negotiations, leadership, decision making, motivation, communication process sensitive to verbal and non-verbal languages, and controlling operation results against international cross-cultural performance standards.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Develop strategies for sustaining international business competition in a global setting.
- Discuss cross-cultural business ethics and corporate social responsibility in subsidiary assignments.
- Describe the challenges of international management.
SM220 MANAGEMENT SKILL DEVELOPMENT
Credits: 3
This is a course that emphasizes the development and application of fundamental skills needed for the successful practice of management. The goals and objectives formulated from the firm's mission statement will be the focus of the course. Students will concentrate on the Planning and Organizing functions. In addition, students will apply the control function on the firm's performance against its strategic plan. Policy considerations drive the theme of this course.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Explain the traditional four functions of management: planning, organizing, leading, and controlling.
- Discuss the eight-steps used in the structured decision making process.
- Describe the needs for technology in management operations.
SM225 LEADERSHIP
Credits: 3
This course uses a unique three-prong approach of theory, application, and skill development. Students will be provided with the best coverage of traditional leadership theories and cutting-edge leadership philosophies. It will provide opportunities for students to apply leadership theories and concepts to develop their critical thinking skills and other skill building exercises to handle leadership situations that can be used in their professional and personal lives such as understanding personalities, dealing with ethical dilemmas, motivation, managing behaviors, setting objectives, giving praise, coaching, resolving conflicts, delegating, and negotiating.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Articulate values, qualities, and skills important to leadership positions.
- Develop skills for understanding visioning, goal setting, strategic planning, critical thinking, and ethical decision-making.
- Build productive relationships with others in any situation through effective communication, coaching/mentoring, and empowerment and motivation.
- Summarize in writing their feelings about applied leadership concepts.
SM230 BUSINESS LAW APPLICATIONS
Credits: 3
This course is an introduction to the substantive law that governs American commerce, state and federal statutes and traditional Common Law principles. Uniform Commercial Code (UCC), and the Restatements of the Laws form the foundation upon which the following legal principles are presented: contract law, agency law, partnership and corporate law, real and personal property law, negotiable instruments, and secured transactions. Special emphasis, however, is placed on Cyber law (laws governing Internet transactions) as it applies to e-commerce transactions such as e-contracts; intellectual property rights; online issues relating to copyrights, trademarks, patents, and trade secrets; privacy rights in the online world; cyber law court jurisdictional issues; and cybercrimes (cyber theft, cyber identity theft, cyber stalking, cyber hacking, and cyber terrorism). This course is for anyone contemplating a career in business and anyone interested in the legal requirements governing business decisions and activities.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Discuss the law of contracts as it relates to offers/acceptances, consideration, and competency.
- Identify the key elements of intentional, negligence, and strict liability torts.
- Summarize in writing feelings about applied business law concepts.
SM240 EMPLOYMENT & LABOR LAW
Credits: 3
This course introduces Employment and Labor Law for the non-legal professional in management and labor relations. The course emphasizes employment, labor, and social issues in the work environment as they cover federal and state law governing employer/union and employee/employer relationships. The student will learn how daily supervisory and management decisions made within the context of employment and labor law can have far-reaching consequences in their firm’s legal liabilities. This course provides the knowledge and tools for Supervision and Management graduates to make management decisions that eliminate or minimize their firm’s liability.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Discuss the history of American labor unions and its impact on the enactment of federal labor laws.
- Explain how Title VII of the Civil Rights Act protects covered employees prohibiting any discrimination based on race, color, religion, sex or national origin.
- Summarize in writing ideas and feelings about applied labor and employment law concepts.
SM245 ETHICS & STAKEHOLDER MANAGEMENT
Credits: 3
This course uses cutting-edge research along with case histories to help students understand the relationships between business and society stakeholders. The managerial perspective of this course emphasizes the twin themes of stakeholders and ethics. Students are shown how to integrate ethical consideration into the entire decision-making. The course employs a stakeholder management framework that emphasizes the firm's social and ethical responsibilities to both internal and external stakeholders.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Describe and explain actions or strategies that management may take to improve a firm's ethical climate.
- Describe ethical standards in management and identify its role in contemporary business practices.
- Differentiate between management of internal and external stakeholders.
SM292 SUPERVISION & MANAGEMENT PRACTICUM
Credits: 3-6
Prerequisite: Must be in the last two semesters of the program.
This course provides students with a supervised work experience where they apply the skills necessary to be successful in a supervision and management career.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Apply theory learned in the classroom to the work environment.
- Practice effective interpersonal skills in the workplace.
- Document the synthesis of knowledge and skills gained through the work experience in an electronic presentation.
SO099 STUDENT-CENTERED SUCCESS IN COLLEGE
Credits: 3
This course integrates a balance of motivational, study, and life skills; students will understand themselves as individuals who appreciate their own strengths, identify their challenges, and work to strengthen current skills and create new ones. Students will work on their non-cognitive skills such as attitudes, behaviors, and skills such as critical thinking, self-efficacy, resilience, and interpersonal relations. Students will utilize the Academic and Career Excellence System (ACES) to help identify their strengths and challenges and create a Personal Success Plan (PSP). The course will enable students’ explorations of workforce and college opportunities using information from ACES and their PSP.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Develop skills to locate, evaluate, and interpret career information.
- Identify career clusters and related pathways that match career and education goals.
- Describe and apply elements of team-building, problem-solving, and decision-making as they relate to workplace and postsecondary education opportunities.
SO130 INTRODUCTION TO SOCIOLOGY
Credits: 3
This course provides a scientific overview of human social interaction. Students will learn the foundational history, methodology, and theoretical analysis of sociology. Upon completion, students will demonstrate a basic knowledge of sociology, engaging in the analysis of social issues.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Identify open questions upon which a controversy depends, while taking into account a diversity of perspectives.
- Recognize and explain a problem, position, or question.
- Analyze sociological arguments for the strength of their evidence, internal consistency, and logic.
- Distinguish facts from inferences and opinions in the field of Sociology.
SS063 AMERICAN GOVERNMENT
Credits: 3
This course focuses on the foundations of democracy in America, examining the operation of the legislative, executive, and judicial branches of government at the federal, state, and local levels. Topics covered include rights and responsibilities of citizenship, voting, political parties, interest groups, the US Constitution (including the Bill of Rights), bureaucracy, national policies relating to foreign policy, taxation, spending priorities, government regulations, and entitlement.
This course incorporates the College and Career Readiness Standards (CCRS) for Adult Education. The standards sharpen the focus on the close connection between comprehension of the text and attainment of knowledge. Relevant individualized instruction provides reading, writing, language, and speaking and listening activities to enable students to become empowered, competent, critical, and reflective in their assignments.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Make logical inferences about the importance of American Government and Politics.
- Analyze the series of events which led to the creation of the United States Constitution and Bill of Rights.
- Analyze U.S. documents of historical and literary significance for their themes, purposes, and rhetorical features.
SS081 U.S. HISTORY I
Credits: 3
This course focuses on the reconstruction of the United States of America after the Civil War through World War II. The objective is to examine and evaluate the political, social and economic development of the United States during this era.
This course incorporates the College and Career Readiness Standards (CCRS) for Adult Education. The standards sharpen the focus on the close connection between comprehension of the text and attainment of knowledge. Relevant individualized instruction provides reading, writing, language, and speaking and listening activities to enable students to become empowered, competent, critical, and reflective in their assignments.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Identify logical inferences about central issues that took place during the Reconstruction Era to World War II.
- Cite specific evidence from literary and informational texts that explains the importance of the various events during the Reconstruction Era to World War II.
- Analyze the sequence of events and explain how specific events interacted and developed during the Reconstruction Era to World War II.
- Identify the major economic developments and specific events from the Reconstruction Era to World War II.
SS082 U.S. HISTORY II
Credits: 3
This course focuses on the economic and political changes during the Cold and Vietnam War, including the Civil Rights movement, and the recent events and trends that have shaped present-day America.
This course incorporates the College and Career Readiness Standards (CCRS) for Adult Education. The standards sharpen the focus on the close connection between comprehension of the text and attainment of knowledge. Relevant individualized instruction provides reading, writing, language, and speaking and listening activities to enable students to become empowered, competent, critical, and reflective in their assignments.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Identify logical inferences about central issues during the Cold and Vietnam Wars to present- day America.
- Cite specific evidence from literary and informational texts that explains the importance of the various events during the Cold and Vietnam Wars to present-day America.
- Analyze the sequence of events and explain how specific events interacted and developed during the Cold and Vietnam Wars to present-day America.
- Identify the major economic developments and specific events during the Cold and Vietnam Wars to present-day America.
SU100 SURVEYING DRAFTING
Credits: 3
This course deals with typical job responsibilities of an office draftsperson or survey party chief in completing a graphic description of survey field work. These descriptions/plans result from a great variety of engineering field work requiring diverse methods of graphic resolution.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Discuss the roles of office draft persons or survey party chiefs.
- Define common terminology in the surveying drafting career.
- Explain the diverse engineering fieldwork and methods of graphic resolution used.
SU101 SURVEYING PROBLEMS
Credits: 3
This is a mathematics course designed to give the student an understanding of the fundamentals of basic survey computation. Emphasis is placed on basic arithmetic, trigonometric and geometric operations pertaining to traverse, triangulation and general survey calculation.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Demonstrate an understanding of basic mathematics needed for survey computations.
- Apply basic arithmetic, trigonometry and geometric operations to given surveying problems.
- Discuss and identify solutions to various surveying problems encountered in the work setting.
SU230 ADVANCED SURVEYING
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: CE222
This course will cover advanced topics in surveying including highway and construction surveying, property and legal issues in boundary surveying, concepts of elementary geodetic surveying, and an overview of Global Positioning Systems (GPS) as applied to surveying for centimeter accuracy measurement.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Demonstrate proficiency in the mathematical computations of horizontal and vertical surveys including the process of laying out horizontal and vertical curves.
- Apply proper survey processes in construction surveys and layouts.
- Demonstrate an understanding of boundary surveying and the legal aspects of property surveying.
- Analyze boundary and property survey problems using applicable survey methods.
- Demonstrate understanding of concepts of geodetic and GPS surveying.
SU240 BOUNDARY LAW I
Credits: 3
This course introduces the concepts of boundary control and legal principles. Topics covered include proportionate measurement, rights in land, junior/senior title rights, retracement of original surveys, deed first/survey first, common and case law, ranking/prioritizing evidence, controlling monuments and corners, errors in legal descriptions, and plats and case studies.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Demonstrate an understanding of boundary control and legal principles to include identification of error in legal descriptions.
- Discuss legal principles such as deed first/survey first, common and case law.
- Define the basic elements of a boundary survey and the proper sequence of events/actions.
- Evaluate boundary evidence and make decisions based on this ranking.
- Identify controlling corners and boundaries.
SU241 BOUNDARY LAW II
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: SU240 Boundary Law I and permission of Advisor
This course is a continuation of Boundary Law I and covers the subjects of evidence and procedures for determining real property boundaries. Statutes and case law, conflicting evidence, proper methods and procedures for collecting evidence, riparian rights, surface and subsurface rights and eminent domain are studied in detail. Boundary agreements and legal instruments prepared by the land surveyor are introduced. The role of the land surveyor as an expert witness is presented.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Explain in detail the subjects of evidence and procedures used for determining real property boundaries.
- Demonstrate proficiency of reading legal instruments prepared by land surveyors.
- Describe the surveyor’s role in court cases.
- Write a legal and technical description and prepare a surveyor’s report.
SU250 INTRODUCTION TO GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS
Credits: 3
This course will provide students with basic knowledge of Geographic Information Systems (GIS) (e.g., sources of GIS data, various data models). Special emphasis will be given to the manipulation of digital spatial vector data with application to cadastral surveys. One of the objectives of the course is to provide students with hands-on experience with GIS software and hardware components.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Describe the fundamental concepts of GIS and the major functionality contained within the ArcGIS software.
- Explain the GIS analytical process and be proficient with a variety of ArcGIS tools to solve realistic problems. (The course emphasizes practical GIS skills.)
- Demonstrate an understanding of the basics of geodatabase and the more advanced functionality that makes the geodatabase such a powerful data model.
- Design presentation-quality maps and create a personal geodatabase.
SU251 ADVANCED GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: SU250 Introduction to GIS
This course is a more advanced study of Geographic Information Systems (GIS) with particular emphasis on manipulation and analysis of raster data. This course will also provide introduction to ArcGIS Spatial Analyst and 3D Analyst.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Produce and control raster data using ArcGIS Spatial Analyst.
- Work within the new ArcGIS geoprocessing environment to create, execute, and automate spatial analysis workflows.
- Analyze three-dimensional modeling using ArcGIS 3D Analyst software.
- Create realistic models by draping aerial photographs over surfaces and displaying two-dimensional features in three dimensions.
SU280 SPECIAL TOPICS IN GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: SU250 Introduction to GIS
This course will introduce students to the applications of Geographic Information Systems (GIS) in cadastral and land information systems and in land use planning. Geographic data is increasingly important in understanding society and the environment. Using advanced tools and software, students will have an opportunity to focus on local and global planning problems.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Produce and manipulate cadastral data and create parcel data using the Survey Analyst Extension and the Cadastral Editor tools in the ArcGIS software.
- Apply Survey Analyst GIS tools on cadastral datasets and perform analysis of these datasets to ensure survey accuracy.
- Use ArcGIS tools to address real-world social, economic, and environmental planning problems.
SU292 SURVEYING PRACTICUM
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: CE222
This course covers the application of field and office techniques related to the lessons covered in the surveying and drafting courses. Students will do actual field and office survey work to learn proper use of surveying and related instruments including computers and data collectors.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Demonstrate proficiency in the operations of typical survey instruments including electronic total stations, levels, and data collectors.
- Apply proper field operations in traversing, leveling, and topographic surveying.
- Demonstrate proficiency in the preparation of survey drawings using computer aided surveying software.
- Transfer data to and from survey instruments, data collectors, and computers.
- Demonstrate understanding of errors and error propagation in field work.
TH101 INTRODUCTION TO THE THEATER
Credits: 3
This course is designed to provide a basic introduction to the study of theatre. It explores theatre as a fine art and how theatre practitioners work. Course lectures include theatre history and production practices. Attendance at a local theatre production is recommended. Students will collaborate in the making of a short, fully-realized production.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Analyze the elements of a play to appreciate theatre as an art.
- Develop a clear understanding of theatre history and recent developments.
- Implement production practices.
VC101 INTRODUCTION TO VISUAL COMMUNICATIONS
Credits: 3
This course introduces and emphasizes the historical development and current applications of various theories and practices associated with media production. This course increases students’ critical thinking skills needed to navigate the various fields of visual communications.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Identify the six typeface families and explain how each one expresses a mood.
- Apply critical thinking skills in the practice of media production.
- Explain ethical and legal standards regarding the use of media.
VC125 DIGITAL GRAPHICS: RASTER
Credits: 3
This course is designed to introduce the fundamental skills and theory required in the production and manipulation of raster graphics. The curriculum emphasizes both craft and visual problem solving. Emphasis is placed on the development of the students’ ability to apply creative thinking and contemporary techniques in creating meaningful and effective design.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Create effective communications solutions through the application of theories, tools, and best practices in the field.
- Demonstrate an understanding of the fundamental tools and techniques of raster design software.
- Apply various techniques and methodologies in the editing and refinement of digital media.
VC126 DIGITAL GRAPHICS: VECTOR
Credits: 3
This course is designed to introduce the fundamental skills and theory required in the production and manipulation of vector graphics. The curriculum emphasizes both craft and visual problem solving. Emphasis is placed on the development of the students’ ability to apply creative thinking and contemporary techniques in creating meaningful and effective design.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Demonstrate innovation and creativity through the production of self-generated digital images.
- Demonstrate an understanding of the fundamental tools and techniques of vector design software.
- Apply various techniques and methodologies in the generation and development of vector graphics.
VC127 DIGITAL PHOTOGRAPHY
Credits: 3
This course explores digital photography as a powerful communication tool central to a variety of creative careers. Students explore visual communication applications and dynamic career trajectories within fine art, advertising, and editorial photography. Students also learn to apply basic digital imaging concepts, techniques, and practices to image compositions and other advanced design applications.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Demonstrate functional knowledge of photographic theories, composition techniques, and camera operation to obtain a desired result.
- Create effective communication solutions through the application of theories, tools, and best practices in the field.
- Apply various techniques and methodologies in the editing and refinement of digital media.
VC128 DESIGN PRINCIPLES AND ELEMENTS
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: VC126
This course explores the process of design, starting with understanding design elements and how to effectively apply design principles. Students learn about formal design elements like line, shape, plane, form, pattern, value, and texture. Through practical exercises, students gain skills in using design principles such as figure/ground, contrast, balance, unity, repetition, rhythm, and hierarchy. The acquired skills are directly applicable to various fields in art and design, including painting, art direction, illustration, interior design, and interactive design.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Identify the elements of design and their various applications.
- Describe the principles of design and their various applications.
- Create effective solutions to graphic design problems.
VC211 DESIGN STUDIO I
Credits: 3
Corequisite: VC212
In this course, students discover how to organize text, graphics, and images for impactful print communication. Emphasis is placed on using advanced desktop publishing software and its tools to create a variety of projects. The skills gained are directly useful for those in graphic design, print and digital publishing, and advertising.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Define basic terms and tools used in desktop publishing software.
- Apply graphic design, layout, and typography techniques to create effective design solutions.
- Develop audience-focused layouts to meet professional publishing requirements.
VC212 DESIGN STUDIO II
Credits: 3
Corequisite: VC211
In this course, students explore how to create appealing brochures, ads, posters, and newsletters. The curriculum covers design elements, color principles, typography, and printing technologies. Additionally, students learn to create assets for web and social media platforms. The skills acquired are directly applicable to careers in art, design, illustration, print and digital publishing, and interactive design.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Explain the fundamental terminology and concepts of desktop publishing.
- Employ various techniques and methodologies in the creation of desktop publishing solutions.
- Create effective publications through thoughtful synthesis of theories, tools, and best practices in design.
VC221 INTERACTIVE STUDIO I
Credits: 3
Corequisite: VC222
This course is designed to provide students with the knowledge and skills to design and create an effective website. Students will learn the basics of planning, constructing, testing, publishing, marketing and maintaining a website.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Explain the basic terminology, technology, and tools utilized in website development.
- Design the structure and style of a website using HTML (HyperText Markup Language) and CSS (Cascading Style Sheets).
- Analyze design and development choices, ensuring adherence to industry standards and optimizing user experience across multiple pages.
VC222 INTERACTIVE STUDIO II
Credits: 3
Corequisite: VC221
This course introduces UX (user experience) and UI (user interface) design with a focus on responsive website design by means of advanced animations, transitions, and modern frameworks used for website development. This course requires a basic understanding of HTML (HyperText Markup Language) and CSS (Cascading Style Sheets).
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs):
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Explain the basic terminology, technology, and tools utilized in responsive web design.
- Create a responsive layout for a website using responsive design technologies.
- Develop responsive multi-page websites showcasing an optimized user experience across various devices.
VC231 VIDEO PRODUCTION I
Credits: 3
Corequisite: VC232
This course is designed to provide students with the fundamental knowledge and skills used in video productions including all aspects of pre-production, production, and post-production. This course emphasizes the pre-production and production stages with special focus on the planning and capture of quality video using industry standard techniques and equipment. Students will apply theory and best practices in hands-on production exercises that are designed to address a variety of standard video production tasks.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Describe the three fundamental stages of video production.
- Produce high-quality video content using video production tools and techniques.
- Explain potential legal and ethical challenges that may emerge in video production.
VC232 VIDEO PRODUCTION II
Credits: 3
Corequisite: VC231
This course is designed to provide students with the fundamental knowledge and skills used in video productions including all aspects of pre-production, production, and post-production. This course emphasizes the post-production (editing) stage with special focus on using industry standard techniques and equipment. Students will apply theory and best practices in hands-on production exercises that are designed to address a variety of standard video production tasks.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Describe the fundamental terminology and tools of video editing software.
- Deploy various techniques and methodologies in the editing of video projects.
- Produce impactful video content by applying theories, tools, and best practices in the field.
VC291 PROJECT MANAGEMENT & MARKETING SOLUTIONS
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: VC212
This course integrates all the skills and concepts learned throughout the Visual Communications program experience. Students conceptualize, plan, and produce media projects according to client-based criteria. Students develop production schedules and learn to manage their tasks within a deadline. Students develop interpersonal relationship skills working with clients and team members. Emphasis is placed on developing solutions, remaining focused, being flexible, and cooperating with team members to complete visual communications projects in a real-world and/or simulated work environment.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Identify the core principles of Design Thinking.
- Develop potential product solutions based on identified target markets.
- Conceptualize and create visual messages for clients and customers using appropriate print, video, and/or web media.
VC292 VISUAL COMMUNICATION PRACTICUM
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: Advisor’s approval
This course provides an opportunity for students to gain supervised work experience in the Visual Communications field.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Apply theory and technical skills learned in the classroom to the work environment.
- Demonstrate effective interpersonal skills in the workplace.
- Evaluate professional growth through the capstone experience.
WG101 INTRODUCTION TO WOMEN AND GENDER STUDIES
Credits: 3
Prerequisite: Placement into EN110 or successful completion of EN097
This course provides an introduction to basic concepts and key issues in Women’s and Gender studies. This interdisciplinary course will highlight the fundamental role of intersectionality (the ways gender, sex, class, race, ethnicity, culture, sexual orientation, etc. interact to shape our identities and life experiences) in systems of societal privileges and oppressions in the Marianas and other regions. Students will learn about family, education, work, and popular culture.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Identify fundamental questions and issues in Women’s and Gender Studies.
- Discuss how gender intersects with other categories of social difference, such as sexuality, race, ethnicity, class, and ability.
- Analyze how gender is represented in the diverse cultures of the Marianas, Asia-Pacific, and the world.
WT100 INTRODUCTION TO WATERWORKS TECHNOLOGY
Credits: 3
Introduction to Water Technology is a three credit course designed for a waterworks operator or prospective operator. This course provides basic knowledge of water and wastewater treatment, microbial, physical, and chemical analysis, a basic introduction to fluid transport and hydraulics and in-depth examination of water treatment operations.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Recognize the sources, sinks, and potential contaminants of water.
- Describe various water and wastewater treatment and distribution methods.
- Apply physical concepts (e.g., fluid motion, hydraulics, etc.) to design or evaluate the soundness of a water or wastewater treatment system.
- Identify physical, biological, and chemical parameters critical for operating a water or wastewater treatment facility
- Indicate appropriate tests to monitor water and wastewater quality.
- Demonstrate an understanding of local and federal water quality regulations.
Board of Trustees
| Carlo Leon Guerrero | Chairperson |
| Rose P. Grino | Vice Chairperson |
| Yolanda M. Padrones | Secretary |
| Gina Y. Ramos | Treasurer |
| Frank P. Arriola | Member |
| Richard P. Sablan | Member |
| Faith Velasco | Student Member (2025-2026) |
| Francine N. Galao | Faculty Advisory |
| Kenneth C. Bautista | Support Staff Advisory |
| Mary A.Y. Okada, Ed.D., AIF | Chief Executive Officer & President, Executive Officer of the Board |
| Bertha M. Guerrero | Board Recording Secretary |
Office of the President
| Mary A.Y. Okada, Ed.D., AIF | President |
| John K. Dela Rosa | Assistant Director, Communications & Promotions |
| Bonnie Mae M. Datuin | Program Specialist, Development & Alumni Relations |
| Patrick F. Maloney, GPC | Program Specialist, Development & Alumni Relations |
| Julie Ulloa-Heath, Ed.D. | Assistant Director, Planning & Development |
| Francisco E. Palacios | Sustainability and Projects Coordinator |
Office of the Vice President for Academic Affairs
| Virginia C. Tudela, Ph.D. | Vice President, Academic Affairs |
| Denise M. Mendiola | Assistant Director, Continuing Education & Workforce Development |
| Adrian E. Davis | Program Specialist, Continuing Education & Workforce Development |
| Shaun M. Hosei | Program Specialist, Continuing Education & Workforce Development |
| Joachim Peter Roberto | Program Specialist, Continuing Education & Workforce Development |
| Kimberly Ann Taitano | Program Specialist, Continuing Education & Workforce Development |
| Catherine M. Solidum | Assistant Director, Assessment, Institutional Effectiveness & Research |
| Mark Joseph A. Burgos | Institutional Researcher, Assessment, Institutional Effectiveness & Research |
| Mariesha Cruz-San Nicolas | Acting Coordinator, Admissions & Registration |
School of Trades and Professional Services
| Pilar Perez Williams | Dean, School of Trades & Professional Services |
| Christine B. Sison, Ph.D. | Associate Dean, School of Trades & Professional Services |
| Dorothy-Lou M. Duenas, R.N. | Associate Dean, School of Trades & Professional Services |
| Mariesha Cruz-San Nicolas | Associate Dean, School of Trades & Professional Services |
| Esther A. Rios | Program Specialist, Reach for College |
School of Technology and Student Services
| Michael L. Chan, Ed.D. | Dean, School of Technology & Student Services |
| Gerald A.B. Cruz | Associate Dean, School of Technology & Student Services |
| Jason G. Soliva | Instructional Designer, School of Technology & Student Services |
| John F. Payne | Program Specialist, Accommodative Services |
| James Fathal | Program Specialist, Student Support Services |
Office of the Vice President for Finance and Administration
| Clarissa T. Padua | Vice President, Finance and Administration |
| Edwin E. Limtuatco | Controller, Business Office |
| Apolline C. San Nicolas, SHRM-CP | Chief Human Resources Officer |
| Gemma-Lee P. Santos | Financial Aid Coordinator |
| Ricky S. Tyquiengco | Chief Information Technology Officer |
| Joleen M. Evangelista | Procurement and Inventory Administrator |
| Huan F. Hosei | Environmental Health & Safety Officer |
EEO Office and Title IX Office
| Christine B. Sison, Ph.D. | EEO Compliance Officer |
| John F. Payne | Title IX Coordinator |
Burgos, Mark Joseph A.
Institutional Researcher, Assessment, Institutional Effectiveness & Research
M. S. Mathematics, Industrial Mathematics Track
University of Central Florida 2019
B.S. Mathematics
University of Guam 2014
Chan, Michael L., Ed.D.
Dean, Technology & Student Services
Ed. D. Educational Leadership
Argosy University 2011
M.Ed. Education
University of Portland 2003
B.A. Mathematics
California State University, Sacramento 1999
Cruz, John T.
President Emeritus, June 1988-June 2000
M.Ed. Administration and Supervision
University of Guam 1983
B.A. Secondary Education, General Social Science
University of Guam 1973
Cruz, Gerald A.B.
Associate Dean, Technology & Student Services
M.P.A. Public Administration
Excelsior College 2017
B.A. Asian Studies
University of San Francisco 2011
Cruz-San Nicolas, Mariesha J.
Associate Dean, Trades & Professional Services
M.Ed. Secondary Education
University of Guam 2007
B.A. Communications
Regis College 1997
Datuin, Bonnie Mae M.
Program Specialist, Development & Alumni Relations
B.A. Psychology
University of Guam 2001
Davis, Adrian E.
Program Specialist, Continuing Education & Workforce Development
M.P.A. Public Administration
University of Guam 2022
B.S.W. Social Work
University of Guam 2018
Dela Rosa, John K.
Assistant Director, Communications & Promotions
B.A. English
University of Texas-Austin 1990
Duenas, Dorothy-Lou M., R.N.
Associate Dean, Trades & Professional Services
M.S. Nursing
University of Phoenix 2012
B.S. Nursing
University of Portland 2003
Registered Nurse, Guam License
Evangelista, Joleen M.
Procurement and Inventory Administrator
B.A. Business Administration
Seattle University 1992
Fathal, James
Program Specialist, Night Administration
B.B.A. International Business
University of Guam 1999
Hosei, Huan F.
Environmental Health & Safety Officer, Environmental Health & Safety
M.A. Education, Educational Leadership
San Diego State University 2003
B.A. Anthropology
University of Guam 1992
Hosei, Shaun M.
Program Specialist, Continuing Education & Workforce Development
M.P.A. Public Administration
University of Guam 2021
B.S. Public Administration
University of Guam 2018
Limtuatco, Edwin E.
Controller, Business Office
B.B.A. Accounting
University of Guam 1997
Maloney, Patrick F., GPC
Program Specialist, Development & Alumni Relations
Grant Professional Certified
Grant Professionals Certification Institute
M.A. Nonprofit Management
Regis University 2007
B.B.A. Business Administration
University of Great Falls 2003
Mendiola, Denise M.
Assistant Director, Continuing Education & Workforce Development
B.S. Public Administration
University of Guam 2020
A.S. Marketing
Guam Community College 2020
Okada, Mary A.Y., Ed.D., AIF
President
Ed.D. Educational Leadership
University of Phoenix 2009
M.P.A Public Administration
University of Guam 1997
B.B.A Accounting & Management
University of Guam 1988
Accredited Investment Fiduciary
Center for Fiduciary Studies 2016
Padua, Clarissa T.
Vice President, Finance and Administration
M.A.C. Business Administration
University of Guam 2023
P.M.B.A. Business Administration
University of Guam 2022
B.B.A. Accounting
University of Guam 2001
B.B.A. Management
University of Guam 2001
Palacios, Francisco E.
Sustainability & Projects Coordinator, Planning & Development
M.Ed. Curriculum and Instruction
Concordia University 2013
B.A. Communication Studies
University of Guam 2010
Payne, John F.
Program Specialist, Accommodative Services
M.H.R. Human Relations
University of Oklahoma 1991
B.S. Social Science
University of Guam 1985
Licensed Professional Counselor
Internationally Certified Alcohol & Drug Counselor
Certified Substance Abuse Treatment Counselor III
Rios, Esther A.
Program Specialist, Reach for College
M.A. Counseling
University of Guam 2008
B.A. Psychology
University of Guam 2002
Roberto, Joachim Peter
Program Specialist, Development & Alumni Relations
M.S.W. Social Work
Washington University 1988
B.A. Sociology
Washington State University 1986
Academy of Certified Social Workers
San Nicolas, Apolline, SHRM-CP
Chief Human Resources Officer
M.B.A. Business Administration
United States University 2015
B.B.A. Business Management
University of Guam 2003
SHRM Certified Professional
Society for Human Resources Management 2017
Santos, Gemma-Lee P.
M.A. Executive MAC: Accounting
Florida Atlantic University 2017
B.B.A. Management
University of Guam 2003
Sison, Christine B., Ph.D.
Associate Dean, Trades & Professional Services/EEO Compliance Officer
Ph.D. Education
Capella University 2022
M.P.A. Public Administration
University of Guam 2002
B.B.A. International Business
Seattle University 1995
Solidum, Catherine M.
Assistant Director, Assessment, Institutional Effectiveness and Research
B.S. Mathematics
University of Santo Tomas, 1997
Soliva, Jason G.
Instructional Designer
B.S. Computer Science
University of Guam 2012
Teaching Online Certified (TOC)
Quality Matters 2023
Taitano, Kimberly Ann
Program Specialist, Continuing Education & Workforce Development
M.L.S. Library and Information Services
University of Maryland 2016
B.B.A. International Business
University of Guam 1999
Tudela, Virginia C., Ph.D.
Vice President for Academic Affairs
Ph.D. Education
University of Southern California 2002
M.P.A. Public Administration
University of Guam 1997
B.B.A. Management
University of Guam 1992
Tyquiengco, Ricky S.
Instructor, Technology-Electronics
A.A. Education
Guam Community College 2010
Certificate Education
Guam Community College 2010
A+ Certified Professional IT Technician
The Computing Technology Industry Association 2009
Certified Fiber Optics Installer
Electronics Technicians Association
Certified Data Cabling Installer
Electronics Technicians Association
Teaching Online Certified (TOC)
Quality Matters 2020
Ulloa-Heath, Julie, Ed.D.
Assistant Director, Planning & Development
Ed.D. Educational Leadership
University of San Diego
M.S. Educational Leadership
Troy State University 1994
B.A. Psychology
University of Guam 1982
A.A. Liberal Arts
Kemper Military School and College 1980
Williams, Pilar Perez
Dean, Trades & Professional Services
M.A. Catholic School Leadership
University of San Francisco 2007
B. A. Behavioral Science
Mount Mary College 1991
Teaching Online Certified (TOC)
Quality Matters 2021
Abrahamsen, Loren L.
Instructor, Education-Cosmetology
Certificate Cosmetology
Guam Community College 2002
Cosmetology Instructor, Guam License
Aguilar, Abegail Q., L.P.N.
Assistant Instructor Nursing and Allied Health
A.S. Medical Assisting
Guam Community College 2015
Certificate Practical Nursing
Guam Community College 2017
Licensed Practical Nurse, Guam
Licensed
Aguon, Janice T.A.
Instructor, Education-Cosmetology
B.S. Criminal Justice
University of Guam 1997
Certificate Cosmetology
Guam Community College 2000
Cosmetology Instructor, Guam License
Analista, Hernalin R.
Assistant Professor, Assessment & Counseling-Vocational Guidance
M.A. Counseling
University of Guam 2002
B.A. Psychology
University of Guam 1998
Angay, Roderick R.
Instructor, Technology-Electronics
B.S. Electronics and Communication Engineering
Lyceum of the Philippines University 2001
Teaching Online Certified (TOC)
Quality Matters 2021
Balajadia, Galen P.
Assistant Instructor, Construction Trades
Journeyman Certificate, Marine Technician Specialist
Marine Mechanics Institute 2010
Blas, Joey E.
Instructor, Automotive Technology
Certificate, Automotive, Diesel and industrial
Universal Technical Institute, Houston 2004
ASE Certified Master Automobile Technician
Blas, Leonalynn I., RMA
Instructor, Nursing and Allied Health - Practical Nursing
A.S. Medical Assisting
Guam Community College 2019
Registered Medical Assistant, American Medical Technologists 2024
Blas, Trisha Danielle, Ph.D.
Assistant Professor, Math & Science-Math
Ph.D. E-Learning
Northcentral University 2018
M.Ed. Secondary Education
University of Guam 2007
B.A. Mathematics
University of Guam 2005
B.A. Secondary Education
University of Guam 2005
Teaching Online Certified (TOC)
Quality Matters 2018
Microsoft Certified Educator
Bollinger, Simone E.P.
Associate Professor, English
M.Ed. Language and Literacy
Harvard University 2010
B.A. English
Dickinson College 2005
Certificate Micronesian Studies
University of Guam 2022
Buan, Carlos D.
Instructor, Technology-Computer Science
M.S. Computer Science
AMA Computer University, Philippines 2011
B.S. Computer Science
University of Batangas 1996
Callos, Philip Kelvin T.
Assistant Instructor, Culinary & Food Services
A.A. Culinary Arts
Guam Community College 2016
Certified Food Safety HACCP Manager
National Registry for Food Safety Professionals 2021
Certified ServSafe Instructor
National Restaurant Association Education Foundation 2020
Certified ServSafe Exam Proctor
National Restaurant Association Education Foundation 2020
Certified ServSafe Food Protection Manager
National Restaurant Association Education Foundation 2020
Certified Secondary Foodservice Educator
National Restaurant Association Education Foundation 2022
Camacho, Edward M.
Instructor, Construction Trades
B.A. Board of Governors
East Illinois University 1993
Cepeda, Nita Jeannette P.
Instructor, Business & Visual Communications-Visual Communications
B.A. Communication Studies
University of Guam 1986
Chargualaf, Katherine M.
Assistant Instructor, Business & Visual Communications-Marketing
A.S. Marketing
Guam Community College 1996
Chong, Eric K. L.
Professor, Hospitality & Tourism
M.H.R. Human Relations
University of Oklahoma 2000
B.A. Business Administration
Washington State University 1982
B.A. Hotel & Restaurant Administration
Washington State University 1982
Teaching Online Certified (TOC)
Quality Matters 2021
Certified Guest Service Professional
American Hotel & Lodging Association 2014
Certified Customer Service Specialist
Electronics Technicians Association International 2000
Certified Hotel Administrator
Educational Institute of the American Hotel & Lodging Association 1998
Certified Hospitality Educator
Educational Institute of the American Hotel & Lodging Association 1998
Certified Rooms Division Executive
Educational Institute of the American Hotel & Lodging Association 1997
ServSafe Food Protection Manager Certification
National Restaurant Association Education Foundation 2011
Guam Visitors Bureau Certified Tour Guide
Concepcion, Jonah M.
Associate Professor, Criminal Justice & Social Science-Social Science
M.S. Higher Education
Capella University 2017
M.P.A. Public Administration
University of Guam 2006
B.S. Criminal Justice
University of Guam 2005
Online Teaching Certificate
Online Learning Consortium 2016
Moodle Educator Certified (MEC)
Moodle 2023
Concepcion, Tonirose R., Ph.D.
Professor, Technology-Office Technology
Ph.D. Postsecondary and Adult Education
Capella University 2015
M.Ed. Education, Administration & Supervision
University of Guam, 2009
B.B.A. Accounting & Secondary Education
University of Guam, 2007
Certificate for Online Adjunct Teaching (COAT)
Maryland Online 2015
Moodle Educator Certified (MEC)
Moodle 2023
Cosico, Narciso H.
Instructor, Tourism & Hospitality
B.S. Hotel and Restaurant Management
University of Santo Tomas 1986
Cruz, Carol R.
Associate Professor, Hospitality & Tourism
M.B.A. Business Administration
University of Guam 1999
B.B.A. Business Administration
University of Guam 1991
Teaching Online Certified (TOC)
Quality Matters 2021
Cruz, Donna M., Esq.
Professor, Criminal Justice & Social Science-Criminal Justice
J.D. Law
University of San Diego Law School 1990
B.S. Management and Marketing
University of Guam 1985
Teaching online Certified (TOC)
Quality Matters 2021
Cruz, Jesse Q.
Assistant Instructor, Automotive Technology
A.S. Occupational Studies, Automotive and Diesel Technology
Universal Technical Institute Phoenix 1996
ASE Certified Master Automobile Technician
Cruz, Nenita P.
Instructor, Business & Visual Communications-Marketing
B.S. Business Administration
San Francisco State University 1994
Cundiff, Tressa C.
Assistant Professor, English
M.Ed. Language and Literacy
University of Guam 2004
B.A. English
University of Guam 2001
Certificate for Online Adjunct Teaching (COAT)
Maryland Online 2015
Datuin, Theresa A. H., Ed.D.
Professor, Math & Science-Math
Ed.D. Educational Leadership
Argosy University 2014
M.S. Environmental Science
University of Guam, 2009
B.A. Math & Secondary Education
University of Guam 2001
Online Teaching Specialization in Online Management
Online Learning Consortium 2016
Dingcong, David John P.
Instructor, Hospitality & Tourism
B.B.A. International Tourism and Hospitality Management
University of Guam 2011
Egana, Joel E.
Instructor, Automotive Technology
A.A. Education
Guam Community College 2010
Certificate Education
Guam Community College 2010
ASE Certified Master Automobile Technician
Ellen, Deborah, Ed.D.
Associate Professor, Education
Ed.D. Instructional and Curriculum Leadership
Northcentral University 2014
M.A. Education
Northern Michigan University 1995
B.A. Elementary Education
Michigan State University 1985
Esturas, Raniel P.
Assistant Instructor, Technology - Electronics
A.S. Computer Networking
Guam Community College 2021
Certified Fiber Optics Installer
Electronics Technicians Association
Certified Data Cabling Installer
Electronics Technicians Association
Evangelista, Frank F.
Instructor, Culinary & Food Services
A.S. Food and Beverage Management
Guam Community College 2006
Certified Hospitality Educator
Educational Institute of the American Hotel & Lodging Association 2001
Certified Food & Beverage Executive
Educational Institute of the American Hotel & Lodging Association 2004
Certified ServSafe Instructor & Registered ServSafe Examination Proctor
National Restaurant Association Education Foundation 2020
Certified Techniques of Alcohol Management (TAM) Instructor
National Hospitality Institute 2015
ServSafe Food Protection Manager Certification
National Restaurant Association Education Foundation 2020
Fadhel, Jamal
Instructor, Automotive Technology
Certificate, Automotive, Diesel and industrial
Universal Technical Institute, Phoenix 2004
ASE Certified Automobile Technician
ASE Certified Advanced Level Specialist
Fernandez, Christine M.
Assistant Instructor, Hospitality & Tourism
A.S. Tourism & Travel Management
Guam Community College 2020
Franquez, Arwen A.
Assistant Professor, Criminal Justice & Social Science-Human Services
M.A. Counseling
University of Guam 2010
B.A. Classics
Reed College 2002
Teaching Online Certified (TOC)
Quality Matters 2020
Galao, Francine N.
Instructor, Education-Cosmetology
Certificate Cosmetology
Guam Community College 2002
Cosmetology Instructor, Guam License
Guerrero, Jermaine H.
Assistant Instructor, Construction Trades
B.A. History
University of Guam 2015
Guerrero, Norma R.
Assistant Professor, Business & Visual Communications-Marketing
M.B.A. Marketing
University of Phoenix 2012
B.B.A. Marketing
University of Guam 1992
Teaching Online Certified (TOC)
Quality Matters 2020
Haurillon, Bertrand J.
Assistant Instructor, Culinary & Food Services
C.A.P. Professional Training Diploma Classic Cuisine
French National Ministry of Education 1982
Ikeda, Daisaku
Honorary Professor
Honorary Doctorates and Professorships from over 270 Academic Institutions
Graduate of Fuji College Economics Department, 1967 (now Tokyo Fuji University)
Ji, Eric
Associate Professor, Hospitality & Tourism
M.S. Hospitality Management
Florida International University 2013
B.A. Teaching Korean as a Foreign Language
National Institute for Lifelong Education 2019
B.S. Hospitality Management
Florida International University 2011
Diploma Hotel and Tourism Management
Cesar Ritz Colleges Switzerland 2008
Teaching Online Certified (TOC)
Quality Matters 2019
Certification in Hotel Industry Analytics (CHIA)
Educational Institute of the American Hotel & Lodging Association (EI/AH&LA) 2018
Certified Hospitality Educator (CHE)
Educational Institute of the American Hotel & Lodging Association (EI/AH&LA) 2016
Certified Guest Service Professional (CGSP)
Educational Institute of the American Hotel & Lodging Association (EI/AH&LA) 2014
Certified ServSafe Instructor & Certified ServSafe Examination Proctor
National Restaurant Association Education Foundation 2022
Certified ServSafe Food Protection Manager
National Restaurant Association Education Foundation 2022
Certified Korean Language Teacher
Minister of Culture, Sports and Tourism, Republic of Korea 2019
Ji, Minhee
Assistant Professor, Hospitality & Tourism
M.S. Hospitality Management
Florida International University 2018
B.S. Hospitality Management
Florida International University 2011
Teaching Online Certified (TOC)
Quality Matters 2020
Jocson, John M.U.
Assistant Professor, Math & Science-Science
M.S. Environmental Science
University of Guam 1998
B.A. Mathematics
University of Guam 1995
Kerner, Paul N.
Instructor, Culinary & Foodservices
A.A. Culinary Arts
Guam Community College 2015
A.A. Education
Guam Community College 2010
Certificate Education
Guam Community College 2010
Certified Executive Chef
American Culinary Federation
Certified Hospitality Educator (CHE)
American Hotel & Lodging Association 2020
ServSafe Food Protection Manager Certification
National Restaurant Association Education Foundation 2001
Kerr, Jonita Q.
Associate Professor, Math & Science-Science
M.S. Biology
University of Guam, 1994
B.A. Chemistry
North Carolina State University, 1985
Kuper, Terry F.
Instructor, Technology-Electronics
A.S. Computer Networking
Guam Community College 2008
A.S. Electronic Networking
Guam Community College 2008
Teaching Online Certified (TOC)
Quality Matters 2020
A+ Certified Technician
The Computing Technology Industry Association 1995
Photovoltaic Entry Level
North American Board of Certified Energy Practitioners 2012
Lee, Christina S.
Instructor, English
M.A. English
University of Guam 2021
B.A. English
University of Guam 2018
Leon Guerrero, Catherine U.
Associate Professor, Work Experience
M.H.R. Human Relations
University of Oklahoma 1996
B.S. Marketing
Arizona State University 1986
Teaching Online Certified (TOC)
Quality Matters 2020
Certified Hospitality Educator
Educational Institute of the American Hotel & Lodging Association
Lizama, Dion M.A.
Assistant Instructor, Education-Cosmetology
Certificate Cosmetology
Guam Community College 2003
Cosmetology Instructor, Guam License
Lizama, Sean
Instructor, Business & Visual Communications-Visual Communications
B.A. Psychology and Philosophy
University of Guam 2008
Lizama, Troy E.
Associate Professor, Assessment & Counseling
M.A. Counseling
University of Guam 1996
B.A. Psychology
University of Guam 1992
Mafnas, Barbara C., R.N.
Assistant Professor, Nursing & Allied Health-Allied Health
M.S.N. Nurse Educator
Chamberlain College of Nursing 2017
B.S.N. Nursing
Chamberlain College of Nursing 2013
A.A. Nursing
Alpena Community College 1992
Teaching Online Certified (TOC)
Quality Matters 2020
Certified Allied Health Instructor
American Medical Technologies 2016
Registered Nurse, Guam License
Manzana, Amada A.
Professor, Business & Visual Communications-Marketing
M.A. Business Administration
University of Guam 1995
B.B.A. Marketing
University of Guam 1992
Martinez, Becky A.
Instructor, Education, Early Childhood Education
B.A. Psychology
University of Guam 2021
A.S. Early Childhood Education
Guam Community College 2011
Miranda, Kennylyn C.
Assistant Professor, Culinary & Foodservices
M.S. Hospitality Management
Johnson & Wales University 2018
B.A. Le Cordon Bleu Culinary Management
Le Cordon Bleu College of Culinary Arts 2016
A.A. Culinary Arts
Guam Community College 2013
Journeyman Certificate, Culinary Cook
Guam Community College 2013
Teaching Online Certified (TOC)
Quality Matters 2020
Google Certified Educator Level I
Google for Education 2021
Certified Secondary Foodservice Educator
National Restaurant Association Education Foundation 2022
Certified Hospitality Educator
American Hotel & Lodging Association Educational Institute 2020
Moodle Educator Certified (MEC)
Moodle 2021
Mui, Eva Marie L., L.P.N.
Instructor, Nursing & Allied Health-Allied Health
Certificate Practical Nursing
Guam Community College 2008
A.S. Medical Assisting
Guam Community College 2005
Licensed Practical Nurse, Guam License
Mummert, Courtney A.
Instructor, Business & Visual Communications-Supervision & Management
M.A.T. Secondary Education
University of Guam 2022
B.A. Business Administration-Marketing
Washington State University 2002
Munoz, Jose U.
Associate Professor, Criminal Justice & Social Science-Social Science
M.Ed. Education
University of Portland 1994
B.A. Political Science
University of Colorado 1984
Nanpei, Rose Marie D.
Associate Professor, Assessment & Counseling-Vocational Guidance
M.A. Counseling
University of Guam 2002
B.A. Psychology
University of Guam 1995
Licensed Professional Counselor
Nguyen, Dior R.
Assistant Instructor, Technology – Electronics / Telecommunications
B.S. Computer Science
University of Guam 2024
A.S. Computer Science
Guam Community College 2021
Olarte, Regine Erika F.
Assistant Instructor, Culinary & Food Services
A.A. Culinary Arts
Guam Community College 2016
Certified ServSafe Instructor
National Restaurant Association Education Foundation 2017
Certified ServSafe Exam Proctor
National Restaurant Association Education Foundation 2019
Certified ServSafe Food Protection Manager
National Restaurant Association Education Foundation 2017
Certified Culinarian
American Culinary Federation 2020
Certified Hospitality Educator
Educational Institute of the American Hotel & Lodging Association 2020
Teaching Online Certified (TOC)
Quality Matters 2021
Oliveros, Sharon J.V.
Assistant Professor, Assessment & Counseling-Vocational Guidance
M.A. Counseling
University of Guam 2012
B.A. Humanities
Bob Jones University 2003
Pajarillo, Lyndon B.
Instructor, Automotive Technology
A.A. Education
Guam Community College 2012
Journeyman Certificate, Construction Equipment Mechanic
Guam Community College 1989
ASE Certified Master Automobile Technician
ASE Certified Master Medium/Heavy Truck Technician
Palomo, Melissa L.C.
Instructor, Education-Early Childhood Education
B.S. Speech and Hearing Science
University of Arizona 1998
A.S. Early Childhood Education
Guam Community College 2005
Pangelinan, Mariana P.
Instructor, Math & Science-Math
M.A. Teaching-Secondary Math
University of Guam 2022
B.S. Mathematics
University of Guam 2014
Pangelinan, Pilar O., CGFM
Professor, Business & Communications-Accounting
M.B.A. Business Administration
University of Guam 1998
B.S. Business Administration
University of Arizona 1991
A.S. Business Administration
Pima Community College 1991
Teaching Online Certified (TOC)
Quality Matters 2021
Certified Government Financial Manager 2023
Certified Bookkeeper
The American Institute of Professional Bookkeepers 2020
Accredited Financial Counselor
Financial Counseling & Planning Education 2009
Paulino, Cindy G.
Instructor, Technology-Electronics
A.S. Computer Networking
Guam Community College 2020
Journeyworker Certificate, Telecommunications Technician
Guam Community College 2020
Paulino, Ronaldo M., Dr.P.H.
Assistant Professor, Math & Science-Science
Dr.P.H. Public Health
Loma Linda University 2015
M.S. Biology
University of Guam 2008
B.A. Biology
University of Guam 2004
Pereda, Jaclyn L.
Instructor, Adult Basic Education
M.A. English
University of Guam 2017
B.A. English (Literature)
University of Guam 2010
Pereda, John V.G.
Instructor, English
M.A. English
University of Guam 2016
B.A. English (Literature)
University of Guam 2011
Perez, Jonathan J.
Instructor, Automotive Technology
A.S. Occupational Studies, Automotive and Diesel Technology
Universal Technology Institute Phoenix 2003
ASE Certified Master Automobile Technician
ASE Certified Maintenance and Light Repair Technician
ASE Certified Advanced Level Specialist
Postrozny-Torres, Marsha M., Ed.D.
Professor, Education-Early Childhood Education
Ed. D. Child & Youth Studies
Nova Southeastern University 2006
M.Ed. Education – NCATE and state approved program elementary education 1-6, primary k-3; also pre-k handicapped environment
University of Florida 1995
B.A. Education
University of Florida 1994
Online Teaching Certificate
Online Learning Consortium 2016
Quinata, Keith N.
Instructor, Construction Trades
B.A. Project Management
ITT Technical Institute 2013
A.S. HVAC Sciences
Universal Technical Institute 1995
Career Pathways Leadership Certification 2018
Quitugua, Karen Rose J.
Assistant Instructor, Culinary & Food Services
A.A. Culinary Arts
Guam Community College 2015
Certificate Nutrition and Food Services
University of North Dakota 2018
Certified ServSafe Instructor
National Restaurant Association Education Foundation 2018
Certified ServSafe Food Protection Manager
National Restaurant Association Education Foundation 2017
Certified Dietary Manager
Certifying Board of Dietary Managers 2018
Certified Food Professional
Certifying Board of Dietary Managers 2018
Certified Culinarian
American Culinary Federation 2020
Quitugua, Kiana C.
Assistant Instructor, Adult Basic Education
B.S. Public Administration
University of Guam 2017
Randle, Michelle D.
Assistant Professor, Business & Visual Communications-Marketing
M.B.A. Global Management
University of Phoenix 2006
B.S. Business and Management
University of Maryland University College 2002
A.A. Business and Management
University of Maryland University College 1999
Repil, Mercy L., L.P.N.
Assistant Instructor, Nursing & Allied Health-Allied Health
Certificate Practical Nursing
Guam Community College 2007
Licensed Practical Nurse Guam License
Roden, Wendell M.
Instructor, Math & Science-Mathematics
M.S. Mathematics
Michigan State University 1997
B.S. Civil Engineering
Michigan State University 1994
Teaching Online Certified (TOC)
Quality Matters 2021
Rosario, Barbara Ann B.
Assistant Professor, Assessment & Counseling-Vocational Guidance
M.A. Counseling
University of Guam 2008
B.A. Psychology
University of Guam 2000
A.S. Clerical Studies
Guam Community College 1998
Rosario, Kirsten L.B.
Instructor, Education
B.A. Child Development
Ashford University 2013
A.A. Education
Guam Community College 2010
Advanced Specializations in Deaf Education
College of the Marshall Islands 2018
Rowland, Christopher D.
Assistant Instructor, Business & Visual Communications-Visual Communications
A.S. Visual Communications
Guam Community College 2011
Sablan, Sally C.
Associate Professor, Assessment & Counseling
M.A. Counseling
University of Guam 2002
B.A. Psychology
University of Guam 1994
San Nicolas, Teresa A.D.
Assistant Instructor, Adult Basic Education
B.S. Biology
University of Guam 2023
Santos, David T.
Assistant Instructor, Construction Trades
George Washington High School 1984
Schrage, Marivic C.
Associate Professor, Education
Ed.Sp. Learning Technologies and Design
University of Missouri – Columbia 2022
M.Ed. Career and Technical Education
Concordia University 2015
B.S. Business Administration/Accounting
Lyceum University 1984
B.S. Business Administration/Management
University of Nueva Caceres 1980
Teaching Online Certified (TOC)
Quality Matters 2020
Moodle Educator Certified (MEC)
Moodle 2021
Nationally Certified Work Ethic Trainer
The Center for Work Ethic Development 2019
Serafico, Angelenne P.
Assistant Instructor, Adult Basic Education
B.A. English: Linguistics/ESL Emphasis
University of Guam 2017
Sunga, Anthony Jay J., Ph.D.
Professor, Math & Science-Science
Ph.D. Biochemistry & Molecular Biology
Oregon Health & Science University 2009
M.S. Biochemistry & Molecular Biology
Oregon Health & Science University 1999
B.S. Biology
University of Guam 1997
Tabunar, James M.
Instructor, Automotive Technology
A.A. Education
Guam Community College 2010
Certificate Education
Guam Community College 2010
ASE Certified Collision Repair Technician
Tam, Wilson W.B., Ph.D.
Associate Professor, English
Ph.D. English Second Language
Northcentral University 2017
M.Ed. TESOL
University of Guam 1997
B.S. Industrial Technology
Walla Walla College 1982
A.S. General Contracting
Walla Walla College 1981
Teaching Online Certified (TOC)
Quality Matters 2021
Teacher of English as a Foreign Language (TEFL) Certificate
UNI-Prep Institute 2019
Teng, Zhaopei
Professor, Technology-Computer Science
M.S. Management Administration
University of South Carolina 1999
M.Ed. Early Childhood Education
University of South Carolina 1996
B.A. Education English
Shandong Normal University 1983
Online Teaching Specialization in Online Design
Online Learning Consortium
Microsoft Certified Professional 2002
Microsoft Office 2013 Certified Specialist (Access, PowerPoint & Word)
Tenorio, Juanita M., Ph.D.
Professor, English
Ph.D. Interdisciplinary Studies
Union Institute and University 2021
Certificate Women’s and Gender Studies
Union Institute and University 2021
M.A. English Language & Literature
University of Minnesota 1993
B.A. English
Marquette University 1986
Teaching Online Certified (TOC)
Quality Matters 2021
Terlaje, Patricia M.
Professor, Assessment & Counseling
M.A. Counseling
University of Guam 2002
B.A. Ed. Secondary Education/Language Arts
University of Guam 1985
Certified Administrator, Myers-Briggs Type Indicator
Center for Applications of Psychological Type (CAPT)
Topasna, Francine M.
Instructor, Adult Basic Education
M.A. Counseling
University of Guam, 2020
B.A. Sociology
University of Guam, 2016
Torres II, Carl E.
Instructor, Math & Science-Math
B.A. Math
University of Guam 2006
Tudela, Erwin F.
Instructor, Automotive Technology
A.S. Automotive Technology
Guam Community College 2005
ASE Certified Collision Repair Technician
Tyquiengco, Rolland R., R.N.
Instructor, Nursing & Allied Health-Allied Health
B.S. Nursing
University of Guam 2004
Registered Nurse, Guam License
Uchima, Katsuyoshi
Instructor, Nursing & Allied Health-Allied Health
M.H.A. Health Administration
University of Phoenix 2015
B.S. Health Administration
University of Phoenix 2011
A.A. Biological Sciences
Mira Costa College 2000
Registered Medical Assistant
American Medical Technologists 1994
Certified Allied Health Instructor
American Medical Technologists 2013
Webb, Carle D., R.N.
Assistant Instructor, Nursing and Allied Health - PN
B.S. Nursing
Southern Illinois University 2020
Registered Nurse, Guam License
Yanger, Gil T.
Assistant Instructor, Construction Trades
George Washington High School 1984
Appendix A: Pacific Postsecondary Education Council (PPEC) Statement On Transfer and Articulation of Courses and Programs
All Pacific Postsecondary Education Council (PPEC) member colleges are accredited by the Western Association and Schools and Colleges (WASC). The two-year colleges are accredited by the WASC Accrediting Commission for Community and Junior Colleges (ACCJC), and the four-year colleges are accredited by the WASC Accrediting Commission for Senior Colleges and Universities (ACSCU). Regional accreditation not only signifies a level of institutional quality, but is a requirement for any institution to become a recipient of US government funding, including student financial aid, Title III support for developing institutions, Carl Perkins Vocational Education Act, etc. Maintaining accreditation is critical to the survival of all PPEC institutions.
PPEC higher education institutional leaders have worked collaboratively to serve the needs of member institutions as they address regional and postsecondary education. One of these issues includes articulating the compatibility of educational programs to facilitate transferability of academic credits among member institutions. Additionally, the WASC 2001 Handbook of Accreditation states, "it is important for reasons of social equity and educational effectiveness, as well as for the wise use of resources, for all institutions to develop reasonable and definitive policies and procedures for acceptance of transfer of credit. Such policies and procedures should provide maximum consideration for the individual student who has changed institutions or objectives."
The goal of the Pohnpei Accord (signed by PPEC member institutions on December 11, 2003) is to clearly articulate transfer of credit guidelines for students entering the University of Guam and to exchange academic knowledge and expertise in cooperative transfer policies with the framework of accreditation and current best practices. Specifically,
- This statement makes specific the guaranteed transfer of courses taken by students at the College of the Marshall Islands (CMI), the College of Micronesia-FSM (COMFSM), the Northern Marianas College (NMC), the Guam Community College (GCC), and Palau Community College (PCC). Guaranteed transfer credit will be awarded for courses passed with a grade of "C" or higher only.
- Students transferring to the University of Guam to earn a baccalaureate degree must finish all courses in their major area of study and must take 32 credits in residence at the University of Guam, regardless of the transfer credit award. In residence means any course offered through the University of Guam and transcripted from the University of Guam.
- Students transferring to the University of Guam to earn a baccalaureate degree must complete at least 40 upper division credits.
- All students entering the University of Guam must take English and Mathematics Placement test unless exempt due to transfer credit awarded, or by other criteria as determined by the Registrar. If a student is found to be deficient (this is not expected and should be rare), developmental coursework outside of their major may be required.
- Courses that are developmental, vocational or technical in nature may transfer individually articulated within a program or specified on a course substitution form.
Students completing an Associate of Arts of Interdisciplinary Arts & Sciences degree from accredited colleges will have fulfilled lower division General Education course requirements at the University of Guam. This does not include the waiving of those general education courses that are Prerequisite to upper division and major courses, unless that specific course has been articulated with the appropriate course at the University of Guam and was taken by the student in the course of his/her study. All lower division, upper division and major course requirements for a baccalaureate degree must be taken unless an equivalent was completed prior to transferring to the University of Guam. Additional degree specific requirements may need to be completed prior to graduation.
Chaminade University and Guam Community College have established guidelines for a series of 2+2 pathways leading to a baccalaureate degree at CUH.
Criteria for 2+2 Completion
Completion of the AA or AS at GuamCC as outlined in each specific pathway outlined in the tables below enable GuamCC transfer students to waive the Chaminade General Education requirements. Students transferring into CUH for one of the degree pathways specified below should take the courses identified for each specific pathway at GuamCC prior to transfer to CUH in order to meet the two year degree completion timeline at CUH. All CUH admissions criteria otherwise apply, as noted in the CUH catalog, updated annually.
Guam Community College Degrees & Chaminade Pathways Covered by this Agreement
Pathway | Guam CC Degree | CUH Degree |
| AS CJ to BS CCJ | AS in Criminal Justice | BS Criminology & Criminal Justice |
| AS MKT to BA BA | AS in Marketing | BA Business Administration |
| AS SM to BA BA | AS Supervision & Management | BA Business Administration |
| AA LS to BA ID | AA Liberal Studies | BA Interdisciplinary Studies |
| AA LS to BA HPS | AA Liberal Studies | BA Historical & Political Studies |
| AA LS to BA ENG | AA Liberal Studies | BA English |
| AA Education to BS Elementary Education | AA Education | BS Elementary Education |
| AA Education to BS Secondary Education | AA Education | BS Secondary Education |
AS Criminal Justice to BS Criminology & Criminal Justice Degree Completion Pathway
Eligibility Requirements
Awarded AS degree in Criminal Justice from GuamCC, which must include the following courses, completed with a C or better:
GuamCC | CJ 100 | Intro to Criminal Justice (CUH 151) |
| CJ 200 | Criminal Law (CUH 223) | |
| CJ 101 | Juvenile Justice Process (CUH 291) | |
| CJ 204 | Intro to Criminology (CUH 201) |
Two Year Plan for Degree Completion at CUH
Fall I | Credits | Spring I | Credits | ||
| CJ 220 Criminal Investigation | 3 | CJ 321 Research Methods | 3 | ||
| CJ 315 Behavioral Science Stats | 3 | CJ 375 Contemporary Issues | 3 | ||
| CJ 327 Career Development | 3 | CJ 451 Corrections | 3 | ||
| Elective | 3 | Elective | 3 | ||
| Upper Division Elective | 3 | Upper Division Elective | 3 | ||
Total Credits | 15 | Total Credits | 15 | ||
| |||||
Fall II | Credits | Spring II | Credits | ||
| CJ 491 Juv Deviance & Justice | 3 | CJ 424 Criminal Procedures | 3 | ||
| CJ 423 Criminal Law | 3 | CJ 490 Seminar in CJ | 3 | ||
| CJ 432 Law Enforcement | 3 | PSY 321 or PSY 424 | 3 | ||
| Elective | 3 | Elective | 3 | ||
| Upper Division Elective | 3 | Upper Division Elective | 3 | ||
Total Credits | 15 | Total Credits | 15 | ||
Note: This program may also be completed as an online program, students would transfer and complete this degree in an online, flexible format through the Chaminade Flex Program (https://chaminade.edu/admissions/online-students/).
AS Marketing to BA Business Administration Degree Completion Pathway
Eligibility Requirements
Awarded AS Degree in Marketing from GuamCC, which must include the following courses, completed with a C or better:
GuamCC | MA 115 | College (CUH MA 103) |
| MKT 123 | Principles of Marketing (MKT 301) |
*Waive CUH BUS 200
Two Year Plan for Degree Completion at CUH
Fall I | Credits | Spring I | Credits | ||
| CIS 103 Comp & App Soft | 3 | EC 202 Microeconomics | 3 | ||
| EC 201 Macroeconomics | 3 | ACC 202 Principles of AC II | 3 | ||
| ACC 201 Principles of AC 1 | 3 | FIN 301 Principles of Finance | 3 | ||
| BU 224 Applied BUS Statistics | 3 | BU 308 Professional Writing and Presentation | 3 | ||
| MGT 305 MGT of Info Resources | 3 | BU 362 Legal and Ethical Issues in Business | 3 | ||
Total Credits | 15 | Total Credits | 15 | ||
| |||||
Fall II | Credits | Spring II | Credits | ||
| MGT 306 Human Resource MGT | 3 | BU 460 Business Strategy | 3 | ||
| BU 324 Quantitative Methods | 3 | BU 470 Senior field Experience | 3 | ||
| BU 402 International Business | 3 | Upper Division Elective | 3 | ||
| BU 416 Career Development | 3 | Upper Division Elective | 3 | ||
| MGT 407 operations Management | 3 | Upper Division Elective | 3 | ||
| Upper Div Elective | 3 | Upper Division Elective | 3 | ||
Total Credits | 18 | Total Credits | 18 | ||
Note: This program may also be completed as an online program, students would transfer and complete this degree in an online, flexible format through the Chaminade Flex Program (https://chaminade.edu/admissions/online-students/).
AS Supervision & Management to BA Business Administration Degree Completion Pathway
Eligibility Requirements
Awarded AS Degree in Supervision & Management from GuamCC, which must include the following courses, completed with a C or better:
GuamCC | MA 115* | College (CUH MA 103) |
| MKT 123* | Principles of Marketing (MKT 301) | |
| *MKT 205 OR | Entrepreneurship | |
| OA 250 OR | Office Procedures | |
| PY 125 OR | Interpersonal Relations | |
| SM 205 | Purchasing |
*Should be taken as part of Guam CC Electives
Two Year Plan for Degree Completion at CUH
Fall I | Credits | Spring I | Credits | ||
CIS 103 Comp & App Soft | 3 | EC 202 Microeconomics | 3 | ||
EC 201 Macroeconomics | 3 | ACC 202 Principles of AC II | 3 | ||
ACC 201 Principles of AC 1 | 3 | FIN 301 Principles of Finance | 3 | ||
BU 224 Applied BUS Statistics | 3 | BU 308 Professional Writing and Presentation | 3 | ||
MGT 305 MGT of Info Resources | 3 | BU 362 Legal and Ethical Issues in Business | 3 | ||
Total Credits | 15 | Total Credits | 15 | ||
| |||||
Fall II | Credits | Spring II | Credits | ||
| MGT 306 Human Resource MGT | 3 | BU 460 Business Strategy | 3 | ||
| BU 324 Quantitative Methods | 3 | BU 470 Senior field Experience | 3 | ||
| BU 402 International Business | 3 | Upper Division Elective | 3 | ||
| BU 416 Career Development | 3 | Upper Division Elective | 3 | ||
| MGT 407 operations Management | 3 | Upper Division Elective | 3 | ||
| Upper Div Elective | 3 | Upper Division Elective | 3 | ||
Total Credits | 18 | Total Credits | 18 | ||
Note: This program may also be completed as an online program, students would transfer and complete this degree in an online, flexible format through the Chaminade Flex Program (https://chaminade.edu/admissions/online-students/).
AALS to BA Interdisciplinary Studies Degree Completion Pathway
Eligibility Requirements
Awarded AALS degree from GuamCC.
Two Year Plan for Degree Completion at CUH
Fall I | Credits | Spring I | Credits | ||
| Major Requirement Elective | 3 | Major Requirement Elective | 3 | ||
| Major Requirement Elective | 3 | Major Requirement Elective | 3 | ||
| Major Requirement Elective | 3 | Major Requirement Elective | 3 | ||
| Upper Division Elective | 3 | Upper Division Elective | 3 | ||
| Upper Division Elective | 3 | Upper Division Elective | 3 | ||
Total Credits | 15 | Total Credits | 15 | ||
| |||||
Fall II | Credits | Spring II | Credits | ||
| Major Requirement Elective | 3 | Major Requirement Elective | 3 | ||
| Major Requirement Elective | 3 | Major Requirement Elective | 3 | ||
| Major Requirement Elective | 3 | Major Requirement Elective | 3 | ||
| Upper Division Elective | 3 | Upper Division Elective | 3 | ||
| Upper Division Elective | 3 | Capstone/Senior Thesis | 3 | ||
Total Credits | 18 | Total Credits | 18 | ||
This unique program may include studies in history, literature, philosophy, religion, foreign languages, education, and cultural anthropology. Humanities-related courses in other disciplines such as studio and performing arts, art history and criticism, geography, sociology, political theory, science, and economics may be selected after consultation with the program advisor.
AALS to BA Historical & Political Studies Degree Completion Pathway
Eligibility Requirements
Awarded ASLS degree from GuamCC, which must include the following courses, completed with a C or better:
GuamCC | HI 121 | History of World Civilization I |
| HI 122 | History of World Civilization II |
Two Year Plan for Degree Completion at CUH
Fall I | Credits | Spring I | Credits | ||
| Path Elective | 3 | Path Elective | 3 | ||
| Path Elective | 3 | Path Elective | 3 | ||
| Path Elective | 3 | Upper Division Elective | 3 | ||
| Upper Division Elective | 3 | Upper Division Elective | 3 | ||
| Upper Division Elective | 3 | Upper Division Elective | 3 | ||
Total Credits | 15 | Total Credits | 15 | ||
| |||||
Fall II | Credits | Spring II | Credits | ||
| Path Elective | 3 | HI/POL 494 Research Seminar | 3 | ||
| Path Elective | 3 | Upper Division Elective | 3 | ||
| Upper Division Elective | 3 | Path Elective | 3 | ||
| Upper Division Elective | 3 | Path Elective | 3 | ||
| Upper Division Elective | 3 | Path Elective | 3 | ||
Total Credits | 15 | Total Credits | 15 | ||
Students work with their academic advisor to determine a path and choose electives from within that path. The three paths include:
Career in Law
Career in Education
Career in Government
Note: This program may also be completed as an online program, students would transfer and complete this degree in an online, flexible format through the Chaminade Flex Program (https://chaminade.edu/admissions/online-students/).
AALS to BA English Degree Completion Pathway
Eligibility Requirements
Awarded ASLS degree from GuamCC, which must include the following courses, completed with a C or better:
GuamCC | EN 210 or EN 200 Level Elective | Introduction to Literature Or 200 Level English Elective |
Two Year Plan for Degree Completion at CUH
Fall I | Credits | Spring I | Credits | ||
| EN 314 Backgrounds in American Literature | 3 | EN 315 Backgrounds in British Literature | 3 | ||
| EN 300 or 400 elective | 3 | EN 300 or 400 elective | 3 | ||
| Major Concentration Course | 3 | Major Concentration Course | 3 | ||
| Upper Division Elective | 3 | Upper Division Elective | 3 | ||
| Upper Division Elective | 3 | Upper Division Elective | 3 | ||
Total Credits | 15 | Total Credits | 15 | ||
| |||||
Fall II | Credits | Spring II | Credits | ||
| Major Concentration Course | 3 | EN 499 Senior Seminar | 3 | ||
| Major Concentration Course | 3 | Major Concentration Course | 3 | ||
| Major Concentration Course | 3 | Upper Division Elective | 3 | ||
| Upper Division Elective | 3 | Upper Division Elective | 3 | ||
| Upper Division Elective | 3 | Upper Division Elective | 3 | ||
Total Credits | 15 | Total Credits | 15 | ||
AA Education to BS Elementary Education Pathway
Eligibility Requirements
Awarded AA Education degree from GuamCC, which must include the following courses, completed with a C or better:
GuamCC | CD 221 Child Growth and Development |
| CD 110 Intro to Early Childhood |
This program is an online program, students would transfer and complete this degree in an online, flexible format through the Chaminade Flex Program (https://chaminade.edu/admissions/online-students/).
Courses required for BS Elementary Education degree completion at Chaminade:
- ED 222 Educational Technology (3)
- ED 413 Children’s Literature (3)
- ED 433 Developmentally Appropriate Practice I (3)
- ED 434 Developmentally Appropriate Practice II (3)
- ED 471 Language Arts: Curriculum & Methods (3)
- ED 473 Math Curriculum & Methods (3)
- ED 474 Curriculum Foundation (3)
- ED 479 Leadership & Guidance in Ed (3)
- ED 491A Seminar (2)
- ED 491B Seminar (1)
- ED 498A Fieldwork Experience (3)
- ED 498B Fieldwork Experience (3)
- 15 Credits of Upper Division Elective
- 12 Credits of Elective (any level)
AA Education to BS Secondary Education Pathway
Eligibility Requirements
Awarded AA Education degree from GuamCC, which must include the following courses, completed with a C or better:
GuamCC | PY 120 General Psychology* |
*Student may take PSY 101 General Psychology at Chaminade
This program is an online program, students would transfer and complete this degree in an online, flexible format through the Chaminade Flex Program (https://chaminade.edu/admissions/online-students/).
Courses required for BS Secondary Education degree completion at Chaminade:
- PSY 304 Psychology of Adolescence (3)
- ED 201 Intro to Secondary Education (3)
- ED 220 Educational Foundations (prerequisite for ED 221) (3)
- ED 221 Educational Psychology (prerequisite for 300-400 level ED courses) (3)
- ED 222 Educational Technology (3)
- ED 462 Multicultural Education (3)
- ED 326 Exceptional Children (prerequisite for ED 427) (3)
- ED 404 Managing School Environments (prerequisite for ED 427) (3)
- ED 408 Assessment (prerequisite for ED 427) (3)
- ED 423 Teaching Strategies – Secondary (3)
- ED 427 Teaching in the Area of Specialization (prerequisite for ED 423) (3)
- ED 490 Secondary Ed Seminar (3)
- ED 495 Secondary Ed Student Teaching (9)
- 12 Credits of Upper Division Elective
- 3 Credits of Elective (any level)
The following list indicates transfer courses acceptable by the University of Hawaii at Manoa. This agreement applies only to Associate of Arts transfers from GCC.
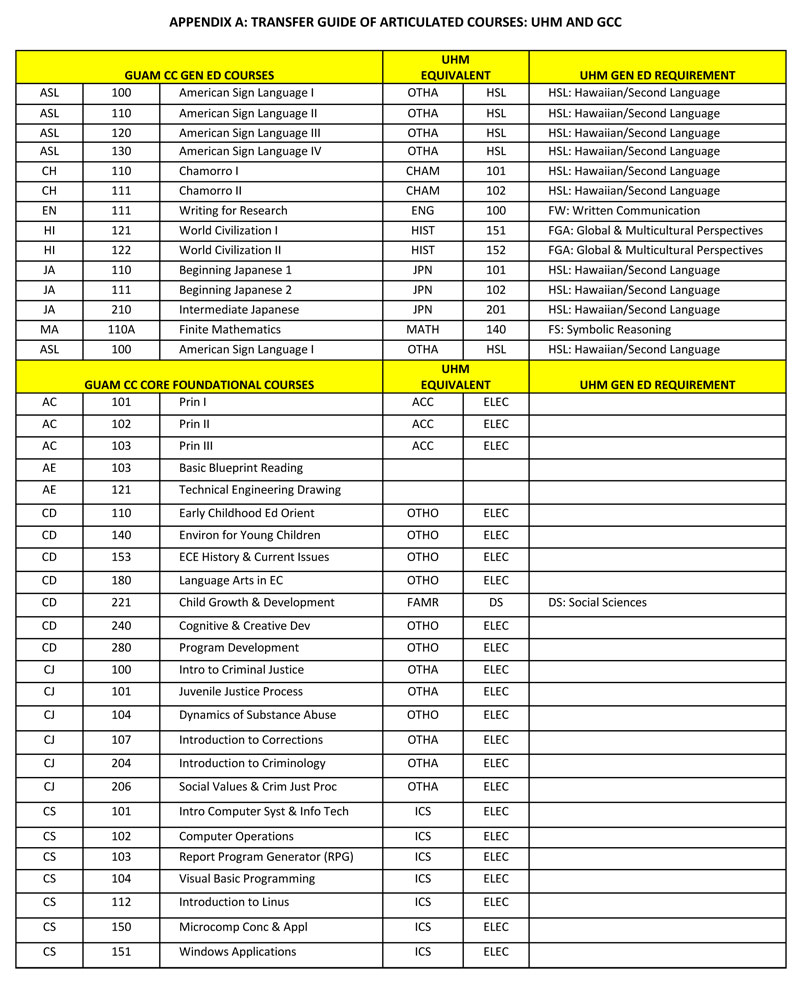
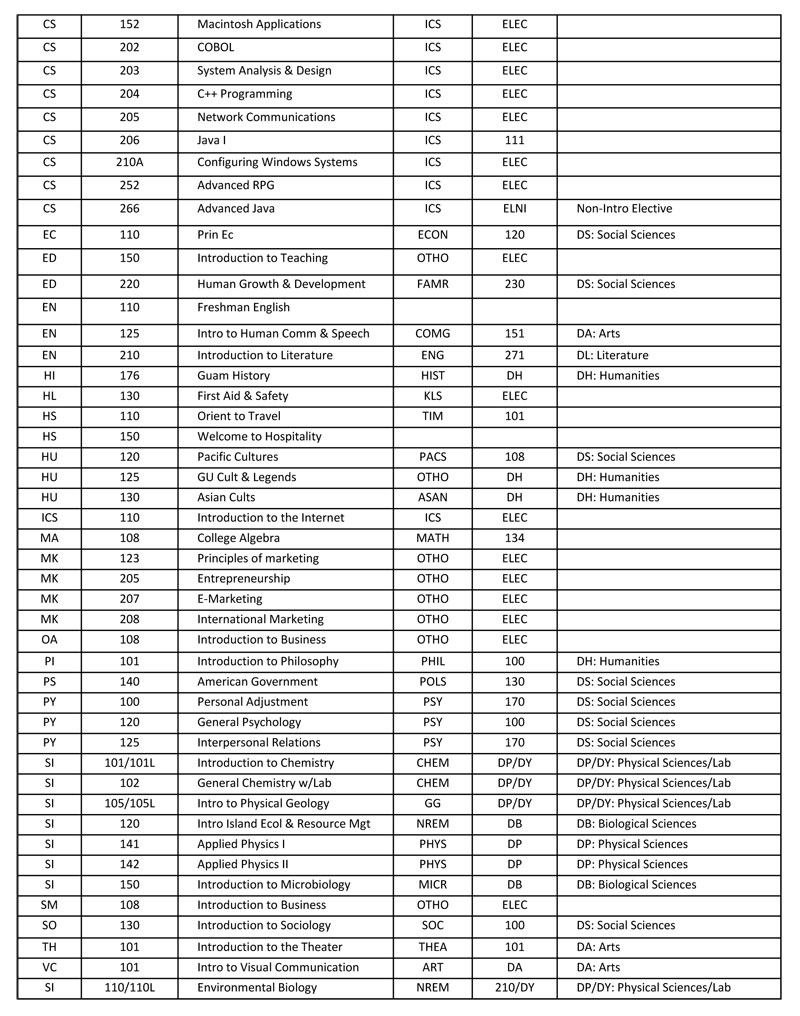
Since Guam Community College is fully accredited with the Accrediting Commission for Community and Junior Colleges (ACCJC), GCC courses and some programs articulate, or transfer to other accredited postsecondary institutions and organizations through certain arrangements or agreements. These agreements offer GCC students various opportunities with which to expand and enrich their postsecondary educational experiences.
However, meeting graduation and transfer requirements is still the responsibility of students. Students interested in pursuing transfer to the following institutions or organizations that GCC has agreements with should contact a GCC advisor, counselor, or the Office of Admissions and Registration:
| Institution/Organization | Website |
| University of Guam | http://www.uog.edu |
| Chaminade University- Honolulu, Hawaii | https://www.chaminade.edu |
| University of Alaska Fairbanks | http://www.uaf.edu |
| Bellevue University- Bellevue, Nebraska | https://www.bellevue.edu/ |
| University of Phoenix (online) | https://www.phoenix.edu |
AA Education - BS Education/Elementary Education | |
AA IAS - BS Business (all concentrations) | |
AA IAS - BS Criminal Justice Administration/Management | |
| University of Makati-Makati City, Philippines | http://umak.edu.ph/v3 |
| First Asia Institute of Technology and Humanities-Batangas, Philippines | http://www.firstasia.edu.ph/ |
| Grand Canyon University | https://www.gcu.edu/ |
| University of Hawaii at Manoa | https://manoa.hawaii.edu/ |
Institutions identified in the previous page have varying agreements with GCC as indicated in the following arrangements below:
A to B Agreements (A to B) - Associate to Bachelor (A to B) Agreements provide students the opportunity to complete an associate's degree while working towards a bachelor's degree. Most, if not all, the credits in the associate's degree transfer to the four-year institution, often with the student starting as a junior.
General Education Articulation - GCC has General Education articulation with selected postsecondary institutions. Please consult a counselor, advisor or the Office of Admissions and Registration for further information. It is important to note though that some institutions have college-wide General Education requirements whereas other institutions have different requirements depending on a student's major (i.e. Education, Criminal Justice, etc.)
Course by Course Articulation - The articulation matrices found in this catalog list specific GCC courses that selected postsecondary institutions will accept as equivalent to their courses. Course by course guides are helpful if the student knows the exact course or courses needed to transfer.
Secondary to Postsecondary Articulation - An array of programs, initiatives and support services provide opportunities for high school students to gain college credits while earning a high school diploma. Dual Enrollment Accelerated Learning (or DEAL) and Dual Credit Articulated Programs of Study (or DCAPS) are two examples.
Reverse Transfer - Academic credits for course work completed at a 4-year institution may be transferred back to Guam Community College to satisfy associate degree requirements.
General Information:
The SROTC is an Army leadership training program that has a contractually agreed upon cooperative effort with the University of Guam (UOG). The SROTC's purpose is to commission Army Officers, the future leadership of the U.S. Army.
This information is being included in this catalog to give Guam Community College (GCC) students an opportunity to explore military career options.
Eligibility:
Any full-time GCC student may take a lower level Military Science course at no cost to the student registering in the same manner as any other undergraduate course. However, to qualify for enrollment as an ROTC cadet in the program leading to a commission, a student must meet the following requirements:
- U.S. citizenship is required prior to commissioning.
- Be at least 17 years of age with consent at time of contracting and no more than 35 years of age at time of commissioning.
- Be a full time student at UOG, GCC, or a combination of the two. Or be a full time student at the Northern Marianas College (NMC).
- Not be convicted of a felony.
- Be approved by the Professor of Military Science.
- Specific questions regarding the above criteria should be directed to the Military Science Department at the university.
Tuition:
Military Science courses at UOG are tuition free. However, students must be full time in order to enroll in the Advance Course (junior and senior year) of the SROTC program. All Military Science required uniform and equipment are provided on a loan basis. All Military Science course texts are also provided to students at no cost.
For particular courses, program-specific questions and other related costs, please contact John Howerton, Recruiting Operations Officer, Military Science Department at the University of Guam, phone (671) 735-2541 or (671) 858-ROTC.
- Educational Level
- Freshman: A Declared Student who has earned less than 30 credits towards the requirements of a Certificate or Associate Degree.
- Sophomore: A Declared Student who has earned 30 credits or more towards the requirements of a Certificate or Associate Degree.
- Diploma Students: Undeclared Students and Special Students are not assigned educational levels by the College.
- Registration Status
- First Time Student: A new student to GCC and is the first member of their immediate family to attend college.
- Transfer Student: A student who attended another College and has at least 45 credits of completed college coursework or equivalent.
- Continuing Student: A student who has been registered at the College during the previous semester in the same classification.
- Returning (Former) Student: A student who has been enrolled at the College and is returning to the College in the same classification after an absence of one or more semesters (not including Summer Semester).
- Program of Study
- A Declared Student is admitted to the College to work toward a specific certificate or degree. That certificate or degree is that student’s program of study (or Major) unless a Change of Program request has been approved.
- A Declared Student is admitted to the College to work toward a specific certificate or degree. That certificate or degree is that student’s program of study (or Major) unless a Change of Program request has been approved.
- Enrollment Status
A student’s enrollment status is determined after the end of the Course Adjustment period.
During a regular semester, a student is:
- Full-Time: If enrolled for 12 credit hours or more.
- ¾-Time: If enrolled for at least 9 credit hours but less than 12 credit hours.
- ½-Time: If enrolled for at least 6 credit hours but less than 9 credit hours.
During a summer session, a student is:
- Full-Time: If enrolled for 6 credit hours or more.
- ½-Time: If enrolled for less than 6 credit hours.
A student with a disability who has requested accommodations may qualify for certification as a full-time student if enrolled for at least six (6) credit hours in a regular term or three (3) credit hours in a summer session. Contact the Accommodative Services Coordinator, Suite 2139 in the Student Services & Administration Building, phone (671) 735-5640 ext. 5597 for further information.
Declared and Diploma Students enrolled for less than a full course of study during their final semester or summer session at the College will be considered to be full-time students during that semester or summer session for U.S. Immigration and Customs Enforcement purposes, provided that they are registered for at least those courses required to meet graduation requirements at the end of that semester or summer session.
WHEREAS, the Guam Community College Board of Trustees desires to promote and assure public understanding and support of academic freedom in the College; and
WHEREAS, institutions of higher education are conducted for the common good and not to further the interest of either the individual faculty member or the institution as a whole; and
WHEREAS, the common good depends upon the free search for truth and its free exposition; and
WHEREAS, academic freedom is essential to these purposes and applies to both teaching and research; and
WHEREAS, freedom in research is fundamental to the advancement of truth; and
WHEREAS, academic freedom in its teaching aspect is fundamental for the protection of the rights of the faculty member in teaching and of the student in learning; and
WHEREAS, teaching includes but is not limited to: method of teaching, method of presentation, materials used in teaching, presentations and all things related to the students’ classroom learning; and
WHEREAS, it carries with it duties correlative with rights.
NOW, THEREFORE, BE IT RESOLVED, that the Guam Community College Board of Trustees adopts as its policy the following statement on Academic Freedom:
- The faculty member is entitled to full freedom in research and in the publication of the results, subject to the adequate performance of his/her other academic duties.
- The faculty member is a citizen and a member of a learned profession of an educational institution. When the faculty member speaks or writes as a citizen, the faculty member should be free from institutional censorship or discipline. The faculty member’s special position in the community imposes special obligations. As a person of learning and an educational officer, the faculty member should remember that the public may judge his/her profession and institution by his/her utterances. Hence the faculty member should, at all times, be accurate, should exercise appropriate restraint, should show respect for the opinions of others, and should make every effort to indicate that the faculty member is not an institutional spokesperson.
Amended & Adopted: September 9, 2022
Resolution 18-2022
Amended & Adopted: February 3, 2017
Resolution 7-2017
Amended & Adopted: January 8, 2009
Resolution 9-2009
Adopted: May 17, 2000
Resolution 9-2000
Appendix L: Annual Notification of Student Rights Under the Family Educational Rights and Privacy Act (FERPA)
Family Educational Rights and Privacy Act (FERPA) affords students certain rights with respect to their education records. These rights are:
- The right to inspect and review the student’s education records within 45 days of the day the College receives a request for access. Students should submit to the Registrar written requests that identify the record(s) they wish to inspect. The Registrar will make arrangements for access and notify the student of the time and place where the records may be inspected. If the records are not maintained by the Registrar, the Registrar shall advise the student of the correct official whom the request should be addressed to.
- The right to request the amendment of the student’s education records that the student believes is inaccurate or misleading. Students may ask the College to amend a record that they believe is inaccurate or misleading. They should write the College official responsible for the record, clearly identify the part of the record they want changed, and specify why it is inaccurate or misleading. If the College decides not to amend the record as requested by the student, the College will notify the student of the decision and advise the student of his or her right to a hearing regarding the request for amendment. Additional information regarding the hearing procedures will be provided to the student when notified of the right to a hearing.
- The right to consent to disclosures of personally identifiable information contained in the student’s education records, except to the extent that FERPA authorizes disclosure without consent. One exception, which permits disclosure without consent, is disclosure to school officials with legitimate educational interests. A school official is defined as a person employed by the College in an administrative, supervisory, academic, or support staff position (including law enforcement unit and health staff); a person or company with whom the College has contracted (such as an attorney, auditor, or collection agent); a person serving on the Board of Trustees; or assisting another school official in performing his or her tasks. A school official has a legitimate educational interest if the official needs to review an education record in order to fulfill his or her professional responsibility. Upon request, the College discloses education records without consent to officials of another school in which a student seeks or intends to enroll.
- The right to file a complaint with the U.S. Department of Education concerning alleged failures by the College to comply with the requirements of FERPA. The name and address of the Office that administers FERPA is:
Family Policy Compliance Office
U.S. Department of Education
400 Maryland Avenue, S.W.
Washington, DC 20202-4605 - FERPA regulations can be accessed online at www2.ed.gov/policy/gen/guid/fpco/ferpa/index.html
At its discretion, the College may provide Directory Information in accordance with the provisions of the Act to include: student name, address, telephone number, date and place of birth, major field of study, dates of attendance, degrees and awards received, the most recent previous educational agency or institution attended by the student, participation in officially recognized activities and sports, and weight and height of members of athletic teams. Students may withhold Directory Information by notifying the Registrar in writing within two weeks after the first day of class for the fall term.
Requests for nondisclosure will be honored by the College for the academic year; therefore, authorization to withhold Directory Information must be filed annually in the Office of Admissions and Registration.
Middle States Association of Colleges and Schools, Middle States Commission on Higher Education (MSCHE)
Scope of recognition: the accreditation and pre-accreditation ("Candidacy status") of institutions of higher education in Delaware, the District of Columbia, Maryland, New Jersey, New York, Pennsylvania, Puerto Rico, and the U.S. Virgin Islands, including distance education programs offered at those institutions.
Dr. Heather F. Perfetti, President
1007 North Orange Street
4th Floor, MB #166
Wilmington, DE 19801
Phone: (267) 284-5026
E-mail: icommunications@msche.org
www.msche.org
New England Association of Schools and Colleges, Commission on Institutions of Higher Education (NEASC-CIHE)
Scope of recognition: the accreditation and pre-accreditation ("Candidacy status") of institutions of higher education in Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island, and Vermont that award bachelors, masters, and/or doctoral degrees and associate degree-granting institutions in those states that include degrees in liberal arts or general studies among their offerings, including the accreditation of programs offered via distance education within these institutions. This recognition extends to the Board of Trustees of the Association jointly with the Commission for decisions involving pre-accreditation, initial accreditation, and adverse actions.
Staples, Cameron C., President
1115 Westford Street Third Floor
Lowell, MA, 01851 USA
Phone: (781) 425-7707
Toll-free (US): 855-886-3272
E-mail: cstaples@neasc.org
info@neasc.org
New England Association of Schools and Colleges, Commission on Technical and Career Institutions (NEASC-CTCI)
Scope of recognition: the accreditation and pre-accreditation ("Candidate status") of secondary institutions with vocational technical programs at the 13th and 14th grade level, postsecondary institutions, and institutions of higher education that provide primarily vocational/technical education at the certificate, associate, and baccalaureate degree levels in Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island, and Vermont. This recognition extends to the Board of Trustees of the Association jointly with the Commission for decisions involving pre-accreditation, initial accreditation, and adverse actions.
Lawrence M. Schall, President
301 Edgewater Place, Suite 210
Wakefield, MA 01880
Phone: (780) 425-7714
E-mail: lschall@neche.org
info@neche.org
The Higher Learning Commission
Scope of recognition: the accreditation and pre-accreditation ("Candidate for Accreditation") of degree-granting institutions of higher education in Arizona, Arkansas, Colorado, Illinois, Indiana, Iowa, Kansas, Michigan, Minnesota, Missouri, Nebraska, New Mexico, North Dakota, Ohio, Oklahoma, South Dakota, West Virginia, Wisconsin, Wyoming, including schools of the Navajo Nation and the accreditation of such programs offered via distance education within these institutions.
Barbara Gellman-Danley, President
230 South LaSalle Street, Suite 7-500
Chicago, IL 60604-1411
Phone: (800) 621-7440
Fax: (312) 263-7462
E-mail: president@hlcommission.org
www.hlcommission.org
Northwest Commission on Colleges and Universities (NWCCU)
Scope of recognition: the accreditation and pre-accreditation ("Candidacy status") of postsecondary educational institutions in Alaska, Idaho, Montana, Nevada, Oregon, Utah, and Washington and the accreditation of such programs offered via distance education within these institutions.
Dr. Jeff Fox, Interim President
8060 165th Avenue, NE, Suite 100
Redmond, WA 98053
Phone: (425) 558-4224
Fax: (425) 376-0596
E-mail: president@nwccu.org
www.nwccu.org
Southern Association of Colleges and Schools, Commission on Colleges (SACS)
Scope of recognition: the accreditation and pre-accreditation ("Candidate for Accreditation") of degree-granting institutions of higher education in Alabama, Florida, Georgia, Kentucky, Louisiana, Mississippi, North Carolina, South Carolina, Tennessee, Texas, and Virginia, including distance education programs offered at those institutions.
Belle S. Wheelan, President
1866 Southern Lane
Decatur, GA 30033
Phone: (404) 679-4500
Fax: (404) 679-4528
E-mail: bwheelan@sacscoc.org
questions@sacscoc.org
Distance Education Accrediting Commission (DEAC) is a private, non-profit organization founded in 1926 that operates as an institutional accreditor of distance education institutions. www.deac.org
Western Association of Schools and Colleges, Accrediting Commission for Community and Junior Colleges (WASC-ACCJC)
Scope of recognition: the accreditation and pre-accreditation ("Candidate for Accreditation") of community and junior colleges located in California, Hawaii, the United States territories of Guam and American Samoa, the Republic of Palau, the Federated States of Micronesia, the Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands, and the Republic of the Marshall Islands, and the accreditation of such programs offered via distance education at these colleges.
Mac Powell, President
428 J Street, Suite 400
Sacramento, California 95814
Phone: (415) 506-0234
Fax: (415) 506-0238
E-mail: mac@accjc.org
www.accjc.org
Western Association of Schools and Colleges, Accrediting Commission for Senior Colleges and Universities (WASC-ACSCU)
Scope of recognition: the accreditation and pre-accreditation ("Candidate for Accreditation") of senior colleges and universities in California, Hawaii, the United States territories of Guam and American Samoa, the Republic of Palau, the Federated States of Micronesia, the Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands and the Republic of the Marshall Islands, including distance education programs offered at those institutions.
Maria Toyoda, President
1080 Marina Village Parkway
Suite 500
Alameda, CA 94501
Phone: (510) 748-9001
Fax: (510) 748-9797
E-mail: mtoyoda@wscuc.org
www.wascsenior.org
The Dual Credit Articulated Programs of Study (DCAPS) gives secondary students an opportunity to gain up to nine postsecondary credits to be awarded upon successful completion of respective aligned secondary courses at no cost. DCAPS involves secondary courses that articulate into GCC post secondary courses in a Guam Department of Education (GDOE) High School. Students who complete their Career & Technical Education (CTE) courses with a “B” or better and 180 hours of work experience earn a Certificate of Mastery (COM) upon their high school graduation. Students who earn a Certificate of Completion (COC), may articulate the introductory courses into the student’s post secondary equivalent course. The following programs are a part of the DCAPS:
ALLIED HEALTH | |
GCC Secondary Courses | GCC Postsecondary Courses |
CTHCO60B Health Careers & Sciences II | HL120 Medical Terminology |
| HL131 Basic Life Support for Healthcare Providers |
AUTOMOTIVE (AST) | |
GCC Secondary Courses | GCC Postsecondary Courses |
CTME050A | AST100 Intro to Automotive Services (3 credits) |
CTME050B | AST140 Suspension & Steering (3 credits) |
CTME077 | AST150 Brakes (3 credits) |
VEME075 | AST160 Electrical (3 credits) |
VEME065 | AST180A Engine Performance I (3 credit) |
VEME066 |
|
BUSINESS EDUCATION (GDOE) | |
GDOE Secondary Cluster Courses | GCC Postsecondary Courses |
BS108 Keyboarding | OA101 Keyboarding Applications |
BS403 Business Math Using Excel | OA109 Business Math Using Excel |
BS203 Information Processing | OA130 Information Processing |
CONSTRUCTION TECHNOLOGY | |
CARPENTRY TRACK | |
GCC Secondary Courses | GCC Postsecondary Courses |
The learning outcomes of CT140 Industrial Safety are covered and incorporated in CTCT053 & CTCT073 | CT140 Industrial Safety (3) |
CTCT053 Intro to Basic Carpentry A/B | CT153 Intro to Carpentry (3) |
CTCT073 Carpentry Level II A/B | CT173 Rough Framing and Exterior Finishing (3) |
EMPHASIS IN AUTOCAD | |
GCC Secondary Courses | GCC Postsecondary Courses |
VECT080 Intro to AutoCADD | AE103 Basic Blueprint Reading (3) |
VECT081 Advanced AutoCAD | AE150 Computer Aided Drafting (CAD I) (3) |
EARLY CHILDHOOD EDUCATION | |
GCC Secondary Courses | GCC Postsecondary Courses |
CTEC050 Intro to Early Childhood Education A/B | CD110 Intro to Early Childhood Education (3) |
CTEC060 Language Arts in Early Childhood Education A/B | CD180 Language Arts Development in ECE (3) |
ELECTRONICS | |
GCC Secondary Courses | GCC Postsecondary Courses |
CTEE080 IT Essentials I | IT211 IT Essentials (4) |
HTMP Hospitality & Tourism | |
GCC Secondary Courses | GCC Postsecondary Courses |
CTETT054 Hospitality & Tourism Management Program IA | HS150 Welcome to Hospitality (3) |
CTETT054 Hospitality & Tourism Management Program IIB | HS152 Customer Service (3) |
CTETT064 Hospitality & Tourism Management Program IIA | HS157 Tourism Planning & Development (3) |
CTETT064 Hospitality & Tourism Management Program IIB | HS158 Intro to MICE (3) |
CTETT074 Hospitality & Tourism Management Program IIA | HS160 Hospitality Supervision (3) |
| HS292 Hospitality & Tourism Practicum (3) |
MARKETING | |
GCC Secondary Courses | GCC Postsecondary Courses |
CTMK050 Marketing I (.5/sem, total 1.0) | MK123 Principles of Marketing (3) |
CTMK060 Marketing II (1.0/sem, total 2.0) | MK124 Selling (3) |
CTMK062 Marketing, Sales & Services Lab A (.5/sem, total 1.0) | MK205 Entrepreneurship (3) |
CTMK070 Marketing III (.5/sem, Total 1.0) |
|
CTMK072 Marketinig III (.5/sem, Total 1.0) |
|
PROSTART & CULINARY | |
GCC Secondary Courses | GCC Postsecondary Courses |
CTTT055A Prostart IA: Food Safety & Sanitation | FSM120 Food Safety & Sanitation (2) |
CTTT055B Prostart IB: Intro to Foodservice Profession | FSM100 Intro to Foodservice Profession (2) |
CTTT065A Prostart IIA: Professional Dining Room Services | FSM110 Professional Dining Room Service Theory (2) |
| FSM110L Professional Dining Room Service Lab (1) |
CTTT075A Prostart IIIA: Restaurant Purchasing | FSM115 Purchasing & Receiving (2) |
CTTT065B Prostart IIB: Foodservice Nutrition | FSM154 Foodservice Nutrition (3) |
| CUL293A Culinary Practicum Part I (2) |
There will be a limit of nine (9) post secondary credits to be awarded upon successful completion of respective aligned secondary courses at NO COST; a student may be immediately awarded three (3) or more post secondary credits (1 post secondary course) upon initially applying for DCAPS.
Students must complete at least nine (9) credits at the college before the remaining articulated post secondary credits are awarded and the student must apply for these post secondary credits to be awarded within two years after completing high school.
If a student fails to apply for DCAPS within two years, the credits will be considered null and the credits must be acquired through the successful completion of its corresponding post secondary course(s).
A dual credit recording fee will be assessed to award the remaining postsecondary credits should a program contain a DCAPS agreement that states that there are more than nine credits. The cap per program is 15 post secondary credits to be awarded.
All programs participating in DCAPS will have a course grade of a “B” or better as a minimum requirement for articulation of courses.
Students must provide the following documents to apply for DCAPS:
- DCAPS application for immediate awarding of credits
- Copy of Certificate of Mastery
- Copy of Certificate of Completion
- Office High school transcript
*After students have completed nine (9) credits at GCC, there is a separate application called “DCAPS Awarding of Remaining Credits” that students must submit in order to be awarded any remaining post secondary credits.
Guam Community College | College Credits | Guam Department of Education (GDOE) | High School Credit | |
EN110-Freshman Composition | 3 | LA411DEG Advanced Placement Language and Composition | 1 | |
EN210-Introduction to Literature | 3 | LA410DEG Advanced Placement Literature and Composition | 1 | |
MA110A-Finite Mathematics | 3 | MA203DEG Algebra 2 Honors | 1 | |
MA161A-College Algebra and Trigonometry I and | 3 | 6 | MA405DEG Pre-Calculus Honors | 1 |
3 | ||||
MA165-PreCalculus | 5 | |||
Guam Community College | College Credits | Father Duenas Memorial School (FDMS) | High School Credit | |
EN110-Freshman Composition | 3 | EL09 Composition | 1 | |
MA161B-College Algebra and Trigonometry II | 3 | MA04 Pre-Calculus | 1 | |
Guam Community College | College Credits | Notre Dame High School (NDHS) | High School Credit | |
EN110-Freshman Composition | 3 | Composition | 1 | |
Guam Community College | College Credits | Guam Adventist Academy (GAA) | High School Credit | |
EN110-Freshman Composition | 3 | Composition | 1 | |
MA161B-College Algebra and Trigonometry II; or | 3 | Pre-Calculus | 1 | |
MA165-PreCalculus | 5 | |||
SI103-Introduction to Marine Biology; and | 3 | 4 | Science Requirement | 1 |
SI103L-Introduction to Marine Biology Laboratory | 1 | |||
SI110-Environmental Biology; and | 3 | 4 | Science Requirement | 1 |
SI110L-Environmental Biology Laboratory | 1 | |||
SI131-Human Anatomy and Physiology I: Theory; and | 3 | 4 | Science Requirement | 1 |
SI131L-Human Anatomy and Physiology I: Laboratory | 1 | |||
Guam Community College | College Credits | Guam Adventist Academy (GAA) | High School Credit | |
EN110-Freshman Composition | 3 | ELA 13 DEG Advanced Placement Language & Composition | 1 | |
EN210-Introduction to Literature | 3 | ELA 14 DEG Advanced Placement Literature & Composition | 1 | |
MA110A-Finite Mathematics | 3 | MA 13 DEG Algebra 2 Honors | 1 | |
MA161A-College Algebra & Trigonometry I; and | 6 | ELA 14 DEG Pre-Calculus Honors | 1 | |
MA161B-College Algebra & Trigonometry II; or | 6 | |||
MA165-Pre Calculus | 5 | |||
| College-level courses in other content areas (science, social science, foreign languages, or occupational/technical courses) will be considered for future dual enrollment articulation upon agreement between GCC and GAA. | ||||